100% found this document useful (1 vote)
6K views29 pagesSilicones
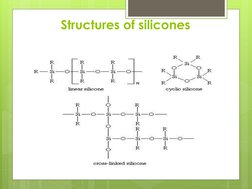
Silicones, also known as polysiloxanes, are polymers made up of repeating units of siloxane, which is a chain of alternating silicon atoms and oxygen atoms, combined with carbon, hydrogen, and sometimes other elements. Silicones take numerous forms and can be engineered to deliver an almost unlimited range of enabling and problem-solving benefits.
Uploaded by
Jim LivingstonCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
100% found this document useful (1 vote)
6K views29 pagesSilicones
Silicones, also known as polysiloxanes, are polymers made up of repeating units of siloxane, which is a chain of alternating silicon atoms and oxygen atoms, combined with carbon, hydrogen, and sometimes other elements. Silicones take numerous forms and can be engineered to deliver an almost unlimited range of enabling and problem-solving benefits.
Uploaded by
Jim LivingstonCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd