100% found this document useful (1 vote)
383 views13 pagesProject Management Essentials
This document discusses key aspects of project management including defining a project and its attributes, principles of project management, requirements for a successful project, threats and ways to minimize them, determining a project strategy, and constraints and life cycles. It provides definitions for project management, programs, and program management. It also outlines learning objectives and various frameworks and models for project management.
Uploaded by
Shah KamalCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
100% found this document useful (1 vote)
383 views13 pagesProject Management Essentials
This document discusses key aspects of project management including defining a project and its attributes, principles of project management, requirements for a successful project, threats and ways to minimize them, determining a project strategy, and constraints and life cycles. It provides definitions for project management, programs, and program management. It also outlines learning objectives and various frameworks and models for project management.
Uploaded by
Shah KamalCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
- Principles of Project Management: Introduces the chapter by stating its title, setting the framework for the project management discussion.
- Chapter Learning Objectives: Describes the key learning goals for understanding project management attributes, structures, processes, and strategies.
- A Project and its Attributes: Defines what constitutes a project and its various attributes, following guidelines by the Association of Project Managers.
- Definitions: Provides definitions for project management, program, and program management, outlining their individual roles and interconnections.
- Requirement of a Successful Project: Lists the essential elements required for executing a successful project, focusing on stakeholder engagement and planning.
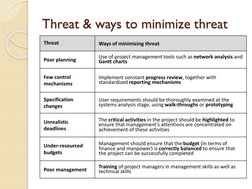
- Threat & Ways to Minimize Threat: Identifies potential threats to projects and proposes methods to mitigate them using tools and structured approaches.
- Ways to Determine a Project Strategy: Explores strategic planning and decision-making processes for project implementation and management.
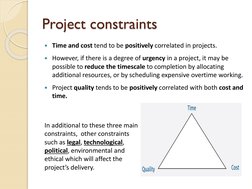
- Project Constraints: Discusses constraints such as time, cost, and quality, explaining how they relate and affect project outcomes.
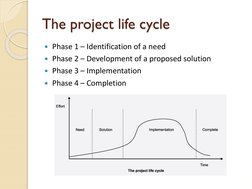
- The Project Life Cycle: Outlines the four phases of the project life cycle, illustrating the flow from inception to completion.
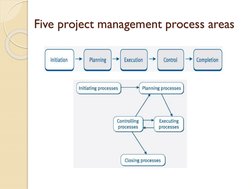
- Five Project Management Process Areas: Breaks down the five core areas of project management processes that guide successful execution and closing.
- 4d Project Management Model: Introduces the 4D project management model, correlating it with project lifecycle phases for comprehensive management.
- An Alternative Project Life Cycle: Proposes an iterative process for the project life cycle, emphasizing continuous improvement and adaptation.
- Project Structures: The McKinsey 7-S Model: Explains the McKinsey 7-S framework for aligning project structures with strategy and shared values.