Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Sintesis Protein - English
Uploaded by
Marlina Lina0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
79 views11 pagesThe genetic code consists of three nucleotide codons in mRNA that are translated by tRNA to specific amino acids through base pairing, forming a universal code across organisms.
Original Description:
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe genetic code consists of three nucleotide codons in mRNA that are translated by tRNA to specific amino acids through base pairing, forming a universal code across organisms.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
79 views11 pagesSintesis Protein - English
Uploaded by
Marlina LinaThe genetic code consists of three nucleotide codons in mRNA that are translated by tRNA to specific amino acids through base pairing, forming a universal code across organisms.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 11
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
Presented by
GROUP 7
•• Mulqiyati Zikra (8)
•• Lu’luan Thahura H (4)
•• Marlina (34)
DEFINITION
Protein is a macromolecule composed by various
amino acids. Meanwhile, enzymes are proteins that
have the ability as a catalyst for biochemical reactions
in the process of cellular metabolism. Based on the
results of Beadle and Tatum’s (1941) experiment,
genes controlling the metabolic processes or the lives
of individuals through the process of enzyme control.
Thus, changes in gene structure can cause changes in
protein structure at amino acid level, which in turn
will cause changes in metabolic processes
Protein is not synthesized directly
by genes, but through the process
of transcription and translation
(the gene is a functional, is a
DNA structure). Transcription is
the process of DNA replication to
form the RNA-d. Meanwhile, the
translation is the process of
translating genetic information
contained in RNA-d into the
polypeptide amino acid runs. In
transcription, DNA is used as a
model for protein synthesis.
1. TRANSCRIPTION
Transcription is the process of transfer of genetic information
from DNA segments (genes) into RNA molecules which are
guided by a katalisatornya transcriptase enzyme. Pieces of
base sequence on RNA-d is determined by the base of runs
contained in one segment of DNA, and each of these bases
will be searched ribonukleotidanya counterparts, then bundled
into the RNA chain-d. Readings by the beginning of the
earliest signs transcriptase (promoter) to mark the end
(terminator). Only the segment flanked by two signs that will
be transcribed. Gene is a gene controlling the protein so that
there should be at the link between the promoter and
terminator.
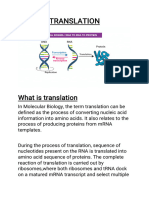
2. TRANSLATION
After the process of transcription in the nucleus of cells is
completed, then the RNA-d out from the core to be printed in
the preparation of a series of model amino acids in the
translational process. Genetic information carried by RNA-d
contained in the base runs, they contain. Each type of
combination of three adjacent bases that contain the genetic
code (codon) specific, which can be translated into one type of
amino acid. In one chain of RNA-d, only certain parts of a
mold pattern in protein synthesis, namely segment flanked by
initial codon (AUG) and the final codon (UAA, UAG, UGA)
After RNA-d to the ribosome, RNA-t begin
transporting amino acids into the complex translation
(ribosomes), also read codes (codons) RNA-d.
Furthermore, the amino acids brought by the RNA-t
assembled into polypeptides. The ability of RNA-t
perform these tasks, due to the anti-codon loop and
the ability of a compound with an amino acid called
aminoacyl-t RNA. The process of translating a series
of RNA codons-d into the polypeptide amino acid
sequence called a translation.
STAGES OF PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
1. Conduct DNA transcription (print dRNA) to bring the code - the code-
forming proteins, based on the sequence of nitrogenous bases
2. mRNA to escape from the DNA and carry the code - the genetic code
(codon) exit from the nucleus to the ribosomes in the cytoplasm. This mRNA
acts as a template (matrix). In this ribosomes attached to mRNA ribosomal
RNA (rRNA)
3. tRNA in the cytoplasm came with amino acids in accordance with the code
- the code that was brought by the mRNA. tRNA is attached (coupled) with
the mRNA in accordance with pasngan - nitrogen base pairs (with a triple
from nitrogenous bases of tRNA).
4. acids - amino acids that are brought by the tRNA will be holding each other
and form a series of polypeptide chains to form proteins that are expected in
the ribosome. Proteins that form this is an enzyme that regulates cellular
metabolism.
GENETIC CODE
The genetic code is the code carried by
messenger RNA (mRNA) to be submitted to the
transfer RNA (tRNA). The genetic code is a
sequence of three nitrogenous bases that make up
a so-called codon tripet (kodogen)
DELIVERY MECHANISM OF GENETIC CODE
Each code (one codon) is comprised of three nitrogen bases
located in the mRNA sequence. Codon - codon on the mRNA
must be translated by the tRNA, to learn which amino acids
should he brought
Example: if the codon on the mRNA read urasi-uracil-uracil
(UUU), the tRNA must deliver the amino acid phenylalanine.
The genetic code is universal to all organisms, meaning that
an organism's genetic code can be translated by other
organisms and form the same amino acid.
Example: AAA codon in human cells and in bacterial cells
will generate Lysine
You might also like
- Protien Synth 11thDocument3 pagesProtien Synth 11thtewoldeNo ratings yet
- Bio AssessmentDocument5 pagesBio Assessmentxx nataliaNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis: Indian Institute of Technology PatnaDocument29 pagesProtein Synthesis: Indian Institute of Technology PatnaHritik KumarNo ratings yet
- Genes AssignmentDocument4 pagesGenes AssignmentKyle Hilary MatundingNo ratings yet
- TranscriptionDocument25 pagesTranscriptionYamunaa ElencovanNo ratings yet
- 05b. Part 2 of Nucleic Acids For BSRadTechDocument26 pages05b. Part 2 of Nucleic Acids For BSRadTechBea Abigail BrocalNo ratings yet
- Central Dogma of Molecular GeneticsDocument3 pagesCentral Dogma of Molecular GeneticsDiana RomeroNo ratings yet
- RNA Protein SynthesisDocument14 pagesRNA Protein SynthesisLAL BUKHSHNo ratings yet
- Lab 4Document3 pagesLab 4Roben CasiongNo ratings yet
- Heredity - How A Protein Is Made Using DNA InformationDocument45 pagesHeredity - How A Protein Is Made Using DNA Informationkath chandriaNo ratings yet
- Chapter IV Introduction To Bacterial Genetics-1Document67 pagesChapter IV Introduction To Bacterial Genetics-1temesgensemahegn55No ratings yet
- How Cells Work CompilationDocument18 pagesHow Cells Work CompilationJocelyn Diaz AbangNo ratings yet
- CHE 461 Module 5Document30 pagesCHE 461 Module 5Danladi VictoriaNo ratings yet
- Protein SynthesisDocument18 pagesProtein SynthesisRussel OtillaNo ratings yet
- Types of RNA'sDocument17 pagesTypes of RNA'sRohit100% (2)
- Translation 1Document9 pagesTranslation 1akarshsingh111111No ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Section 4: Andrew BurtsfieldDocument10 pagesChapter 10 Section 4: Andrew BurtsfieldAndrew BurtsfieldNo ratings yet
- From Gene To ProteinDocument9 pagesFrom Gene To ProteincrookedspookNo ratings yet
- Q3 WEEK 4 Protein SynthesisDocument65 pagesQ3 WEEK 4 Protein SynthesisAdonis SanielNo ratings yet
- 2006 CHM6108 L9L10 SlidesDocument40 pages2006 CHM6108 L9L10 Slidesaidar.seralinNo ratings yet
- L18 Polypeptide SynthesisDocument18 pagesL18 Polypeptide Synthesisareejhussaini26No ratings yet
- Transcription and RNA ProcessingDocument37 pagesTranscription and RNA ProcessingEarl ReyesNo ratings yet
- Transcription and Translation.: Protein SynthesisDocument2 pagesTranscription and Translation.: Protein SynthesisShivani SriramNo ratings yet
- Dna ProcessesDocument28 pagesDna Processesvivas.kznne.9No ratings yet
- Worksheet Q3 Week 4&5 PDFDocument4 pagesWorksheet Q3 Week 4&5 PDFJaybie TejadaNo ratings yet
- RNA Ribonucleic Acid (English Pronunciation: /raɪbɵ - Nju Kleɪ - Ɨk Æsɪd/), or RNA, Is One of The Three MajorDocument1 pageRNA Ribonucleic Acid (English Pronunciation: /raɪbɵ - Nju Kleɪ - Ɨk Æsɪd/), or RNA, Is One of The Three MajorPRINTDESK by DanNo ratings yet
- Gene ExpressionDocument58 pagesGene ExpressionJunirose PanesNo ratings yet
- Biology InformationDocument6 pagesBiology InformationIgnacio LeonNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Q3 Week 4Document4 pagesWorksheet Q3 Week 4Jaybie TejadaNo ratings yet
- CH 12Document69 pagesCH 12ᄋᄂᄋᄂNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5Document27 pagesLecture 5Animikh RayNo ratings yet
- Transcription and TranslationDocument35 pagesTranscription and TranslationJaneNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology: InstructorDocument20 pagesCell Biology: Instructorahmed mediaNo ratings yet
- 1 The Central Dogma of Molecular BiologyDocument6 pages1 The Central Dogma of Molecular Biologydeladestianiaji2490100% (1)
- Protein BiosynthesisDocument7 pagesProtein BiosynthesisOlusola OtasanyaNo ratings yet
- Gene ExpressionDocument29 pagesGene ExpressionZainab Jamal SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Protein SynthesisDocument4 pagesProtein Synthesisyossifwaleed611No ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis With Video LinksDocument31 pagesProtein Synthesis With Video LinksSmilingNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis FinalDocument27 pagesProtein Synthesis FinalPatricia BonganayNo ratings yet
- Heredity: 10 - AmaziahDocument33 pagesHeredity: 10 - AmaziahAlice KrodeNo ratings yet
- RNA PowerPointDocument20 pagesRNA PowerPointAnki0391100% (1)
- Ribosome and Protein Synthesis: By: Delfi Zurita NIM: RSA1C411009Document16 pagesRibosome and Protein Synthesis: By: Delfi Zurita NIM: RSA1C411009Atikatul MutmainahNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 Protein SynthesisDocument8 pagesLesson 5 Protein SynthesisMarc Laurence LadoresNo ratings yet
- Unit 6. Proteins SynthesisDocument57 pagesUnit 6. Proteins Synthesismunyanezaolivier422No ratings yet
- Transcription &translation: Mol. Biology Lec-4 TranscriptionDocument12 pagesTranscription &translation: Mol. Biology Lec-4 TranscriptionAhmed Ali AssafNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acids OnlineDocument4 pagesNucleic Acids OnlineIsabel DizonNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acid Metabolism AllDocument31 pagesNucleic Acid Metabolism AllRaufur Rahman AkandaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Lec.22 (Nucleic Acids 6)Document6 pagesChemistry Lec.22 (Nucleic Acids 6)Muhammed AbdulsamadNo ratings yet
- TranslationDocument18 pagesTranslationMehwish IqbalNo ratings yet
- Protein SynthesisDocument135 pagesProtein SynthesisCarlaNo ratings yet
- Protein SynthesisDocument4 pagesProtein SynthesisEvans MogakaNo ratings yet
- Genetics Auto Saved)Document7 pagesGenetics Auto Saved)natseeaNo ratings yet
- Gene ExpressionDocument44 pagesGene Expressionaymnhssn2020No ratings yet
- 13 - Translation, Transcription and Processing of RnaDocument13 pages13 - Translation, Transcription and Processing of Rnawhether913No ratings yet
- Topic 15-18 Content ADocument28 pagesTopic 15-18 Content ALeanne Krystel CastroNo ratings yet
- From Dna To ProteinDocument6 pagesFrom Dna To ProteinMadona BadoevNo ratings yet
- Gene Expression and Regulation-TRFDocument6 pagesGene Expression and Regulation-TRFAnanya PriyadarsineeNo ratings yet
- Translation: By: Nathaniel Craig G. de GuzmanDocument30 pagesTranslation: By: Nathaniel Craig G. de GuzmanCristie Ann GuiamNo ratings yet
- ChatGPT talks on science for young people: Molecular Biology!: Discover the secrets of life with the help of artificial intelligenceFrom EverandChatGPT talks on science for young people: Molecular Biology!: Discover the secrets of life with the help of artificial intelligenceNo ratings yet
- Powerpoint Protein LocalizationDocument54 pagesPowerpoint Protein LocalizationJoseph BenaiahNo ratings yet
- Classic ExperimentsDocument53 pagesClassic ExperimentsAbhay Kumar100% (1)
- Ch8 Predictive Methods Using Protein SequencesDocument18 pagesCh8 Predictive Methods Using Protein Sequencesmirabilis_anneeNo ratings yet
- Manual. Qubit - RNA - XR - Assay - Kits - UGDocument18 pagesManual. Qubit - RNA - XR - Assay - Kits - UGRaquel Ramírez MorenoNo ratings yet
- Dna Rna Protein Synthesis Homework 2Document4 pagesDna Rna Protein Synthesis Homework 2tifqbfgig100% (2)
- 2 - Lipid BiosynthesisDocument44 pages2 - Lipid BiosynthesisAhmed HamarnehNo ratings yet
- Genomic and cDNA LibrariesDocument26 pagesGenomic and cDNA LibrariesSwapnil Kaldhone100% (1)
- O M Study Guide AnswerkeyDocument2 pagesO M Study Guide Answerkeyapi-237676607No ratings yet
- Step by Step Protocol For Multiplex PCR With The FastStartHigh Fidelity PCR System and The PCR Optimization KitDocument28 pagesStep by Step Protocol For Multiplex PCR With The FastStartHigh Fidelity PCR System and The PCR Optimization KittanjentNo ratings yet
- PCR HistoryDocument5 pagesPCR HistoryGisele HolandaNo ratings yet
- Bio 112 UBC MT2 Practice Exam Qs - Oct25th2013Document13 pagesBio 112 UBC MT2 Practice Exam Qs - Oct25th2013Cherica Oñate0% (1)
- Introduction To BioinformaticsDocument34 pagesIntroduction To BioinformaticsSaqlain Ali ShahNo ratings yet
- H4K20me0 Recognition by BRCA1-BARD1 Directs HR To Sister Chromatids. Nakamura K Et Al.-Nat Cell Biol 2019 PDFDocument14 pagesH4K20me0 Recognition by BRCA1-BARD1 Directs HR To Sister Chromatids. Nakamura K Et Al.-Nat Cell Biol 2019 PDFhutten7No ratings yet
- DNA Structure and Replication Online Classes I 1 2 3 MYPDocument36 pagesDNA Structure and Replication Online Classes I 1 2 3 MYPMedinaNo ratings yet
- Doc. AP Bio FRQ Biotech KEY PDFDocument11 pagesDoc. AP Bio FRQ Biotech KEY PDFMichael JuniorNo ratings yet
- 3D Structural Insights Into Glucans and Their BindingDocument13 pages3D Structural Insights Into Glucans and Their BindingjoseNo ratings yet
- Basic Science Quick Facts Step1Document31 pagesBasic Science Quick Facts Step1Hannah Jackson100% (20)
- DNA StructureDocument6 pagesDNA StructureSebastian RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Molecular Biology Previous Year QuestionsDocument7 pagesMolecular Biology Previous Year QuestionsKrutika SNo ratings yet
- Electrochemical Methods For The Analysis of Clinically RelevantDocument90 pagesElectrochemical Methods For The Analysis of Clinically Relevantch_ymyaaNo ratings yet
- Amplifying RNA Vaccine Development: Clinical Implications of Basic ResearchDocument3 pagesAmplifying RNA Vaccine Development: Clinical Implications of Basic ResearchxtineNo ratings yet
- Antibody Source Book EURDocument66 pagesAntibody Source Book EURchristina_finkeNo ratings yet
- Revised Cambridge Reference SequenceDocument6 pagesRevised Cambridge Reference SequenceRiemha Tiquie PurpleNo ratings yet
- Biological Stain Analysis: DNA: Fourth EditionDocument88 pagesBiological Stain Analysis: DNA: Fourth Editionccondeiu1No ratings yet
- Genotyping by Sequencing in Almond: SNP Discovery, Linkage Mapping, and Marker DesignDocument12 pagesGenotyping by Sequencing in Almond: SNP Discovery, Linkage Mapping, and Marker DesignNicol TatelNo ratings yet
- SHS PHYSICAL-SCIENCE Q1 M4 Biological-MacromoleculesDocument30 pagesSHS PHYSICAL-SCIENCE Q1 M4 Biological-Macromoleculesjastinkim334No ratings yet
- Chapter 13.4 & 15.4 Active Reading GuideDocument5 pagesChapter 13.4 & 15.4 Active Reading GuidedorothyNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry II MCQDocument5 pagesBiochemistry II MCQMuhammad Bilal100% (2)
- Dna Sequencing (Sanger's Method)Document12 pagesDna Sequencing (Sanger's Method)Ajay KumarNo ratings yet
- Basic in Obstetrics and Gynecology 4th PDFDocument384 pagesBasic in Obstetrics and Gynecology 4th PDFsandraamoNo ratings yet