Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Professor Izham Cheong, FRCP DR Tan Hui Jan, Mmed, MRCP DR Wong Ming, Mmed, MRCP DR Chang Sau Kong, MRCP
Uploaded by
ghufran adnan0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
61 views5 pagesA 60-year-old man presented with 6 months of progressive memory loss and difficulty walking with frequent falls. Brain CT showed enlarged ventricles disproportionate to widened sulci, consistent with normal pressure hydrocephalus (NPH). NPH is characterized by the triad of dementia, ataxia, and urinary incontinence. It results from distortion of brain structures by enlarged ventricles. Management of suspected NPH includes neuropsychological evaluation, timed walking tests, and lumbar puncture to evaluate improvement in symptoms before considering surgical placement of a CSF shunt.
Original Description:
q
Original Title
Session 12
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentA 60-year-old man presented with 6 months of progressive memory loss and difficulty walking with frequent falls. Brain CT showed enlarged ventricles disproportionate to widened sulci, consistent with normal pressure hydrocephalus (NPH). NPH is characterized by the triad of dementia, ataxia, and urinary incontinence. It results from distortion of brain structures by enlarged ventricles. Management of suspected NPH includes neuropsychological evaluation, timed walking tests, and lumbar puncture to evaluate improvement in symptoms before considering surgical placement of a CSF shunt.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
61 views5 pagesProfessor Izham Cheong, FRCP DR Tan Hui Jan, Mmed, MRCP DR Wong Ming, Mmed, MRCP DR Chang Sau Kong, MRCP
Uploaded by
ghufran adnanA 60-year-old man presented with 6 months of progressive memory loss and difficulty walking with frequent falls. Brain CT showed enlarged ventricles disproportionate to widened sulci, consistent with normal pressure hydrocephalus (NPH). NPH is characterized by the triad of dementia, ataxia, and urinary incontinence. It results from distortion of brain structures by enlarged ventricles. Management of suspected NPH includes neuropsychological evaluation, timed walking tests, and lumbar puncture to evaluate improvement in symptoms before considering surgical placement of a CSF shunt.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 5
SELF ASSESSMENT COLOUR
REVIEW OF
CLINICAL MEDICINE
Professor Izham Cheong, FRCP
Dr Tan Hui Jan, MMed, MRCP
Dr Wong Ming, MMed, MRCP
Dr Chang Sau Kong, MRCP
A 60 year old man presents with progressive memory loss of 6
months duration. He had difficulty in walking and had frequent falls
at home.
Q: What is the diagnosis?
A: Normal pressure hydrocephalus
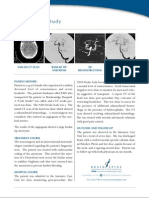
The brain CT showed dilatation of the ventricles which was out of
proportion to the widening of the sulci.
Normal pressure hydrocephalus (NPH) is characterized by the
triad of dementia, ataxia and urinary incontinence.
It accounts for 5% demented pts in the older age group (late
middle aged and elderly). NPH may begin with a transient high-
pressure hydrocephalus with subsequent ventricular enlargement.
With further enlargement of the ventricles, CSF pressure returns
to normal. There is intermittent intracranial hypertension.
Clinical symptoms result
from distortion of the central
portion of the corona radiata
by the distended ventricles.
Involvement of the sacral
motor fibres that innervate
the legs and the bladder
gives rise to the ataxia and
urinary incontinence.
Parkinson’s like features
results from intermittent
high pressure leading to
seepage of CSF destroying
the striatonigral area.
Dementia results from
distortion of the
periventricular limbic
system.
CT scan brain showing dilated
ventricles. The white arrow
points to a rounded frontal
horn
Management of these patients suspected to have NPH include a
baseline neuropsychological evaluation and a timed walking test. Prior
to lumbar puncture, the patient is required to walk a fixed distance
and the duration will be timed. A lumbar puncture is then performed
to remove 30 – 50 cc of CSF. After which, the patient walks the same
distance again while being timed. Improvement in gait may be seen in
the form of reduced time to walk a fixed distance, reduced gait apraxia
or reduced freezing of gait. A clear cut improvement in mental status
and/or gait after the timed walking test predicts a favourable response
to shunt surgery.
Surgical CSF shunting includes ventr
You might also like
- Spinal and Epidural Anesthesia: Jedarlyn G. Erardo, RPH, MDDocument101 pagesSpinal and Epidural Anesthesia: Jedarlyn G. Erardo, RPH, MDjedarlynNo ratings yet
- Increased Intracranial PressureDocument34 pagesIncreased Intracranial PressureshykitijaNo ratings yet
- M A N A G E M E NT OF H E A D I NJ UR Y & I NT R A CR A N I A L P RE SS UR EDocument19 pagesM A N A G E M E NT OF H E A D I NJ UR Y & I NT R A CR A N I A L P RE SS UR EmugihartadiNo ratings yet
- Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus: From Diagnosis to TreatmentFrom EverandNormal Pressure Hydrocephalus: From Diagnosis to TreatmentRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Nursing Care Plans - Ineffective Cerebral Tissue PerfusionDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plans - Ineffective Cerebral Tissue PerfusionKate Cruz75% (8)
- Ineffective Cerebral Tissue PerfusionDocument3 pagesIneffective Cerebral Tissue PerfusionHanya Bint Potawan88% (25)
- Normal Pressure HydrocephalusDocument59 pagesNormal Pressure Hydrocephalusrys239No ratings yet
- Hydrocephalus & ShuntsDocument9 pagesHydrocephalus & ShuntsVaseem ZamairNo ratings yet
- 55421-Gagal JantungDocument21 pages55421-Gagal JantungAngie CouthalooNo ratings yet
- NPHDocument2 pagesNPHbimaindra97No ratings yet
- CSFHypotensionDocument52 pagesCSFHypotensionSoumavo DasNo ratings yet
- Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus (NPH) : Clinical SyndromeDocument6 pagesNormal Pressure Hydrocephalus (NPH) : Clinical SyndromeDesyana PerwitahatiNo ratings yet
- Intracranial Cerebrospinal FluDocument4 pagesIntracranial Cerebrospinal FluAffan AdibNo ratings yet
- ENLS Sub-Arachnoid Hemorrhage ProtocolDocument22 pagesENLS Sub-Arachnoid Hemorrhage ProtocolFransiskus MikaelNo ratings yet
- (Journal of Neurosurgery) Pathophysiology of Long-Standing Overt Ventriculomegaly in Adults PDFDocument8 pages(Journal of Neurosurgery) Pathophysiology of Long-Standing Overt Ventriculomegaly in Adults PDFKusumaningrum WijayantiNo ratings yet
- Invasive Neuromonitoring TechniqueDocument20 pagesInvasive Neuromonitoring TechniqueReza ManefoNo ratings yet
- Lumbar Puncture ResearchDocument6 pagesLumbar Puncture Researchanon_464104226No ratings yet
- 296 FullDocument4 pages296 FullDora MukupaNo ratings yet
- Caso Clínico 2 NeuroDocument4 pagesCaso Clínico 2 NeuroAna Maria GarciaNo ratings yet
- Procedure: Positioning in Lumbar PunctureDocument7 pagesProcedure: Positioning in Lumbar PunctureUsama El BazNo ratings yet
- Explain The Physiological Mechanism That Maintain Normal Intracranial PressureDocument25 pagesExplain The Physiological Mechanism That Maintain Normal Intracranial PressureRAFNo ratings yet
- Grand Round Discussion: Dr. Nyaoncha A. NDocument36 pagesGrand Round Discussion: Dr. Nyaoncha A. NomoturetiNo ratings yet
- Tadevosyan 2021Document26 pagesTadevosyan 2021W Antonio Rivera MartínezNo ratings yet
- Block 2 Assignment Edited Catherine Ruguru SamsonDocument12 pagesBlock 2 Assignment Edited Catherine Ruguru Samsonmoses karituNo ratings yet
- A Lumbar PunctureDocument6 pagesA Lumbar PunctureNivinj KennedyNo ratings yet
- Emergency Neurological Life Support - Subarachnoid HemorrhageDocument9 pagesEmergency Neurological Life Support - Subarachnoid HemorrhageIsabel VillalobosNo ratings yet
- Clinical Manifestations of Hydrocephalus: A ReviewDocument5 pagesClinical Manifestations of Hydrocephalus: A Reviewvane06No ratings yet
- Increased Intracranial PressureDocument13 pagesIncreased Intracranial PressureLudmila PirtacNo ratings yet
- Increased Intracranial Pressure: CEU ProfessorDocument9 pagesIncreased Intracranial Pressure: CEU ProfessorJah AcabNo ratings yet
- ABC ResuscitationDocument5 pagesABC ResuscitationIamTineshNo ratings yet
- The Syndrome of Normal-Pressure Hydrocephalus VassilioutisDocument9 pagesThe Syndrome of Normal-Pressure Hydrocephalus VassilioutisPablo Sousa CasasnovasNo ratings yet
- Acupuncture 5Document5 pagesAcupuncture 5abraham rumayaraNo ratings yet
- Efek SpinalDocument11 pagesEfek SpinalFaundraAriezaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document9 pagesChapter 5Aristya EkaputraNo ratings yet
- Traumatic Head InjuriesDocument50 pagesTraumatic Head InjuriesVasudha BuddyNo ratings yet
- AISDocument40 pagesAISMohamed AbdoNo ratings yet
- Cheng 2017Document6 pagesCheng 2017Lepaca KliffothNo ratings yet
- Documento PDFDocument5 pagesDocumento PDFJose Miguel CastellonNo ratings yet
- Head Injury Management: Ahimbisibwe Alaphael Lecturer DR - JulietDocument33 pagesHead Injury Management: Ahimbisibwe Alaphael Lecturer DR - JulietNinaNo ratings yet
- Tiers IcpDocument12 pagesTiers IcpjheyfteeNo ratings yet
- Management OF Head Injury: DR Echebiri, PDocument26 pagesManagement OF Head Injury: DR Echebiri, PLuther ThengNo ratings yet
- Icp and Anaesthesia DrugsDocument56 pagesIcp and Anaesthesia DrugsKhawer MuneerNo ratings yet
- Spinal Anaesthesia A Practical GuideDocument14 pagesSpinal Anaesthesia A Practical GuideNovita WulandariNo ratings yet
- Hyper Eusinophillia AyushDocument44 pagesHyper Eusinophillia Ayushpriyank kumarNo ratings yet
- Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus: Lo-Call 1890 20 22 60Document5 pagesNormal Pressure Hydrocephalus: Lo-Call 1890 20 22 60Amelia ArnisNo ratings yet
- Intracranial Pressure Concerns in LateralDocument8 pagesIntracranial Pressure Concerns in Lateralapi-19500641No ratings yet
- Siddiqui Et Al. - 2017 - World NeurosurgeryDocument16 pagesSiddiqui Et Al. - 2017 - World NeurosurgeryubaidNo ratings yet
- Neuro Emergencies MccoydDocument56 pagesNeuro Emergencies Mccoydgirolamoancorato84No ratings yet
- Lec 3 4 ICP EllenDocument61 pagesLec 3 4 ICP Ellenkatherinerance331No ratings yet
- Shock: Ivan Mucharry Dalitan - PPDS Orthopaedi & Traumatologi Semester IVDocument5 pagesShock: Ivan Mucharry Dalitan - PPDS Orthopaedi & Traumatologi Semester IVusnulNo ratings yet
- NPH BookletDocument41 pagesNPH BookletDini NanamiNo ratings yet
- Dust inDocument7 pagesDust inlarkspor31No ratings yet
- Flat-Head Positioning Increases Cerebral Blood Flow in Anterior Circulation Acute Ischemic Stroke. A Cluster Randomized Phase Iib TrialDocument12 pagesFlat-Head Positioning Increases Cerebral Blood Flow in Anterior Circulation Acute Ischemic Stroke. A Cluster Randomized Phase Iib TrialNaufal HilmiNo ratings yet
- Cerebrovascular AccidentDocument30 pagesCerebrovascular AccidentRichard Charles UmlasNo ratings yet
- NCM 118L/ 119L (Related Learning Experience) Day 3-ActivityDocument4 pagesNCM 118L/ 119L (Related Learning Experience) Day 3-ActivityNicole Villanueva, BSN - Level 3ANo ratings yet
- Brain DeathDocument36 pagesBrain Deathjustforfun219No ratings yet
- Stroke Case Study - 1finalDocument1 pageStroke Case Study - 1finalBeue YuyuNo ratings yet
- Cerebral Herniation Syndromes and Intracranial HypertensionFrom EverandCerebral Herniation Syndromes and Intracranial HypertensionMatthew KoenigNo ratings yet
- Clinical Autonomic and Mitochondrial Disorders: Diagnosis, Prevention, and Treatment for Mind-Body WellnessFrom EverandClinical Autonomic and Mitochondrial Disorders: Diagnosis, Prevention, and Treatment for Mind-Body WellnessNo ratings yet
- MedicineDocument5 pagesMedicineghufran adnanNo ratings yet
- Ehy340 PDFDocument83 pagesEhy340 PDFghufran adnanNo ratings yet
- LectureDocument30 pagesLectureghufran adnanNo ratings yet
- Outline: - Matched PairsDocument43 pagesOutline: - Matched Pairsghufran adnanNo ratings yet
- Outline: - Matched PairsDocument43 pagesOutline: - Matched Pairsghufran adnanNo ratings yet