Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Linear Elastic Fracture Mechanics (LEFM)
Uploaded by
Jia En0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views19 pagesThis document discusses Linear Elastic Fracture Mechanics (LEFM). It introduces LEFM and how it is used to predict the load-carrying capabilities of cracked structures when plastic deformation at the crack tip is negligible. Griffith first introduced LEFM in 1920 by showing the critical stress required to propagate a crack depends on the material's surface energy and crack length. Later, Irwin incorporated both brittle and ductile surface energies into the critical strain energy release rate. Stress Intensity Factors (SIF) are also introduced to characterize stresses at crack tips under different loading modes. The document assigns analyzing SIF using finite element software and comparing the results to equations. It concludes by defining fracture toughness as the critical SIF
Original Description:
Fatigue notes
Original Title
Fatigue
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses Linear Elastic Fracture Mechanics (LEFM). It introduces LEFM and how it is used to predict the load-carrying capabilities of cracked structures when plastic deformation at the crack tip is negligible. Griffith first introduced LEFM in 1920 by showing the critical stress required to propagate a crack depends on the material's surface energy and crack length. Later, Irwin incorporated both brittle and ductile surface energies into the critical strain energy release rate. Stress Intensity Factors (SIF) are also introduced to characterize stresses at crack tips under different loading modes. The document assigns analyzing SIF using finite element software and comparing the results to equations. It concludes by defining fracture toughness as the critical SIF
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views19 pagesLinear Elastic Fracture Mechanics (LEFM)
Uploaded by
Jia EnThis document discusses Linear Elastic Fracture Mechanics (LEFM). It introduces LEFM and how it is used to predict the load-carrying capabilities of cracked structures when plastic deformation at the crack tip is negligible. Griffith first introduced LEFM in 1920 by showing the critical stress required to propagate a crack depends on the material's surface energy and crack length. Later, Irwin incorporated both brittle and ductile surface energies into the critical strain energy release rate. Stress Intensity Factors (SIF) are also introduced to characterize stresses at crack tips under different loading modes. The document assigns analyzing SIF using finite element software and comparing the results to equations. It concludes by defining fracture toughness as the critical SIF
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 19
Chapter 2
Linear Elastic Fracture
Mechanics (LEFM)
Introduction
• The science of predicting
the load - carrying
capabilities of structures
or components containing
cracks.
• LEFM is used when plastic
deformation at the crack
tip is insignificant.
• LEFM is firstly introduced
by Griffith in 1920.
Griffith Equation
• He showed that the critical stress required to propagate a crack in a
brittle material:
• Orowan then modified the Griffith equation:
Griffith Equation
• If the material is highly ductile, plastic surface energy is dominant:
• Irwin then incorporate both types of surface energies into the critical
strain energy release rate, Gc:
• Griffith equation for both brittle and ductile materials:
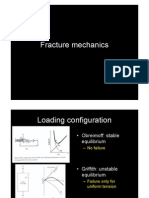
Mode of failure
Stress Intensity Factor (SIF), Mode I and II
Displacements at the crack tip
Stress Intensity Factors (SIF), Mode III
Stress Intensity Factors
• In general, SIF can be calculated using (the unit is MPa√m):
Stress Intensity Factors
Stress Intensity Factor
Stress Intensity Factor
Stress Intensity Factors
Stress Intensity Factor
Stress Intensity Factor
Assignment 2
• Perform finite element analysis to Your report must contain:
analyze the behavior of plate • Introduction
containing a crack.
• Methodology
• Use ANSYS finite element software.
• Results and discussion
• Compare the results obtained using
finite element software with the • Conclusion
results using the equation studied • References
previously.
Submission:
• Use 20 different crack length during
analysis. • Hardcopy
• Google this keywords: “ansys • Email to: emran@uthm.edu.my
fracture tutorial” • Upload to: my WhatsApp
Fracture Toughness
• When applied stress, exceeds some critical value, c, the crack
propagates.
• The critical value of c corresponds to the critical value of SIF and it is
called the fracture toughness, Kc:
• Kc is a measure of the resistance of a material to brittle fracture when
it contains a crack.
Fracture Toughness
Fracture Toughness
You might also like
- Plastic AnalysisDocument51 pagesPlastic AnalysisHafeel Ahamed Ashraf AliNo ratings yet
- Study of Slope Stability Using AbaqusDocument21 pagesStudy of Slope Stability Using AbaqusAdam Sha100% (2)
- Intro To Fracture Mechanics, Fatigue and CreepDocument40 pagesIntro To Fracture Mechanics, Fatigue and CreepM.USMAN BIN AHMED100% (1)
- Griffith Theory of Brittle FractureDocument11 pagesGriffith Theory of Brittle FractureM.Saravana Kumar..M.E100% (1)
- Introduction To Finite Element Method (FEM)Document22 pagesIntroduction To Finite Element Method (FEM)goldencomet100% (1)
- Lecture - 5 - Notes 5 - Fracture - Brittle Ductile Transition PDFDocument100 pagesLecture - 5 - Notes 5 - Fracture - Brittle Ductile Transition PDFrony16nov100% (1)
- Fracture MechanicsDocument13 pagesFracture MechanicsNishant Patil100% (1)
- Fracture MechanicsDocument22 pagesFracture Mechanicsaap1No ratings yet
- Fatigue and Damage Tolerance: Edward Herba, January 29,2004Document38 pagesFatigue and Damage Tolerance: Edward Herba, January 29,2004Nagaraj RamachandrappaNo ratings yet
- Design For Fracture: Lecture Two Lect. Dr. Hind B. Al-AttraqchiDocument35 pagesDesign For Fracture: Lecture Two Lect. Dr. Hind B. Al-AttraqchiTRNADEWNo ratings yet
- Experiment and Calculation of Reinforced Concrete at Elevated TemperaturesFrom EverandExperiment and Calculation of Reinforced Concrete at Elevated TemperaturesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- 5 Mechanical TestingDocument70 pages5 Mechanical TestingLahiru JananjayaNo ratings yet
- Lec 1Document29 pagesLec 1prasobhaNo ratings yet
- Fracture Mechanics: Lecture-IDocument29 pagesFracture Mechanics: Lecture-IArindam MajumderNo ratings yet
- Fracture Mechanics - WikipediaDocument47 pagesFracture Mechanics - WikipediaReeverse MasterminddNo ratings yet
- Presentation - Stress-Strain CurveDocument17 pagesPresentation - Stress-Strain CurveprashantNo ratings yet
- Fracto Non-Linear MechanicsDocument11 pagesFracto Non-Linear MechanicsyatinNo ratings yet
- Fracture Mechanics in Ansys R16: Session Will Begin at 10:00 AM (Pacific Day Time)Document36 pagesFracture Mechanics in Ansys R16: Session Will Begin at 10:00 AM (Pacific Day Time)rockmanqhNo ratings yet
- Non-Linear Structural AnalysisDocument12 pagesNon-Linear Structural AnalysisMohammed SallamNo ratings yet
- ExperimentsDocument22 pagesExperimentsBakkashreya SriNo ratings yet
- Griffith TheoryDocument25 pagesGriffith TheoryHariDharan MNo ratings yet
- NEHA Mechanical Properties BiomaterialsDocument19 pagesNEHA Mechanical Properties BiomaterialsRavishanker BaligaNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes 5 - 2 Fracture MechanicsDocument26 pagesLecture Notes 5 - 2 Fracture MechanicsParash ChakmaNo ratings yet
- Lab 2 Manual-DengDocument3 pagesLab 2 Manual-DengDavid ChenNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Behavior IDocument33 pagesMechanical Behavior IVidushi MakhijaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 (Material Properties) PDFDocument49 pagesLecture 4 (Material Properties) PDFJunhong BapNo ratings yet
- Criterios de FallaDocument55 pagesCriterios de FallaccviafarNo ratings yet
- Srm-Cad-Unit IvDocument92 pagesSrm-Cad-Unit IvVikrant ThakurNo ratings yet
- Lect No - 05 Evaluation of Properties of Manufactured ProductsDocument25 pagesLect No - 05 Evaluation of Properties of Manufactured Productsnitendra kumarNo ratings yet
- My Fem ProjectDocument29 pagesMy Fem ProjectOraib AljaafrehNo ratings yet
- Design of Engineering Materials: Stress-Strain DiagramDocument32 pagesDesign of Engineering Materials: Stress-Strain DiagramTRNADEWNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Materials Technology Esrmnotes - In-1 PDFDocument118 pagesUnit 3 Materials Technology Esrmnotes - In-1 PDFshivam agarwalNo ratings yet
- Toughnessandfracturetoughness 160316060826Document19 pagesToughnessandfracturetoughness 160316060826adelNo ratings yet
- Basic Concept of Finite Element AnalysisDocument23 pagesBasic Concept of Finite Element AnalysisKhairulanwar SaidNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Nonlinear AnalysisDocument12 pagesIntroduction To Nonlinear AnalysisJohn ScottNo ratings yet
- Lecturer 2: Engineering and True Stress-Strain Ductile Materials Brittle MaterialDocument19 pagesLecturer 2: Engineering and True Stress-Strain Ductile Materials Brittle Materialbpkndl7943No ratings yet
- Materials and Metallurgy (ME-209) Week 1 - Lecture 2 Mechanical Properties of MaterialsDocument28 pagesMaterials and Metallurgy (ME-209) Week 1 - Lecture 2 Mechanical Properties of MaterialsFahad afzalNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials: Sức Bền Vật LiệuDocument41 pagesStrength of Materials: Sức Bền Vật LiệuVũ HoàngNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 Revised CMDocument31 pagesTopic 2 Revised CMO. L. K. (On)No ratings yet
- Fracture Mechanics Elastic-Plastic FractureDocument59 pagesFracture Mechanics Elastic-Plastic FractureMansoor AhmadNo ratings yet
- Fracture Mechanics External Course Siemens Winter 2011-12Document22 pagesFracture Mechanics External Course Siemens Winter 2011-12jorgenkrabNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document51 pagesChapter 3Sathiswaran SelvamNo ratings yet
- Selection of Material & ProcessesDocument32 pagesSelection of Material & ProcessesNikhil WaghalkarNo ratings yet
- Material PropertiesDocument95 pagesMaterial PropertiesnarutouzamakiNo ratings yet
- Name: Ritik Janbandhu Roll No.: SCH 19 Block: B1Document3 pagesName: Ritik Janbandhu Roll No.: SCH 19 Block: B1ritik janbandhuNo ratings yet
- Tensile Testing Lab SheetDocument3 pagesTensile Testing Lab SheetHalaaNo ratings yet
- Unit 3Document31 pagesUnit 3RED EYENo ratings yet
- Explosive Testing of Open CylindersDocument27 pagesExplosive Testing of Open CylindershaithamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Complete Beam DesignDocument18 pagesChapter 3 - Complete Beam DesignAnonymous tjIk84No ratings yet
- Mechanical PropertiesDocument77 pagesMechanical PropertiesGerd FreeNo ratings yet
- Material TechnologyDocument46 pagesMaterial TechnologyVarunNo ratings yet
- 4 Fracture MechanicsDocument17 pages4 Fracture MechanicsSubhash AhujaNo ratings yet
- Fracture IntroductionDocument11 pagesFracture IntroductionPriyank PrasadNo ratings yet
- Btec Higher Nationals-Strengths of Materials - H2 Assignment Strain EnergyDocument6 pagesBtec Higher Nationals-Strengths of Materials - H2 Assignment Strain EnergyFawaaz KhurwolahNo ratings yet
- Btec Higher Nationals-Strengths of Materials - H2 Assignment - Outcome 1Document5 pagesBtec Higher Nationals-Strengths of Materials - H2 Assignment - Outcome 1Fawaaz KhurwolahNo ratings yet
- 2018 10 08 ToughnessDocument54 pages2018 10 08 ToughnessSara JaberNo ratings yet
- UNIT-II Mechanical Property MeasurementDocument127 pagesUNIT-II Mechanical Property Measurementlol WANo ratings yet
- Module-Iv: Strength of ConcreteDocument9 pagesModule-Iv: Strength of ConcreteirshadNo ratings yet
- Failure Analysis: Al Emran Ismail, PHDDocument12 pagesFailure Analysis: Al Emran Ismail, PHDJia EnNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Fatigue and Fracture: Al Emran Ismail, PHDDocument11 pagesIntroduction To Fatigue and Fracture: Al Emran Ismail, PHDJia EnNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Boundary Layer TheoryDocument37 pagesChapter 3 - Boundary Layer TheoryJia En100% (1)
- Trigonometric Definitions and Basic IdentitiesDocument3 pagesTrigonometric Definitions and Basic IdentitiesJia EnNo ratings yet