Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Mccabe Thiele
Uploaded by
sparsh datey0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views9 pagesmccabe T
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentmccabe T
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views9 pagesMccabe Thiele
Uploaded by
sparsh dateymccabe T
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 9
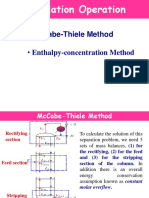
McCabe Thiele Method
McCabe and Thiele (1925) developed a graphical
method to determine the theoretical number of
stages required to effect the separation of a binary
mixture. This method uses the equilibrium curve
diagram to determine the number of theoretical
stages (trays) required to achieve a desired degree
of separation.
What is McCabe Thiele Method
This method uses the equilibrium curve
diagram to determine the number of
theoretical stages (trays) required to achieve a
desired degree of separation
Assumptions
(i) Molal heats of vaporization of the
components are roughly the same.
(ii) Heat effects are negligible.
Description
The feed has a concentration of xF (mole
fraction) of the more volatile component, and
a distillate having a concentration of xD of the
more volatile component and a bottoms
having a concentration of xB is desired. In its
essence, the method involves the plotting on
the equilibrium diagram three straight lines:
the rectifying section operating line (ROL), the
feed line (also known as the q-line) and the
stripping section operating line (SOL). R = L / D
Steps
• 1. Determination of the Rectifying section
operating line (ROL).
2. Determination the feed condition (q).
3. Determination of the feed section
operating line (q-line)
4. Determination of required reflux ratio (R).
5. Determination of the stripping section
operating line (SOL).
6. Determination of number of theoretical
stage.
Determination of the Rectifying
section operating line (ROL)
Determination of the Rectifying section
operating line (ROL) (continue…)
Determination of the Rectifying section
operating line (ROL) (continue…)
Determination of number of
theoritical plates
• In last graph we will continue to make the
triangles up to (xw,xw), then the no. of
theoretical plates= no. of triangles and no. of
actual plates = no. of theoretical plates-1.
If the mole fractions are not given we will
calculate it by using the value of α
and relation between x and y is
y= αx/(1+(α-1)x)
You might also like
- Kuwait Crude AssayDocument5 pagesKuwait Crude Assaysparsh dateyNo ratings yet
- DistillationDocument29 pagesDistillationgebremichaelNo ratings yet
- Steam Table Problems PDFDocument5 pagesSteam Table Problems PDFBenedick Jayson P. Marti100% (1)
- 2009 McCabe Thiele DiagramDocument9 pages2009 McCabe Thiele DiagramSyazwan WanNo ratings yet
- Longman Additional Mathematics For A Level (Advanced Level)Document536 pagesLongman Additional Mathematics For A Level (Advanced Level)akakios033% (3)
- Experimental Methods in Wastewater Treatment PDFDocument362 pagesExperimental Methods in Wastewater Treatment PDFfikri fikriNo ratings yet
- Material Balances Without Chemical ReactionDocument223 pagesMaterial Balances Without Chemical Reactionsparsh datey100% (1)
- Material Balances Without Chemical ReactionDocument223 pagesMaterial Balances Without Chemical Reactionsparsh datey100% (1)
- GARCH Models: Structure, Statistical Inference and Financial ApplicationsFrom EverandGARCH Models: Structure, Statistical Inference and Financial ApplicationsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Modeling and Simulation Study of The CSTR For Complex Reation Usong POLYMATHDocument7 pagesModeling and Simulation Study of The CSTR For Complex Reation Usong POLYMATHtocinopNo ratings yet
- Mass Transfer Principles and Operations de SinhaDocument728 pagesMass Transfer Principles and Operations de Sinhahann_dle88% (32)
- DistillationTheory 1Document21 pagesDistillationTheory 1Prashant KumarNo ratings yet
- Chapt4 Part3Document58 pagesChapt4 Part3ShamsMohdNo ratings yet
- Ch4 DesignDocument72 pagesCh4 DesignGebrekiros ArayaNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mathematics: 1qllgiDocument10 pagesEngineering Mathematics: 1qllgiiwonttellyouthatNo ratings yet
- BENG0015 - Distilation Exam QuestionsDocument6 pagesBENG0015 - Distilation Exam QuestionsHercules ArgyNo ratings yet
- SNU 2019 ExamsDocument43 pagesSNU 2019 ExamsSamuel MergaNo ratings yet
- Homework 3 - Further Regression and Tutorial in RDocument5 pagesHomework 3 - Further Regression and Tutorial in RJohn SmithNo ratings yet
- Chapt4 Part3 PDFDocument58 pagesChapt4 Part3 PDFShamsMohdNo ratings yet
- Distillation Column DesignDocument17 pagesDistillation Column Design259Katkar PrathmeshNo ratings yet
- Supplementary-Model DerivationsDocument8 pagesSupplementary-Model DerivationsNourAlsawaftahNo ratings yet
- Computer Graphics Using Open GL, 3 Edition F. S. Hill, Jr. and S. KelleyDocument49 pagesComputer Graphics Using Open GL, 3 Edition F. S. Hill, Jr. and S. KelleyAbrahamNo ratings yet
- A Complete Generalized Solution To The Inverse Kinematics of Robots-UgADocument7 pagesA Complete Generalized Solution To The Inverse Kinematics of Robots-UgAArijit RoyNo ratings yet
- Runge-Kutta Activity4Document5 pagesRunge-Kutta Activity4Daniel GetachewNo ratings yet
- 384 FTPDocument2 pages384 FTPRavindra MRNo ratings yet
- Thermal (TE-411,412,413,414,511)Document25 pagesThermal (TE-411,412,413,414,511)nved01No ratings yet
- Distillation Column Profile Map PaperDocument11 pagesDistillation Column Profile Map PapersdrtfgNo ratings yet
- Mccabe Thiele MethodDocument5 pagesMccabe Thiele MethodSethumadhavan KundumaniNo ratings yet
- m314 TestDocument2 pagesm314 Testapi-490667843No ratings yet
- Continuous Distillation Practice 1Document35 pagesContinuous Distillation Practice 1Najmul Puda PappadamNo ratings yet
- DA-2 - Rishav Kumar Reg No - 17BCM0026 Slot - B1 Course-: Computational Method in Process EngineeringDocument4 pagesDA-2 - Rishav Kumar Reg No - 17BCM0026 Slot - B1 Course-: Computational Method in Process EngineeringRISHAV KUMAR 17BCM0026No ratings yet
- 04.desbloqueadoDocument47 pages04.desbloqueadoJhonatan Gerardo Soto Puelles67% (3)
- PMS Self StudyDocument16 pagesPMS Self StudyAbhishek KabburNo ratings yet
- Ume805 4Document2 pagesUme805 4Raunaq SinghNo ratings yet
- A Simple Design Method For Multicomponent Distillation ColumnsDocument8 pagesA Simple Design Method For Multicomponent Distillation Columnsramantal5No ratings yet
- McCabe-Thiele Distillation Column Design For A Methanol-Propanol SystemDocument12 pagesMcCabe-Thiele Distillation Column Design For A Methanol-Propanol SystemPeyton EllenNo ratings yet
- AHRS LabDocument12 pagesAHRS Labjoshimeet479No ratings yet
- Activity 4 Distillation Using Ponchon-Savarit Method Problem 1 A Mixture of 40 Mol% Benzene and 60 Mol% Toluene Is To Be Separated by Distillation atDocument21 pagesActivity 4 Distillation Using Ponchon-Savarit Method Problem 1 A Mixture of 40 Mol% Benzene and 60 Mol% Toluene Is To Be Separated by Distillation atJonelou CusipagNo ratings yet
- A New Approach Towards The Synthesis of Six-Bar Double Dwell MechanismsDocument9 pagesA New Approach Towards The Synthesis of Six-Bar Double Dwell Mechanismsanon_830784355No ratings yet
- Distillation Design The Mccabe-Thiele MethodDocument24 pagesDistillation Design The Mccabe-Thiele MethodNagwa MansyNo ratings yet
- The Mccabe-Thiele Method: Stream Total Molar Flowrate Composition (Mole Fraction MVC) V YDocument10 pagesThe Mccabe-Thiele Method: Stream Total Molar Flowrate Composition (Mole Fraction MVC) V YRose Dane Escobedo DiestaNo ratings yet
- Simulation IntroductionDocument19 pagesSimulation Introductionanand_upadhyay_9No ratings yet
- Me352 E1 Fa2009 SolDocument21 pagesMe352 E1 Fa2009 SolSteve KrodaNo ratings yet
- S Announcement 3133Document60 pagesS Announcement 3133Zetsu BlackNo ratings yet
- Vector Method For The Synthesis of MechanismsDocument12 pagesVector Method For The Synthesis of MechanismsBilal OraikNo ratings yet
- Fast, Precise Attening of Cubic Be Zier Path and Offset CurvesDocument11 pagesFast, Precise Attening of Cubic Be Zier Path and Offset CurvesThea LandichoNo ratings yet
- 1 Modified Taylor Solution of Equation of Oxygen in A Spherical Cell With Michaelis Menten Uptake KineticsDocument6 pages1 Modified Taylor Solution of Equation of Oxygen in A Spherical Cell With Michaelis Menten Uptake Kineticsmario sandovalNo ratings yet
- Large Scale Optimization Strategies For Zone Configuration of Simulated Moving BedsDocument18 pagesLarge Scale Optimization Strategies For Zone Configuration of Simulated Moving BedsDoctorObermanNo ratings yet
- Mccabe Thiele MethodDocument3 pagesMccabe Thiele Methodmusmanzafar100% (1)
- 4 Excel Inclass Assignment Slider Crank1 PDF FreeDocument8 pages4 Excel Inclass Assignment Slider Crank1 PDF Freezoom_999No ratings yet
- Plotting Mccabe-Thiele Diagrams in Microsoft Excel: Manual, by MacdonaldDocument11 pagesPlotting Mccabe-Thiele Diagrams in Microsoft Excel: Manual, by MacdonaldHarsh DarjiNo ratings yet
- 256 MAT ShortNotesJan26-Feb7 06Document5 pages256 MAT ShortNotesJan26-Feb7 06gombossandorNo ratings yet
- SEMM3023 2021-2022-2 Test 1 SPACEDocument5 pagesSEMM3023 2021-2022-2 Test 1 SPACENur Hanim Abd GhaniNo ratings yet
- Stripping Section: Mccabe-Thiele MethodDocument5 pagesStripping Section: Mccabe-Thiele MethodSata AjjamNo ratings yet
- Stine: Pointwise Dimension (131Document7 pagesStine: Pointwise Dimension (131CvgdnnnyNo ratings yet
- Edo - BoaDocument17 pagesEdo - BoaEdson Jansen MirandaNo ratings yet
- 3K4 2013 Assignment 2 SolutionsDocument9 pages3K4 2013 Assignment 2 SolutionsKhalil LasferNo ratings yet
- Chapter-22 Integration of Equations: Numerical Methods For Chemical Engineers CHE F242Document24 pagesChapter-22 Integration of Equations: Numerical Methods For Chemical Engineers CHE F242Hritik LalNo ratings yet
- Time Harmonic Maxwell EqDocument16 pagesTime Harmonic Maxwell Eqawais4125No ratings yet
- Robot Manipulators: Modeling, Performance Analysis and ControlFrom EverandRobot Manipulators: Modeling, Performance Analysis and ControlNo ratings yet
- Difference Equations in Normed Spaces: Stability and OscillationsFrom EverandDifference Equations in Normed Spaces: Stability and OscillationsNo ratings yet
- CRE NotesDocument89 pagesCRE NotesAneesch PreethaNo ratings yet
- FM NotesDocument15 pagesFM Notessparsh dateyNo ratings yet
- Density Measurement of PlasticsDocument3 pagesDensity Measurement of PlasticsShameekaNo ratings yet
- Subject-Process Modeling and Simulation (PC-701) List of ExperimentsDocument1 pageSubject-Process Modeling and Simulation (PC-701) List of Experimentssparsh dateyNo ratings yet
- Minor Training From CIPET Bhopal On Properties of Plastics (15 Days) - Internship From HPCL, Jalandhar (30 Days)Document1 pageMinor Training From CIPET Bhopal On Properties of Plastics (15 Days) - Internship From HPCL, Jalandhar (30 Days)sparsh dateyNo ratings yet
- Icao ShellDocument19 pagesIcao Shellsparsh dateyNo ratings yet
- REFRENCESDocument1 pageREFRENCESsparsh dateyNo ratings yet
- Minor Training From CIPET Bhopal On Properties of Plastics (15 Days) - Internship From HPCL, Jalandhar (30 Days)Document1 pageMinor Training From CIPET Bhopal On Properties of Plastics (15 Days) - Internship From HPCL, Jalandhar (30 Days)sparsh dateyNo ratings yet
- AdsorptionDocument19 pagesAdsorptionArun DubeyNo ratings yet
- Project PdeDocument16 pagesProject Pdesparsh dateyNo ratings yet
- Identification of PlasticsDocument6 pagesIdentification of PlasticskramechNo ratings yet
- Objective: - Determination of Melt Flow Index of Thermoplastic MaterialDocument1 pageObjective: - Determination of Melt Flow Index of Thermoplastic Materialsparsh dateyNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneueship AssignmentDocument6 pagesEntrepreneueship Assignmentsparsh dateyNo ratings yet
- Flight 370Document21 pagesFlight 370sparsh dateyNo ratings yet
- Flight 370Document21 pagesFlight 370sparsh dateyNo ratings yet
- Bonny Light Oil Is A High Grade of Nigerian CrudeDocument3 pagesBonny Light Oil Is A High Grade of Nigerian Crudesparsh dateyNo ratings yet
- Chemical and Petrochemical Industry in IndiaDocument11 pagesChemical and Petrochemical Industry in Indiasparsh dateyNo ratings yet
- Chemical and Petrochemical Industry in IndiaDocument11 pagesChemical and Petrochemical Industry in Indiasparsh dateyNo ratings yet