Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Group Vii
Group Vii
Uploaded by
Cristine Joy Avanceña Taneo0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views6 pagesis the process of communicating information to an audience. It is usually done before a large audience, like in school, the workplace and even in our personal lives. The benefits of knowing how to communicate to an audience include sharpening critical thinking and verbal/non-verbal communication skills.
Original Title
GROUP-VII
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentis the process of communicating information to an audience. It is usually done before a large audience, like in school, the workplace and even in our personal lives. The benefits of knowing how to communicate to an audience include sharpening critical thinking and verbal/non-verbal communication skills.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views6 pagesGroup Vii
Group Vii
Uploaded by
Cristine Joy Avanceña Taneois the process of communicating information to an audience. It is usually done before a large audience, like in school, the workplace and even in our personal lives. The benefits of knowing how to communicate to an audience include sharpening critical thinking and verbal/non-verbal communication skills.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 6
GROUP VII
Describe the changes in mineral components and
texture of rocks due to change in pressure and
temperature (Metamorphism)
Compare and contrast the formation of the
different types of igneous rocks
Describe how rocks behave under different types
of stress such as compression, pulling apart, and
shearing
The word Metamorphism comes from the
greek: meta = after, morph = form. So
metamorphism means the after form.
In geology, this refers to the change in mineral
assemblage and texture that result from
subjecting a rock to pressure and temperatures
Protolith – original rocks that has undergone
metamorphism.
Metamorphism therefore occurs at temperature and
pressure higher than 200° and 300° MPa. Rocks can
be subjected to these higher temperatures and
pressures as they become buried deeper in the earth.
During metamorphism the protolith undergoes
change in texture of the rock and mineral makes up
of the rocks
Factors that control metamorphism
Temperature
- Temperature increase with depth in the earth
along the geothermal gradient
- Pressure increase with depth of burial
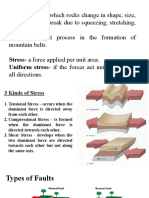
Pressure
- Is defined as a force acting equally from all
directions. It is a type of stress called
Hydrostatic stress or Uniform stress
Fluid phase
- This fluid is mostly H2O, but contains
dissolved ions.
- If chemical alteration of the rocks takes place
as a result of these fluids. The process is called
Metasomatism
Metamorphic rocks type
1. Foliated - there have a planar foliation
2. Non-foliated – there have no evident planar
fabric or foliation
You might also like
- Metamorphic RocksDocument29 pagesMetamorphic RocksTej Pratap SinghNo ratings yet
- Metamorphic, Igneous and Sedimentary Rocks : Sorting Them Out - Geology for Kids | Children's Earth Sciences BooksFrom EverandMetamorphic, Igneous and Sedimentary Rocks : Sorting Them Out - Geology for Kids | Children's Earth Sciences BooksNo ratings yet
- G11 Earth ScienceDocument14 pagesG11 Earth ScienceAlthea RivadeloNo ratings yet
- Metamorphic RocksDocument27 pagesMetamorphic RocksCrafty JigyasaNo ratings yet
- Metamorphism NotesDocument2 pagesMetamorphism NotesMaria Pauline AsiNo ratings yet
- Metamorphic-Rocks 20240313 092412 0000Document16 pagesMetamorphic-Rocks 20240313 092412 0000Ameer FedillagaNo ratings yet
- Metamorphic RockDocument47 pagesMetamorphic RockABU SALEH MOHAMMAD RAFI100% (1)
- Metamorphic RockDocument47 pagesMetamorphic RockYZKNo ratings yet
- MetamorphicDocument22 pagesMetamorphicJoshua Trinidad100% (1)
- What Is MetamorphismDocument1 pageWhat Is Metamorphismfrancisco bonaNo ratings yet
- Engineering Geology For Civil EngineersDocument14 pagesEngineering Geology For Civil EngineersDaljeet SidhuNo ratings yet
- Endogenic Process Part 2 PDFDocument35 pagesEndogenic Process Part 2 PDFIvan ZenitramNo ratings yet
- Black Doodle Group Project PresentationDocument26 pagesBlack Doodle Group Project PresentationJoseph BaclayoNo ratings yet
- TypesmetamorphDocument7 pagesTypesmetamorphapi-19643403No ratings yet
- TypesmetamorphDocument7 pagesTypesmetamorphApuNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science Q1 - M8Document10 pagesEarth and Life Science Q1 - M8Migz Arlz14No ratings yet
- Types of MetamorphismDocument8 pagesTypes of MetamorphismLuis Miguel Mogollon RamosNo ratings yet
- LESSON 4 MetamorphismDocument3 pagesLESSON 4 Metamorphismjustin charles jerimy raymundoNo ratings yet
- Group-5-Earth-Science 20231121 081658 0000Document75 pagesGroup-5-Earth-Science 20231121 081658 0000St. Paul Vernadette ParaisoNo ratings yet
- Group 7 Metamorphism ReviewerDocument8 pagesGroup 7 Metamorphism ReviewermuhamsumandresNo ratings yet
- Metamorphism 2Document76 pagesMetamorphism 2driegran95100% (1)
- Report Metamorphism FINALDocument67 pagesReport Metamorphism FINALKristine Joy ErangNo ratings yet
- MetamorphismDocument35 pagesMetamorphismjerry100% (1)
- Physical Geology 2nd Ed Chapter 7 Metamorphism and Metamorphic RocksDocument39 pagesPhysical Geology 2nd Ed Chapter 7 Metamorphism and Metamorphic RocksYeremia PanggabeanNo ratings yet
- MetamorphismDocument12 pagesMetamorphismJelesa TabanginNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science2.0....Document4 pagesEarth and Life Science2.0....jillgemarino7No ratings yet
- What Is MetamorphismDocument1 pageWhat Is MetamorphismFiveOfThreeNo ratings yet
- Types & MetamorphDocument7 pagesTypes & Metamorphreef_silverNo ratings yet
- 02 Metamorphic Petrology - 1Document10 pages02 Metamorphic Petrology - 1Eadaw100% (1)
- Grad of MetamorphismDocument8 pagesGrad of MetamorphismMuzmmil MianNo ratings yet
- Metamorphic RocksDocument7 pagesMetamorphic RocksAZUAN BIN AHMAD FAUZINo ratings yet
- Metamorphism Group 3 MarsDocument9 pagesMetamorphism Group 3 Marszin GuevarraNo ratings yet
- Q2-Earth Science For STEM-WEEK4Document6 pagesQ2-Earth Science For STEM-WEEK4queancy euleNo ratings yet
- Earth-Science w2 l2 q2 MetamorphismDocument35 pagesEarth-Science w2 l2 q2 MetamorphismCj Padata100% (1)
- Metamorphic RocksDocument6 pagesMetamorphic RocksrolandNo ratings yet
- Metamorphic Rocks Arise From The Transformation of ExistingDocument3 pagesMetamorphic Rocks Arise From The Transformation of ExistingRaj KumarNo ratings yet
- 6 (A) A Metamorphic Rock Is One That Is Formed Directly From A Pre-ExistingDocument4 pages6 (A) A Metamorphic Rock Is One That Is Formed Directly From A Pre-ExistingReza FauziNo ratings yet
- Solid Compaction Rock Mineral: Metamorphism, Mineralogical and Structural Adjustments ofDocument8 pagesSolid Compaction Rock Mineral: Metamorphism, Mineralogical and Structural Adjustments ofJahque LadaranNo ratings yet
- ENDOGENICDocument16 pagesENDOGENICmyrrdaneNo ratings yet
- HANDOUT MetamorphismDocument4 pagesHANDOUT MetamorphismHow Ever100% (1)
- Laporan 4 Agrogeo RarDocument14 pagesLaporan 4 Agrogeo RarSabda Pandita RatuNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science Learning Competency 17Document44 pagesEarth and Life Science Learning Competency 17janine toledoNo ratings yet
- L A M P I R A N: Sumber: Batuan - HTMLDocument52 pagesL A M P I R A N: Sumber: Batuan - HTMLDaniel JayapuraNo ratings yet
- Earth Science: Quarter 2 - Module 4: MetamorphismDocument8 pagesEarth Science: Quarter 2 - Module 4: MetamorphismBea CabacunganNo ratings yet
- ES MetamorphismDocument25 pagesES MetamorphismmertoelaineNo ratings yet
- Group 8Document5 pagesGroup 8Kate Ashley HugoNo ratings yet
- in Your Own Words Explain The Definition of Rock Cycle. Rock CycleDocument4 pagesin Your Own Words Explain The Definition of Rock Cycle. Rock CycleGeology for BeginnersNo ratings yet
- Agents of MetamorphismDocument6 pagesAgents of MetamorphismZahid RahmanNo ratings yet
- Chapter .5 Metamorphic RockDocument5 pagesChapter .5 Metamorphic RockHamzaBaigNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Metamorphism: Earth and Life Science By: Bravo, Jessy Anne G. MseufDocument12 pagesDynamic Metamorphism: Earth and Life Science By: Bravo, Jessy Anne G. MseufBravo,Jessy Anne G.No ratings yet
- Lesson 8. Components and Texture of Rocks (Metamorphism)Document2 pagesLesson 8. Components and Texture of Rocks (Metamorphism)revelachtion02No ratings yet
- Earth Science (Metamorphic Rocks)Document8 pagesEarth Science (Metamorphic Rocks)MA. ALEXIS LAURENNo ratings yet
- Metamorphic PetrologyDocument24 pagesMetamorphic PetrologySanskarNo ratings yet
- Objectives: 7.0 Nature and Classification of Metamorphic Rocks 7.1Document22 pagesObjectives: 7.0 Nature and Classification of Metamorphic Rocks 7.1Akankwasa RonaldNo ratings yet
- Chapter No 4 (Metamorphic Rocks) PDFDocument2 pagesChapter No 4 (Metamorphic Rocks) PDFMudasir HussainNo ratings yet
- Metamorphism Comprises The Solid-State Reactions in RocksDocument5 pagesMetamorphism Comprises The Solid-State Reactions in RocksJherome CastuloNo ratings yet
- Metamorphic RocksDocument13 pagesMetamorphic RocksdsdsdsNo ratings yet
- Earth Science Quarter 2 Module 4-5Document6 pagesEarth Science Quarter 2 Module 4-5Rhianne Grace CastroNo ratings yet
- Lecture 05 Metamorphic RocksDocument31 pagesLecture 05 Metamorphic RocksMuhammad Inam ul HaqNo ratings yet