0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2K views17 pagesPresentation: Basic Structure of Beryllium Nitrate
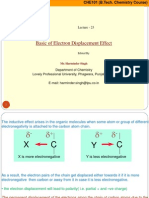
Beryllium nitrate is a chemical compound with the formula Be(NO3)2. It has a molar mass of 133.02 g/mol and density of 1.02 g/mL. Beryllium nitrate can be prepared by reacting beryllium chloride with dinitrogen tetroxide or by reacting beryllium oxides, hydroxides, or carbonates with nitric acid. It exists as both a normal salt and as a basic beryllium nitrate with an unusual tetrahedral structure. Beryllium nitrate trihydrate has uses in making mantles for gas lamps and as a chemical reagent.
Uploaded by
tarun_sahni89Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2K views17 pagesPresentation: Basic Structure of Beryllium Nitrate
Beryllium nitrate is a chemical compound with the formula Be(NO3)2. It has a molar mass of 133.02 g/mol and density of 1.02 g/mL. Beryllium nitrate can be prepared by reacting beryllium chloride with dinitrogen tetroxide or by reacting beryllium oxides, hydroxides, or carbonates with nitric acid. It exists as both a normal salt and as a basic beryllium nitrate with an unusual tetrahedral structure. Beryllium nitrate trihydrate has uses in making mantles for gas lamps and as a chemical reagent.
Uploaded by
tarun_sahni89Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd