Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Concepts, Constructs, Attributes, Variables and Hypotheses
Uploaded by
chirag100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
842 views36 pagesbba notes
Original Title
Concepts,Constructs,Attributes,Variables,Hypotheses
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentbba notes
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
842 views36 pagesConcepts, Constructs, Attributes, Variables and Hypotheses
Uploaded by
chiragbba notes
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 36
Concepts,Constructs,Attributes,
Variables and Hypotheses
Concepts-Significance
• To understand and communicate information
about objects and events, there must be a
common ground on which to do it. Concepts
serve this purpose.
Concept
• A concept is a generally accepted collection of
meanings or characteristics associated with certain
events, objects, conditions, situations, and behaviors.
Classifying and categorizing objects or events that have
common characteristics beyond any single observation
creates concepts. We abstract such meanings from our
experiences and use words as labels to designate them.
• For example, we see a man passing and identify that he
is running, walking, skipping, crawling, or hopping.
These movements all represent concepts. We also have
abstracted certain visual elements by which we identify
that the moving object is an adult male, rather than an
adult female or a truck or a horse.
• Construct = concepts or ideas about an object,
attribute, or phenomenon that are worthy of
measurement.
• A construct is an image or abstract idea specifi
cally invented for a given research and/or
theory-building purpose.
CONSTRUCTS
The Role of Constructs
• A construct is an abstract idea inferred from
specific instances that are thought to be related.
• Typical marketing constructs are brand loyalty,
satisfaction, preference, awareness, knowledge.
• Research objectives typically call for the
measurement of constructs.
• There are customary methods for defining and
measuring constructs.
• Conceptualization and operationalization ….
…of what we want to research – of research
problem
Conceptualization
• Definition: the process through which we specify what
we will mean when we use particular terms in
research.
• Conceptualization produces specific, agreed-upon
meaning for a concept for the purposes of research.
• Process of specifying clearly exactly what you mean by
a term
• This process of specifying exact meaning involves
describing the indicators we’ll be using to measure our
concept and the different aspects of the concept,
called dimensions.
Operationalization
• Operational definition: specifies precisely how
a concept will be measured – the operations it
will perform.
• It is a process whereby researchers specify
empirical concepts that can be taken as
indicators of the attributes of a concept
Operationalization and Measurement
• Three basic questions
• What do you measure?
• How do you measure?
• How well do you measure?
Research Objectives
• Precise
• Detailed
• Clear
• Operational
• Operational definitions describe the
operations to be carried out in order for
constructs to be measured.
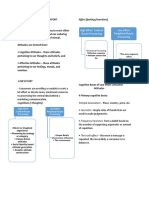
Attribute and Variable
Attribute:
• A characteristic of an object (man, thing, etc.)
• Property, or a conclusion of a characteristic of an
entity or substance
Variable:
• A symbol that represents a quantity in a
mathematical expression, as used in many
sciences (-Mathematics)
• A logical set of attributes (-Research)
• An attribute is usually something that defines
the item: height, width, weight, color, font,
font size, etc… you get the idea.
• Variables are usually much more dynamic and
are usually used for doing calculations: the
area of a circle, something is true or false,
counters, speed, ID’s, descriptions, etc…
Hypotheses and concepts/constructs
and variables
• Propositions and Hypotheses
• We define a proposition as a statement about observable
phenomena (concepts) that may be judged as true or false.
When a proposition is formulated for empirical testing, we
call it a hypothesis. As a declarative statement about the
relationship between two or more variables, a hypothesis is
of a tentative and conjectural nature.
• Hypotheses have also been described as statements in
which we assign variables to cases. A case is defined in this
sense as the entity or thing the hypothesis talks about. The
variable is the characteristic, trait, or attribute that, in the
hypothesis, is imputed to the case.
• Hypotheses – types (repetition from previous
lecture) descriptive hypotheses. They state the
existence, size, form, or distribution of some
variable. Researchers often use a research
question rather than a descriptive hypothesis.
• For example: American cities (cases) are
experiencing budget difficulties (variable).
Brand Manager Jones (case) has a higher-than
average achievement motivation (variable)
Null and Alternate Hypothesis
• The null hypothesis and the alternative
hypothesis are types of conjectures used in
statistical tests, which are formal methods of
reaching conclusions or making decisions on
the basis of data.
• The hypotheses are conjectures about a
statistical model of the population, which are
based on a sample of the population.
• The null hypothesis is a general statement or
default position that there is no relationship
between two measured phenomena, or no
association among groups.
• The null hypothesis is generally assumed to be
true until evidence indicates otherwise.
• a null hypothesis is rejected if the observed data
are significantly unlikely to have occurred if the
null hypothesis were true.
• In this case the null hypothesis is rejected and an
alternative hypothesis is accepted in its place.
• The statement that is being tested against the
null hypothesis is the alternative hypothesis.
• Symbols include H1 or Ha
Example
Given the test scores of two random samples, one of men and one of
women, does one group differ from the other? A possible null
hypothesis is that the mean male score is the same as the mean
female score:
H0: μ1 = μ2
where
H0 = the null hypothesis,
μ1 = the mean of population 1, and
μ2 = the mean of population 2.
A stronger null hypothesis is that the two samples are drawn from the
same population, such that the variances and shapes of the
distributions are also equal.
TASK
Summary
• Concept -Abstract thinking to distinguish it
from other elements
• Construct -Theoretical definition of a concept;
must be observable or measurable; linked to
other concepts
• Variable-Presented in research questions and
hypotheses
• Operationalization - Specifically how the
variable is observed or measured
You might also like
- RESEARCH PROJECT Divyanshi MishraDocument10 pagesRESEARCH PROJECT Divyanshi MishraAshutosh MishraNo ratings yet
- AyurvedaDocument45 pagesAyurvedaKaran MehtaNo ratings yet
- Indian Insight Into TQMDocument13 pagesIndian Insight Into TQMSrinivas Reddy RondlaNo ratings yet
- Impact of Organized Retailing on Unorganized Retailing in IndiaDocument5 pagesImpact of Organized Retailing on Unorganized Retailing in IndiaGauravsNo ratings yet
- Perception - MeaningDocument49 pagesPerception - MeaningRaj Kumari100% (1)
- Challenges and Opportunities in Oraganisational BehaviourDocument5 pagesChallenges and Opportunities in Oraganisational BehaviourRamesh babuNo ratings yet
- Gender Equality: An Imperative For Entrepreneurship Development in India - Strategy & PolicyDocument17 pagesGender Equality: An Imperative For Entrepreneurship Development in India - Strategy & PolicyADBGADNo ratings yet
- Consumer Motivation and PersonalityDocument5 pagesConsumer Motivation and PersonalityParth DhingraNo ratings yet
- Lecture 13 Communication and PerceptionDocument21 pagesLecture 13 Communication and PerceptionUder AhmadNo ratings yet
- A Study On Brand Preference of Mobile Phone UsersDocument6 pagesA Study On Brand Preference of Mobile Phone Usersvaskar_karki100% (1)
- Unit-1 - Research Methodology & Fundamentals of MRDocument31 pagesUnit-1 - Research Methodology & Fundamentals of MRPrashant DubeyNo ratings yet
- Individual Behavior FactorsDocument33 pagesIndividual Behavior FactorsAnchal mandhir100% (1)
- Personality & Consumer BehaviorDocument8 pagesPersonality & Consumer BehaviorsauravkumbhNo ratings yet
- Research MethodologyDocument2 pagesResearch MethodologyGobinathan Rajendra Pillai0% (1)
- The Chi Square TestDocument10 pagesThe Chi Square TestHazwan HamidNo ratings yet
- Knowledge Creation & Knowledge SharingDocument13 pagesKnowledge Creation & Knowledge Sharingrmn_changezi73No ratings yet
- FIANL-FIANL - Factors Influencing Investment DecisionsDocument60 pagesFIANL-FIANL - Factors Influencing Investment DecisionsCabigas WonhamayNo ratings yet
- The Social Responsibility of ManagersDocument19 pagesThe Social Responsibility of Managersshivakumar N33% (3)
- Research Methodology - Primary & Secondary DataDocument20 pagesResearch Methodology - Primary & Secondary Datajinu_john100% (1)
- PERCEPTUAL PROCESS STEPSDocument4 pagesPERCEPTUAL PROCESS STEPSIndrajith KrNo ratings yet
- Tactics in Stategic ManagementDocument7 pagesTactics in Stategic ManagementShubhajit NandiNo ratings yet
- Global Financial Reporting StandardsDocument42 pagesGlobal Financial Reporting StandardsJay ModiNo ratings yet
- Meaning Research MethodsDocument3 pagesMeaning Research MethodsBasappaSarkar100% (1)
- Introduction to Consumer Behavior ChapterDocument10 pagesIntroduction to Consumer Behavior ChapterprashantBhopleNo ratings yet
- Theoritical PerspectiveDocument64 pagesTheoritical Perspectivenurgu100% (3)
- Research Design OverviewDocument16 pagesResearch Design OverviewManjunatha HRNo ratings yet
- Factors Influencing AttitudeDocument3 pagesFactors Influencing AttitudeJoshua PasionNo ratings yet
- Theory of SellingDocument5 pagesTheory of SellingrajendrakumarNo ratings yet
- Synopsis of PraveenDocument8 pagesSynopsis of PraveenNageshwar SinghNo ratings yet
- Importance of HypothesisDocument2 pagesImportance of HypothesisAsghar KhanNo ratings yet
- Balanced Scorecard in Performance ManagementDocument5 pagesBalanced Scorecard in Performance Managementmegha shreeNo ratings yet
- Case Studies Mba 1 AssignmentDocument2 pagesCase Studies Mba 1 Assignmentayushi aggarwalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Sampling and Sampling DistributionDocument23 pagesChapter 2 Sampling and Sampling DistributionManchilot TilahunNo ratings yet
- Question 3 AnsDocument1 pageQuestion 3 Anssirisha chNo ratings yet
- Final PHD Commerce Thesis PDFDocument450 pagesFinal PHD Commerce Thesis PDFMegha Jain BhandariNo ratings yet
- Principles of ManagementDocument107 pagesPrinciples of ManagementalchemistNo ratings yet
- Ethical Issues in Functional AreasDocument31 pagesEthical Issues in Functional AreasAmal RajNo ratings yet
- Attitude Measurement Research MethodologyDocument18 pagesAttitude Measurement Research Methodologyrohan_jangid8100% (7)
- BBA 3rd SemesterDocument7 pagesBBA 3rd Semestersimun3332000No ratings yet
- Impact of Stress On Job Performance An Empirical Study of The Employees Printed PDFDocument4 pagesImpact of Stress On Job Performance An Empirical Study of The Employees Printed PDFUmer QureshiNo ratings yet
- The Impact of Information Technology On Human Resource Practices and PDFDocument8 pagesThe Impact of Information Technology On Human Resource Practices and PDFChetan ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Identifying Variables in Research StudiesDocument131 pagesIdentifying Variables in Research StudiesazharmalurNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 (Introduction of OB)Document11 pagesChapter 1 (Introduction of OB)Nikita AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Vrooms Expectancy Theory of MotivationDocument2 pagesVrooms Expectancy Theory of MotivationHazel OchiengNo ratings yet
- Syllabus: Introduction To Business Research & Uses of Software: Types ofDocument239 pagesSyllabus: Introduction To Business Research & Uses of Software: Types ofvivek guptaNo ratings yet
- Effectiveness of Entrepreneurship Education in Developing Entrepr PDFDocument323 pagesEffectiveness of Entrepreneurship Education in Developing Entrepr PDFSmart B Connect0% (1)
- Comparing research designs and samples over timeDocument32 pagesComparing research designs and samples over timeErka Os25% (4)
- 7.6 NCR Corporation, Known As A World Leader in Atms, Point-Of-Sale (Pos) Retail CheckoutDocument4 pages7.6 NCR Corporation, Known As A World Leader in Atms, Point-Of-Sale (Pos) Retail CheckoutMOIN UDDIN AHMEDNo ratings yet
- Data Collection MethodsDocument29 pagesData Collection MethodsAnkit KumarNo ratings yet
- Investors-Investment BehaviourDocument19 pagesInvestors-Investment Behaviourkarteek reddyNo ratings yet
- BACC 005 Research MethodsDocument5 pagesBACC 005 Research Methodscyka blyat100% (1)
- New Issue MarketDocument15 pagesNew Issue MarketRavi Kumar100% (1)
- Characteristics of A Good Sample DesignDocument3 pagesCharacteristics of A Good Sample DesignVinesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Challenges of OBDocument7 pagesChallenges of OBmonalisa75% (12)
- Women Empowerment Through EntrepreneurshipDocument39 pagesWomen Empowerment Through EntrepreneurshipClassic PrintersNo ratings yet
- Consumer BehaviourDocument16 pagesConsumer BehaviourAnNo ratings yet
- Consumer Attitude Formation and ChangeDocument24 pagesConsumer Attitude Formation and ChangeHarsh AnchaliaNo ratings yet
- Concept Construct Variables RMDocument69 pagesConcept Construct Variables RMmaramreddyleela100% (1)
- Concept Construct Variables RMDocument69 pagesConcept Construct Variables RMmiboyfrendNo ratings yet
- Research Method-FirstlectureDocument31 pagesResearch Method-FirstlecturebajajujjvalNo ratings yet
- 2018 BPS End Term QPDocument1 page2018 BPS End Term QPchiragNo ratings yet
- 2019 Edp Unit 3 PDFDocument17 pages2019 Edp Unit 3 PDFchiragNo ratings yet
- 2019 Edp Unit 3 PDFDocument17 pages2019 Edp Unit 3 PDFchiragNo ratings yet
- Need of The StudyDocument1 pageNeed of The StudychiragNo ratings yet
- 2019 Edp Unit 2 PDFDocument19 pages2019 Edp Unit 2 PDFchiragNo ratings yet
- 2015 BPS End Term QPDocument1 page2015 BPS End Term QPchiragNo ratings yet
- 2019 Edp Unit 1 PDFDocument33 pages2019 Edp Unit 1 PDFchiragNo ratings yet
- 2019 Edp Unit 1 PDFDocument33 pages2019 Edp Unit 1 PDFchiragNo ratings yet
- 2017 BPS End TermDocument1 page2017 BPS End TermchiragNo ratings yet
- Project Management Offers Megatech Competitive AdvantageDocument2 pagesProject Management Offers Megatech Competitive Advantagechirag67% (3)
- 2014 BPS End Term QPDocument1 page2014 BPS End Term QPchiragNo ratings yet
- Jims Jubl VivaDocument14 pagesJims Jubl VivachiragNo ratings yet
- Jims Jubl VivaDocument14 pagesJims Jubl VivachiragNo ratings yet
- Sales & Distribution Management (Assignment 2 BBA)Document7 pagesSales & Distribution Management (Assignment 2 BBA)chiragNo ratings yet
- Research Methods and Data Sources & QuestionnaireDocument99 pagesResearch Methods and Data Sources & QuestionnairechiragNo ratings yet
- Guidlines Summer Internship - Aug 2019Document10 pagesGuidlines Summer Internship - Aug 2019chiragNo ratings yet
- Guidlines Summer Internship - Aug 2019Document10 pagesGuidlines Summer Internship - Aug 2019chiragNo ratings yet
- Consumer Behavior and Preferences for FootwearDocument183 pagesConsumer Behavior and Preferences for FootwearchiragNo ratings yet
- Guidlines Summer Internship - Aug 2019Document10 pagesGuidlines Summer Internship - Aug 2019chiragNo ratings yet
- Historical Milestones in Operations ManagementDocument107 pagesHistorical Milestones in Operations ManagementchiragNo ratings yet
- Business Policy Strategy (Assignment-2)Document7 pagesBusiness Policy Strategy (Assignment-2)chiragNo ratings yet
- Research MethodolgyDocument1 pageResearch MethodolgychiragNo ratings yet
- An Organizational Study at Bata India LTD: Chapter-01Document49 pagesAn Organizational Study at Bata India LTD: Chapter-01shuchiNo ratings yet
- Intro Ducti ON: The Company Was Incorporated On 13th September, 1984 As A Private Limited CompanyDocument26 pagesIntro Ducti ON: The Company Was Incorporated On 13th September, 1984 As A Private Limited CompanychiragNo ratings yet
- Company Profile: Release PanelDocument5 pagesCompany Profile: Release PanelchiragNo ratings yet
- Summer Internship Project Report ON Analysis of Marketing and Sales at AqualiteDocument40 pagesSummer Internship Project Report ON Analysis of Marketing and Sales at AqualitechiragNo ratings yet
- Units of AnalysisDocument15 pagesUnits of AnalysischiragNo ratings yet
- Understanding Business Research Nature and ScopeDocument33 pagesUnderstanding Business Research Nature and ScopeAUGUSTINENo ratings yet
- Guidlines Summer Internship - Aug 2019Document10 pagesGuidlines Summer Internship - Aug 2019chiragNo ratings yet
- Skirmishes Graham Harman PDFDocument383 pagesSkirmishes Graham Harman PDFparaiaNo ratings yet
- Exercise 1 Conversion of UnitDocument1 pageExercise 1 Conversion of UnitSarah Hanifa PurnomoNo ratings yet
- Spencer-Brown - Probability PDFDocument164 pagesSpencer-Brown - Probability PDFJoaquin Rauh100% (1)
- College Physics Volume 1 11th Edition Serway Solutions Manual 1 PDFDocument7 pagesCollege Physics Volume 1 11th Edition Serway Solutions Manual 1 PDFBina56% (9)
- Effective Decision MakingDocument3 pagesEffective Decision MakingAqeeb FaheemNo ratings yet
- BS Statistics Course OverviewDocument2 pagesBS Statistics Course OverviewReemal KhanNo ratings yet
- Maria Cecília de Miranda N. CoelhoDocument9 pagesMaria Cecília de Miranda N. CoelhoalegtrNo ratings yet
- PRINCIPLES OF EFFECTIVE TEACHINGDocument142 pagesPRINCIPLES OF EFFECTIVE TEACHINGDENOMINATORNo ratings yet
- Methods of Research and Thesis Writing by CalmorinDocument3 pagesMethods of Research and Thesis Writing by CalmorinJane Santusidad75% (4)
- Department of Justice Office of The City ProsecutorDocument5 pagesDepartment of Justice Office of The City ProsecutorCandon City LGUNo ratings yet
- Example Cross TabulationDocument6 pagesExample Cross TabulationSamerNo ratings yet
- Attitudes Based On Low EffortDocument2 pagesAttitudes Based On Low EffortClaire CaneteNo ratings yet
- Peka 5S 2012Document211 pagesPeka 5S 2012Yusfalina Mohd YusoffNo ratings yet
- Argumentative EssayDocument2 pagesArgumentative EssayHeleynamarie BeserilNo ratings yet
- Energy vs Millennials Debate RulesDocument6 pagesEnergy vs Millennials Debate RulesLuqman Satria Mursid WicaksonoNo ratings yet
- Business EthicsDocument12 pagesBusiness EthicshezronNo ratings yet
- TEACHING LITERACY and NUMERACYDocument29 pagesTEACHING LITERACY and NUMERACYEstrellita MalinaoNo ratings yet
- Consumer Learning: Consumer Behavior, Ninth Edition Schiffman & KanukDocument73 pagesConsumer Learning: Consumer Behavior, Ninth Edition Schiffman & KanukANCHAL SINGHNo ratings yet
- Improve Legal Analytical SkillsDocument6 pagesImprove Legal Analytical Skillsbrian jay hernandezNo ratings yet
- Corraboration For Dying DeclarationDocument17 pagesCorraboration For Dying DeclarationIkra MalikNo ratings yet
- 4 Sociological and Anthropological Foundations of EducationDocument69 pages4 Sociological and Anthropological Foundations of EducationMarilyn Dacanay100% (1)
- Leading with Compassion: A Guide to Compassionate Healthcare LeadershipDocument73 pagesLeading with Compassion: A Guide to Compassionate Healthcare LeadershipnibretzwNo ratings yet
- HBO. Lecture 1Document6 pagesHBO. Lecture 1YR100% (1)
- Astm G 169Document10 pagesAstm G 169edson alfaNo ratings yet
- Midterm Examination Logical PropositionsDocument4 pagesMidterm Examination Logical PropositionsSantiago BuladacoNo ratings yet
- Validity N Reliability PDFDocument19 pagesValidity N Reliability PDFGurpreet Singh Walia100% (1)
- Becoming A Member of SocietyDocument11 pagesBecoming A Member of SocietyKate CaguioaNo ratings yet
- Journal CritiqueDocument7 pagesJournal CritiqueEli Lilly Cemanes MarasiganNo ratings yet
- Walking Down The Magic Way PDFDocument26 pagesWalking Down The Magic Way PDFMago ReymondNo ratings yet
- Edgar Morin - Complex Thinking For A Complex World PDFDocument9 pagesEdgar Morin - Complex Thinking For A Complex World PDFPedro Gabriel Amaral CostaNo ratings yet