Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 viewsNervous System: Science 6 - Second Quarter
Nervous System: Science 6 - Second Quarter
Uploaded by
maricel pampiloCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Zoology OutlineDocument3 pagesZoology OutlineEj AgsaldaNo ratings yet
- Biology G - Lesson 5 - Nervous SystemDocument59 pagesBiology G - Lesson 5 - Nervous SystemJeremiah Nayosan0% (1)
- Nervous SystemDocument26 pagesNervous SystemAe-jay CacalNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument46 pagesNervous SystemIponla KarlChristianNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemsDocument37 pagesNervous SystemsHannah CabritoNo ratings yet
- The Nervous System (Edited)Document27 pagesThe Nervous System (Edited)Kiarana Fleischer100% (1)
- Nervous System: Javaria ZahraDocument70 pagesNervous System: Javaria ZahraMuneeb JavaidNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument21 pagesEndocrine SystemNo Name100% (1)
- Nervous System 2Document23 pagesNervous System 2TinNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument23 pagesNervous SystemSumaira Noreen100% (1)
- Nervous SystemDocument23 pagesNervous SystemBryan Bries100% (1)
- Central Nervous SystemDocument30 pagesCentral Nervous SystemJames Lacuesta Tabiolo100% (1)
- 1 Nervous SystemDocument155 pages1 Nervous Systemsonali sundramNo ratings yet
- Discuss Action Potential of The Axon and Nerve ImpulseDocument3 pagesDiscuss Action Potential of The Axon and Nerve ImpulsePink PastaNo ratings yet
- Muscular System - WorksheetDocument3 pagesMuscular System - WorksheetsNo ratings yet
- Nervous System PresentationDocument22 pagesNervous System PresentationEnero Ombina PorlaresNo ratings yet
- The Nervous System 1Document57 pagesThe Nervous System 1seno.kirzvhan.bmlsNo ratings yet
- The Nervous SystemDocument80 pagesThe Nervous SystemAngelicaBarbosaNo ratings yet
- 31.1 The NeuronDocument33 pages31.1 The Neuronmoniaguayo98No ratings yet
- BrainDocument35 pagesBrainRonaleen mislang100% (1)
- Introduction and Organization of Nervous System: Presented by Dr. Amen FatimaDocument37 pagesIntroduction and Organization of Nervous System: Presented by Dr. Amen FatimaShanailNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument12 pagesNervous SystemLeon MarkoNo ratings yet
- Energy Forms PPTDocument16 pagesEnergy Forms PPTEdgar Miralles Inales ManriquezNo ratings yet
- 2 Human Body Nervous SystemDocument24 pages2 Human Body Nervous SystemRain HuntsdaleNo ratings yet
- Fisiologi Manusia: DR Mellova Amir MSCDocument52 pagesFisiologi Manusia: DR Mellova Amir MSCRizal AdhityaNo ratings yet
- The Major Divisions of The Nervous SystemDocument17 pagesThe Major Divisions of The Nervous SystemLiana BaluyotNo ratings yet
- Sense OrgansDocument9 pagesSense OrgansЕкатерина КовальNo ratings yet
- The Nervous SystemDocument25 pagesThe Nervous SystemRoan Angela100% (4)
- CHAPTER 2 Physiological Basis of BehaviorDocument37 pagesCHAPTER 2 Physiological Basis of BehaviorIsh Gallito100% (1)
- Lesson 4 - Circulatory SystemDocument21 pagesLesson 4 - Circulatory Systemapi-307592530No ratings yet
- Circulatory System ActivityDocument5 pagesCirculatory System ActivityKeen Jude CaminosNo ratings yet
- Sensory Mechanism: Almozara Francisco Villaflores LorenzoDocument29 pagesSensory Mechanism: Almozara Francisco Villaflores LorenzoMerrylFranciscoNo ratings yet
- Pre-Assessment: Odd Organ OutDocument45 pagesPre-Assessment: Odd Organ OutMelody Miras MacabontocNo ratings yet
- Neurons and Its FunctionDocument4 pagesNeurons and Its FunctionKristol MyersNo ratings yet
- Cell Division Mitosis MeiosisDocument63 pagesCell Division Mitosis MeiosisRinNo ratings yet
- The Nervous System: April Joy A. TalasDocument24 pagesThe Nervous System: April Joy A. TalasPoy Alis100% (1)
- The Nervous System-Final PDFDocument57 pagesThe Nervous System-Final PDFCarlo Makiling100% (1)
- The Nervous System NotesDocument6 pagesThe Nervous System NotesDhea Angela A. CapuyanNo ratings yet
- Nervous System POWERPOINTDocument15 pagesNervous System POWERPOINTZhen Obelidor100% (1)
- Human's Sense OrgansDocument11 pagesHuman's Sense OrgansTiara CalistaNo ratings yet
- The CerebrumDocument27 pagesThe Cerebrumapi-19916399No ratings yet
- (W9) The Skeletal SystemDocument9 pages(W9) The Skeletal SystemReign Heart HayahayNo ratings yet
- Homeostasi S:: Homeostatic Control MechanismsDocument22 pagesHomeostasi S:: Homeostatic Control MechanismsRoxanne CMNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic SystemDocument25 pagesLymphatic Systemumar khanNo ratings yet
- Sci 10 Unit 3 Mod 1 (Lecture)Document41 pagesSci 10 Unit 3 Mod 1 (Lecture)Jonessa BenignosNo ratings yet
- (W3) Cell CycleDocument6 pages(W3) Cell CycleRednaxela Mejico TarucNo ratings yet
- AtomDocument4 pagesAtomanjaliNo ratings yet
- Brain PP 5Document38 pagesBrain PP 5Anjaylyn BañasNo ratings yet
- Human Reproductive SystemDocument23 pagesHuman Reproductive SystemQuennie AceronNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Sense Organ and Their FunctionDocument20 pages1.1 Sense Organ and Their FunctionReduan Ibrahim100% (3)
- Cranial and Spinal NervesDocument5 pagesCranial and Spinal NervesEijunNo ratings yet
- The Muscular SystemDocument14 pagesThe Muscular SystemOana Maria FrancNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 SCIENCE: © Boardworks LTD 2004Document20 pagesGrade 10 SCIENCE: © Boardworks LTD 2004Modesto Valdriz100% (1)
- The Nervous System - PsychologyDocument17 pagesThe Nervous System - Psychologyjanet100% (2)
- The Nervous SystemDocument8 pagesThe Nervous SystemananthNo ratings yet
- Zoology Notes: 017 Chapter 13Document3 pagesZoology Notes: 017 Chapter 13humanupgrade100% (1)
- Grade 8 Science Elective: Nervous SystemDocument2 pagesGrade 8 Science Elective: Nervous SystemVincqNo ratings yet
- Bio 11 - Zoology - Experiment 20 - Types of Tissues: Muscular TissueDocument17 pagesBio 11 - Zoology - Experiment 20 - Types of Tissues: Muscular TissueDenise Cedeño100% (1)
- The Nervous SystemDocument18 pagesThe Nervous Systemvedansh duttNo ratings yet
- The Nervous System Is The BodyDocument18 pagesThe Nervous System Is The Bodyvedansh duttNo ratings yet
- Cmmi 2.0Document13 pagesCmmi 2.0faridin bm2019No ratings yet
- AQA A-Level Physics For A-Level Year 1 and As - GibbsDocument123 pagesAQA A-Level Physics For A-Level Year 1 and As - GibbsNarendra SinghNo ratings yet
- Activity: Can You Identify Ancestry?: European American Indian Sub-Saharan AfricanDocument5 pagesActivity: Can You Identify Ancestry?: European American Indian Sub-Saharan AfricanpoovenmoonoosamyNo ratings yet
- 3.1. Build A List Screen Exercise - En-UsDocument16 pages3.1. Build A List Screen Exercise - En-Usmahesh manchalaNo ratings yet
- How To Get The Teaching Job You Want The Complete Guide For College Graduates, Returning Teachers and Career Changers (PDFDrive) PDFDocument175 pagesHow To Get The Teaching Job You Want The Complete Guide For College Graduates, Returning Teachers and Career Changers (PDFDrive) PDFjomotNo ratings yet
- Natural OrderDocument5 pagesNatural OrderMicah Santon100% (1)
- Rogers, Lisa - Movie Review (EPortfolio)Document14 pagesRogers, Lisa - Movie Review (EPortfolio)Lisa RogersNo ratings yet
- Circuto de Chip 5846Document159 pagesCircuto de Chip 5846Angela Fernandez MonteroNo ratings yet
- ARDS Berlin Definition - RanieriDocument27 pagesARDS Berlin Definition - RanieriLindita KolajNo ratings yet
- The History of Magic in PortugalDocument30 pagesThe History of Magic in PortugalJose SilvestreNo ratings yet
- Export Meaning, Significance and Methods in IndiaDocument9 pagesExport Meaning, Significance and Methods in IndiaPayal AroraNo ratings yet
- Doctor-Patient Relationship - Cultural Aspects and Other Issues - Adel Adly RaghebDocument10 pagesDoctor-Patient Relationship - Cultural Aspects and Other Issues - Adel Adly RaghebAdel Adly100% (1)
- RT TimeGames KeysDocument3 pagesRT TimeGames KeysrubenblascoarmenNo ratings yet
- Arpita Sharma: Experience SkillsDocument2 pagesArpita Sharma: Experience SkillsVaidehi ZoctechNo ratings yet
- KofaxVRSInstallationGuide enDocument13 pagesKofaxVRSInstallationGuide enJorge CastilloNo ratings yet
- The National Dietary and Physical Activity Guidelines For Selected Non-Communicable DiseasesDocument194 pagesThe National Dietary and Physical Activity Guidelines For Selected Non-Communicable DiseasesRajithaHirangaNo ratings yet
- Sap CodesDocument4 pagesSap CodesInfoseek Web DevelopmentNo ratings yet
- A Statistical Model For Indoor Multipath PropagationDocument10 pagesA Statistical Model For Indoor Multipath PropagationRakesh RtNo ratings yet
- System Setup Ex SeriesDocument322 pagesSystem Setup Ex SeriesWaldon HendricksNo ratings yet
- Intersectional Pedagogy - Gal Harmat - Chapter2Document28 pagesIntersectional Pedagogy - Gal Harmat - Chapter2Cloè Saint-NomNo ratings yet
- 8 Pavilion Case Study - NocheDocument18 pages8 Pavilion Case Study - NocheJerick NocheNo ratings yet
- Qualification - and ValidationDocument154 pagesQualification - and ValidationDharmeshkumar Pravinchandra Patel100% (7)
- Wizard Magazine 009 (1992) (No Guide)Document93 pagesWizard Magazine 009 (1992) (No Guide)Teddy Ray Carian100% (2)
- A. H. BullenDocument258 pagesA. H. BullenGutenberg.orgNo ratings yet
- Amadora Gourmet Ice Cream & Sorbet-911Document1 pageAmadora Gourmet Ice Cream & Sorbet-911OL RentNo ratings yet
- Dada, Hanelen (Unified and Final Exam) 1Document7 pagesDada, Hanelen (Unified and Final Exam) 1Hanelen Dada100% (1)
- Tekin Iftar2017 PDFDocument21 pagesTekin Iftar2017 PDFVictor Martin CobosNo ratings yet
- Nachingwea Nickel Project, Tanzania: Research ProposalDocument6 pagesNachingwea Nickel Project, Tanzania: Research ProposalRozalia PengoNo ratings yet
- CDC 13633DS1Document248 pagesCDC 13633DS1SaadAliNo ratings yet
- Journal of Taibah University Medical SciencesDocument2 pagesJournal of Taibah University Medical Sciencesعمر أميرNo ratings yet
Nervous System: Science 6 - Second Quarter
Nervous System: Science 6 - Second Quarter
Uploaded by
maricel pampilo0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views25 pagesOriginal Title
NERVOUS SYSTEM.pptx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views25 pagesNervous System: Science 6 - Second Quarter
Nervous System: Science 6 - Second Quarter
Uploaded by
maricel pampiloCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 25
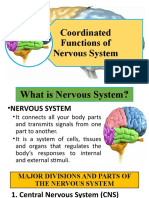
NERVOUS SYSTEM
SCIENCE 6 – SECOND QUARTER
NERVOUS SYSTEM
It is the control center of your entire
body.
Two divisions of Nervous System:
1. Central Nervous System (CNS)
2. Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM
It is made up of the brain and the
spinal cord.
It processes all incoming and outgoing
messages in the body.
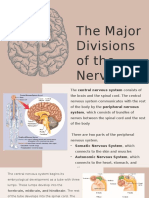
PERIPHERAL NERVOUS
SYSTEM
It is composed of two different nerves:
Cranial Nerves – it has 12 pairs of nerves
originating from the brain which are associated
with motor and sensory functions.
Spinal Nerves – it has 31 pairs of nerves
originating from the spinal cord which supply the
communication links between the central nervous
system and the neck, trunk, arms, and legs.
PERIPHERAL NERVOUS
SYSTEM
It consists of two types of nerves:
Sensory Nerves – gathers information
about your environment and your body’s
condition and send it to the CNS.
Motor Nerves – transmit impulses from the
CNS to the muscles and glands all over the
body.
Two Types of Motor Nerves
Somatic Nervous System – transmit
impulses to skeletal muscles under our
conscious control.
Autonomic Nervous System – regulates
activity of cardiac muscles, smooth muscles,
and glands.
Autonomic Nervous System
It has two opposing systems:
Sympathetic Nervous System – quickens our
heartbeats and breathing in the event of sudden
stress.
Parasympathetic Nervous System – prepares
our body for a restful state and coordinates the
movements of smooth muscles that are involved
in the body processes.
The Brain
The Brain
It is the largest organ in the nervous system.
Skull – a hard case bone that encloses the brain.
Meninges – a brain’s membrane made up of billions
of interacting cells that are covered by three layers of
its membrane.
Cerebrospinal Fluid – a protective fluid acts as a
shock absorber to help prevent injury.
Parts of the Brain
Cerebrum – the largest part of the brain. It controls
voluntary actions through speech and memory. It can
detect senses.
Cerebral Cortex – an outer covering in gray color
which is made up of mostly of cell bodies of neurons.
It is in cortex where most of the brain’s processing of
information is done.
Cerebellum – a small cauliflower like structure that
controls your ability to make coordinated and
balanced motor movements.
Parts of the Brain
Medulla Oblongata (Brain Stem) – part of the brain
that connects to the spinal cord. It controls many
involuntary movements such as breathing, heartbeat,
and digestion.
Midbrain – acts as a cellular switchboard to keep the
different areas of the brain communicating
continuously with the other parts of the nervous
system.
Parts of the Brain
Thalamus – it processes and coordinates sensory
messages from the sense receptors except the
olfactory nerves.
Hypothalamus – it regulates body functions such as
thirst, hunger, sleep patterns, and emotions.
Pons – it is a specialized band of nerve fibers that
connect to the midbrain with medulla oblongata.
TWO HEMISPHERES OF
BRAIN
Left Hemisphere – it directs the right side of the
body that controls activities such as speaking,
reading, writing, and solving problems.
Right Hemisphere – it directs the left side of the
body that controls activities that involve imagination,
appreciation, and creativity.
The Neuron
The Neuron
The basic unit of
structure and function
in the nervous system
Cells that conduct
impulses.
Made up of dendrites,
cell body and an axon
Parts of the Neuron
Dendrites: branch-like extensions that receive
impulses and carry them toward cell body.
Axon: single extension of the neuron that
carries impulses away from the cell body.
The axon branches out at ending to send
impulses to many different neurons. Dendrites
receive impulses from many other axons.
Parts of the Neuron
Axon Terminal: tip of the axon that transmit
messages.
Synapse: the gap between the axon of one
neuron and the dendrite of another neuron.
Neurotransmitter: it is a chemical substance
(from the synapse) that allows the nerve
impulse transfer to the next cell.
IMPULSES – the electrical messages that pass
through the neurons.
Three types of Neurons
Sensory Neurons: carry impulses from inside
and outside the body to brain and spinal cord.
Interneurons: found within brain and spinal
cord, process incoming impulses and pass them
on to motor neurons.
Motor Neurons: carry impulses away from the
brain and spinal cord.
Spinal Cord
The Spinal Cord
It is made up of nerve
fibers that carry
information to and from
the brain.
It is protected by bones
called vertebrate.
It is the information
highway of the
nervous system.
You might also like
- Zoology OutlineDocument3 pagesZoology OutlineEj AgsaldaNo ratings yet
- Biology G - Lesson 5 - Nervous SystemDocument59 pagesBiology G - Lesson 5 - Nervous SystemJeremiah Nayosan0% (1)
- Nervous SystemDocument26 pagesNervous SystemAe-jay CacalNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument46 pagesNervous SystemIponla KarlChristianNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemsDocument37 pagesNervous SystemsHannah CabritoNo ratings yet
- The Nervous System (Edited)Document27 pagesThe Nervous System (Edited)Kiarana Fleischer100% (1)
- Nervous System: Javaria ZahraDocument70 pagesNervous System: Javaria ZahraMuneeb JavaidNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument21 pagesEndocrine SystemNo Name100% (1)
- Nervous System 2Document23 pagesNervous System 2TinNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument23 pagesNervous SystemSumaira Noreen100% (1)
- Nervous SystemDocument23 pagesNervous SystemBryan Bries100% (1)
- Central Nervous SystemDocument30 pagesCentral Nervous SystemJames Lacuesta Tabiolo100% (1)
- 1 Nervous SystemDocument155 pages1 Nervous Systemsonali sundramNo ratings yet
- Discuss Action Potential of The Axon and Nerve ImpulseDocument3 pagesDiscuss Action Potential of The Axon and Nerve ImpulsePink PastaNo ratings yet
- Muscular System - WorksheetDocument3 pagesMuscular System - WorksheetsNo ratings yet
- Nervous System PresentationDocument22 pagesNervous System PresentationEnero Ombina PorlaresNo ratings yet
- The Nervous System 1Document57 pagesThe Nervous System 1seno.kirzvhan.bmlsNo ratings yet
- The Nervous SystemDocument80 pagesThe Nervous SystemAngelicaBarbosaNo ratings yet
- 31.1 The NeuronDocument33 pages31.1 The Neuronmoniaguayo98No ratings yet
- BrainDocument35 pagesBrainRonaleen mislang100% (1)
- Introduction and Organization of Nervous System: Presented by Dr. Amen FatimaDocument37 pagesIntroduction and Organization of Nervous System: Presented by Dr. Amen FatimaShanailNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument12 pagesNervous SystemLeon MarkoNo ratings yet
- Energy Forms PPTDocument16 pagesEnergy Forms PPTEdgar Miralles Inales ManriquezNo ratings yet
- 2 Human Body Nervous SystemDocument24 pages2 Human Body Nervous SystemRain HuntsdaleNo ratings yet
- Fisiologi Manusia: DR Mellova Amir MSCDocument52 pagesFisiologi Manusia: DR Mellova Amir MSCRizal AdhityaNo ratings yet
- The Major Divisions of The Nervous SystemDocument17 pagesThe Major Divisions of The Nervous SystemLiana BaluyotNo ratings yet
- Sense OrgansDocument9 pagesSense OrgansЕкатерина КовальNo ratings yet
- The Nervous SystemDocument25 pagesThe Nervous SystemRoan Angela100% (4)
- CHAPTER 2 Physiological Basis of BehaviorDocument37 pagesCHAPTER 2 Physiological Basis of BehaviorIsh Gallito100% (1)
- Lesson 4 - Circulatory SystemDocument21 pagesLesson 4 - Circulatory Systemapi-307592530No ratings yet
- Circulatory System ActivityDocument5 pagesCirculatory System ActivityKeen Jude CaminosNo ratings yet
- Sensory Mechanism: Almozara Francisco Villaflores LorenzoDocument29 pagesSensory Mechanism: Almozara Francisco Villaflores LorenzoMerrylFranciscoNo ratings yet
- Pre-Assessment: Odd Organ OutDocument45 pagesPre-Assessment: Odd Organ OutMelody Miras MacabontocNo ratings yet
- Neurons and Its FunctionDocument4 pagesNeurons and Its FunctionKristol MyersNo ratings yet
- Cell Division Mitosis MeiosisDocument63 pagesCell Division Mitosis MeiosisRinNo ratings yet
- The Nervous System: April Joy A. TalasDocument24 pagesThe Nervous System: April Joy A. TalasPoy Alis100% (1)
- The Nervous System-Final PDFDocument57 pagesThe Nervous System-Final PDFCarlo Makiling100% (1)
- The Nervous System NotesDocument6 pagesThe Nervous System NotesDhea Angela A. CapuyanNo ratings yet
- Nervous System POWERPOINTDocument15 pagesNervous System POWERPOINTZhen Obelidor100% (1)
- Human's Sense OrgansDocument11 pagesHuman's Sense OrgansTiara CalistaNo ratings yet
- The CerebrumDocument27 pagesThe Cerebrumapi-19916399No ratings yet
- (W9) The Skeletal SystemDocument9 pages(W9) The Skeletal SystemReign Heart HayahayNo ratings yet
- Homeostasi S:: Homeostatic Control MechanismsDocument22 pagesHomeostasi S:: Homeostatic Control MechanismsRoxanne CMNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic SystemDocument25 pagesLymphatic Systemumar khanNo ratings yet
- Sci 10 Unit 3 Mod 1 (Lecture)Document41 pagesSci 10 Unit 3 Mod 1 (Lecture)Jonessa BenignosNo ratings yet
- (W3) Cell CycleDocument6 pages(W3) Cell CycleRednaxela Mejico TarucNo ratings yet
- AtomDocument4 pagesAtomanjaliNo ratings yet
- Brain PP 5Document38 pagesBrain PP 5Anjaylyn BañasNo ratings yet
- Human Reproductive SystemDocument23 pagesHuman Reproductive SystemQuennie AceronNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Sense Organ and Their FunctionDocument20 pages1.1 Sense Organ and Their FunctionReduan Ibrahim100% (3)
- Cranial and Spinal NervesDocument5 pagesCranial and Spinal NervesEijunNo ratings yet
- The Muscular SystemDocument14 pagesThe Muscular SystemOana Maria FrancNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 SCIENCE: © Boardworks LTD 2004Document20 pagesGrade 10 SCIENCE: © Boardworks LTD 2004Modesto Valdriz100% (1)
- The Nervous System - PsychologyDocument17 pagesThe Nervous System - Psychologyjanet100% (2)
- The Nervous SystemDocument8 pagesThe Nervous SystemananthNo ratings yet
- Zoology Notes: 017 Chapter 13Document3 pagesZoology Notes: 017 Chapter 13humanupgrade100% (1)
- Grade 8 Science Elective: Nervous SystemDocument2 pagesGrade 8 Science Elective: Nervous SystemVincqNo ratings yet
- Bio 11 - Zoology - Experiment 20 - Types of Tissues: Muscular TissueDocument17 pagesBio 11 - Zoology - Experiment 20 - Types of Tissues: Muscular TissueDenise Cedeño100% (1)
- The Nervous SystemDocument18 pagesThe Nervous Systemvedansh duttNo ratings yet
- The Nervous System Is The BodyDocument18 pagesThe Nervous System Is The Bodyvedansh duttNo ratings yet
- Cmmi 2.0Document13 pagesCmmi 2.0faridin bm2019No ratings yet
- AQA A-Level Physics For A-Level Year 1 and As - GibbsDocument123 pagesAQA A-Level Physics For A-Level Year 1 and As - GibbsNarendra SinghNo ratings yet
- Activity: Can You Identify Ancestry?: European American Indian Sub-Saharan AfricanDocument5 pagesActivity: Can You Identify Ancestry?: European American Indian Sub-Saharan AfricanpoovenmoonoosamyNo ratings yet
- 3.1. Build A List Screen Exercise - En-UsDocument16 pages3.1. Build A List Screen Exercise - En-Usmahesh manchalaNo ratings yet
- How To Get The Teaching Job You Want The Complete Guide For College Graduates, Returning Teachers and Career Changers (PDFDrive) PDFDocument175 pagesHow To Get The Teaching Job You Want The Complete Guide For College Graduates, Returning Teachers and Career Changers (PDFDrive) PDFjomotNo ratings yet
- Natural OrderDocument5 pagesNatural OrderMicah Santon100% (1)
- Rogers, Lisa - Movie Review (EPortfolio)Document14 pagesRogers, Lisa - Movie Review (EPortfolio)Lisa RogersNo ratings yet
- Circuto de Chip 5846Document159 pagesCircuto de Chip 5846Angela Fernandez MonteroNo ratings yet
- ARDS Berlin Definition - RanieriDocument27 pagesARDS Berlin Definition - RanieriLindita KolajNo ratings yet
- The History of Magic in PortugalDocument30 pagesThe History of Magic in PortugalJose SilvestreNo ratings yet
- Export Meaning, Significance and Methods in IndiaDocument9 pagesExport Meaning, Significance and Methods in IndiaPayal AroraNo ratings yet
- Doctor-Patient Relationship - Cultural Aspects and Other Issues - Adel Adly RaghebDocument10 pagesDoctor-Patient Relationship - Cultural Aspects and Other Issues - Adel Adly RaghebAdel Adly100% (1)
- RT TimeGames KeysDocument3 pagesRT TimeGames KeysrubenblascoarmenNo ratings yet
- Arpita Sharma: Experience SkillsDocument2 pagesArpita Sharma: Experience SkillsVaidehi ZoctechNo ratings yet
- KofaxVRSInstallationGuide enDocument13 pagesKofaxVRSInstallationGuide enJorge CastilloNo ratings yet
- The National Dietary and Physical Activity Guidelines For Selected Non-Communicable DiseasesDocument194 pagesThe National Dietary and Physical Activity Guidelines For Selected Non-Communicable DiseasesRajithaHirangaNo ratings yet
- Sap CodesDocument4 pagesSap CodesInfoseek Web DevelopmentNo ratings yet
- A Statistical Model For Indoor Multipath PropagationDocument10 pagesA Statistical Model For Indoor Multipath PropagationRakesh RtNo ratings yet
- System Setup Ex SeriesDocument322 pagesSystem Setup Ex SeriesWaldon HendricksNo ratings yet
- Intersectional Pedagogy - Gal Harmat - Chapter2Document28 pagesIntersectional Pedagogy - Gal Harmat - Chapter2Cloè Saint-NomNo ratings yet
- 8 Pavilion Case Study - NocheDocument18 pages8 Pavilion Case Study - NocheJerick NocheNo ratings yet
- Qualification - and ValidationDocument154 pagesQualification - and ValidationDharmeshkumar Pravinchandra Patel100% (7)
- Wizard Magazine 009 (1992) (No Guide)Document93 pagesWizard Magazine 009 (1992) (No Guide)Teddy Ray Carian100% (2)
- A. H. BullenDocument258 pagesA. H. BullenGutenberg.orgNo ratings yet
- Amadora Gourmet Ice Cream & Sorbet-911Document1 pageAmadora Gourmet Ice Cream & Sorbet-911OL RentNo ratings yet
- Dada, Hanelen (Unified and Final Exam) 1Document7 pagesDada, Hanelen (Unified and Final Exam) 1Hanelen Dada100% (1)
- Tekin Iftar2017 PDFDocument21 pagesTekin Iftar2017 PDFVictor Martin CobosNo ratings yet
- Nachingwea Nickel Project, Tanzania: Research ProposalDocument6 pagesNachingwea Nickel Project, Tanzania: Research ProposalRozalia PengoNo ratings yet
- CDC 13633DS1Document248 pagesCDC 13633DS1SaadAliNo ratings yet
- Journal of Taibah University Medical SciencesDocument2 pagesJournal of Taibah University Medical Sciencesعمر أميرNo ratings yet