Professional Documents
Culture Documents
10.theories of Labor
Uploaded by
Julia Ramos100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
240 views18 pagestheories of labor
Original Title
10.Theories of Labor
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documenttheories of labor
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
240 views18 pages10.theories of Labor
Uploaded by
Julia Ramostheories of labor
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 18
THEORIES of LABOR
Combination of factors from mother
and fetus are responsible for the
initiation and completion of labor
process:
A. Fetal Adrenal response theory.
Hippocrates, the father of
medicine, was the first person to
propose this theory that certain
hormones produced by the fetal
adrenal and pituitary gland
initiates labor contractions.
B. Oxytocin Stimulation Theory.
Near terms oxytocin production
by the posterior pituitary gland
increases. Oxytocin stimulates
contractions.
Results the uterus becomes ↑
sensitive to oxytocin.
C. Uterine Stretch Theory:
• According to the theory,
“any hollow muscular organ
when stretched to capacity
will contract and empty…”
• The uterus becomes ↑
distended by the growing
fetus, placenta and amniotic
fluid, distention of the uterus
creates pressure on the nerve
endings which stimulates
contractions.
D. Progesterone Deprivation Theory:
• Progesterone helps maintains
pregnancy progesterone by its
relaxant effect on the smooth
muscles of the uterus preventing
uterine contractions.
• As pregnancy nears term, the
production of progesterone by
the placenta ↓, this decline in
progesterone allows the uterine
contractions to occur.
E. Prostaglandin Theory:
• When the fetus reached
maturity, the fetal
membrane produce large
amounts of arachidonic
acid which is converted by
maternal decidua into
prostaglandins, a hormones
that initiates uterine
contractions.
F. Theory of the Aging
Placenta:
• As the placenta “ages”, it
becomes less efficient,
producing ↓ amount of
progesterone.
• This progesterone allows the
concentration of
prostaglandin and estrogen to
rise steadily.
Signs of labor: Weeks
before real labor
“False Labor”
Braxton-Hicks: Irregular
intermittent contractions;
“false labor”; DO NOT
initiate true labor.
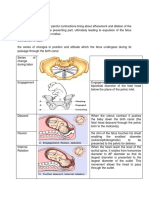
Lightening “The Baby
Dropped”: Fetus settles into pelvic
cavity or pelvic brim or inlet.
• Lightening results in:
Relief of dyspnea
Increase frequency of urination
Leg pain
Increase vaginal discharge
Decreased fundal height
• Floating is when the head is still
movable above the pelvic inlet
on the palpation.
• Engagement is the descent of
the biparietal plane of the fetal
to a level below that of the
pelvic inlet.
• Fixation is the descent of the
fetal head to the inlet to a level
that it can no longer be moved.
Ripening of the Cervix: cervix
effaces [thins] & dilates slightly.
• The cervix must soften in order
for it to be readily dilatable.
• Baby's head in pelvis pushes
against cervix causing
relaxation and effacement.
Increase Level of Activity (Burst of
Energy):
• Initiated by low progesterone level,
the adrenalin secrets large amounts of
epinephrine or adrenalin starting two
weeks prior to labor.
• Nesting instinct; cleans house, sets up
nursery.
• Advice the mother not to use this
energy to save it for labor and delivery.
Weight Loss:
• For about 2-3 pounds weight
loss two weeks before labor-
due to decline in progesterone
level. (progesterone promotes
fluid retention)
Show:
• The blood released from
these ruptured capillaries
mix with operculum (mucus
plug) giving it pinkish
coloration.
• The blood tinged mucus,
called show, is dislodged
from the cervical canal.
Rupture of the Membrane:
• A gush or steady trickle of
clear fluid from the
vagina.
• Rupture of the membrane is
caused by the pressure
of uterine contractions and
dilatation of the cervix.
Signs True Labor: closer to
time of delivery
Uterine Contractions: regular &
frequent compared to
Braxton-Hicks. Increase in
intensity, frequency and
duration.
Bloody Show: pink tinged
secretions d/t softening cervix.(
mucous plug)
Rupture of Membranes: (ROM)
Labor in 24 hrs. Multiparas sooner.
Big gush or slow trickle.
Clear/odorless. Green/brown,
danger sign
Meconium aspiration >
distress/infection.
Immediate medical attention.
PROM or prolonged ROM –
intrauterine infection [pathogens
reach fetus]
True vs False Labor:
False Labor True Labor
No increase in intensity, In crease in intensity,
duration and frequency of frequency and duration
uterine contraction
Contraction disappear with Ambulation increases
ambulation contractions
Discomfort remain in the Discomforts radiates to the
abdomen lower back or lumbosacral
area
Contraction stops when Contraction persists even if
woman is sedated woman is sedated
Absence of cervical Progressive cervical
dilatation dilatation
Duration of Labor
Stage of Labor Primi Multi
1st stage 10-12 hours 6-8 hours
2nd stage 30 min-2 hours 20-90 min.
Ave: 50 minutes Ave. 20 min.
3rd stage 5-20 min 5-20 min
4th stage 2-4 hours 2-4 hours
You might also like
- Hirschsprung’s Disease, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandHirschsprung’s Disease, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Intrapartal - Theories of LaborDocument21 pagesIntrapartal - Theories of LaborJan Oliver YaresNo ratings yet
- Labor and Delivery ConceptsDocument8 pagesLabor and Delivery ConceptsNisah CabugatanNo ratings yet
- Leopold's Maneuver SkillsDocument4 pagesLeopold's Maneuver SkillsCameron De Guzman100% (1)
- Complications With The Passenger 2Document77 pagesComplications With The Passenger 2JudyNo ratings yet
- 5 - Care of The Mother and The FetusDocument36 pages5 - Care of The Mother and The FetusMa Nelia P MagsinoNo ratings yet
- Maternal and Child Health Nursing Framework and TrendsDocument10 pagesMaternal and Child Health Nursing Framework and TrendsSHERYL TEMPLANo ratings yet
- Assessment in PregnancyDocument15 pagesAssessment in PregnancyAna75% (4)
- Leopold's ManueverDocument5 pagesLeopold's Manuevermanhua fanaticNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Fetal Growth and DevelopmentDocument30 pagesAssessment of Fetal Growth and DevelopmentWild Rose100% (2)
- NCM 109 Course Outline For Online LearningDocument7 pagesNCM 109 Course Outline For Online LearningGynesis Lim RoqueroNo ratings yet
- Essential Intrapartum Newborn Care (EINC)Document27 pagesEssential Intrapartum Newborn Care (EINC)josephNo ratings yet
- Care of The Mother and The Fetus During The Prenatal Period (Part 2)Document20 pagesCare of The Mother and The Fetus During The Prenatal Period (Part 2)Austine James Sabenicio PantiloNo ratings yet
- NCM 109 Care of Mother and Child at RiskDocument10 pagesNCM 109 Care of Mother and Child at RiskMia Fe Cuaya Lorenzo100% (1)
- Head To Toe Assessment of Pregnant WomanDocument8 pagesHead To Toe Assessment of Pregnant Womanacademic purposesNo ratings yet
- Problem With The PowersDocument9 pagesProblem With The PowersNicole Claire LegaspiNo ratings yet
- Cesarean Section: A Guide to Procedure, Anesthesia, and RecoveryDocument22 pagesCesarean Section: A Guide to Procedure, Anesthesia, and RecoveryKimberlie Dela Merced TomasNo ratings yet
- Maternal Child Health Nursing FrameworkDocument32 pagesMaternal Child Health Nursing Framework잔잔No ratings yet
- Mechanism of LaborDocument12 pagesMechanism of LaborSaidatul Safarah Md HassanNo ratings yet
- Care of The Mother and The Fetus During Perinatal PeriodDocument11 pagesCare of The Mother and The Fetus During Perinatal PeriodMaria KawilanNo ratings yet
- Maternal Child Health NursingDocument5 pagesMaternal Child Health NursingLuna Sang-anNo ratings yet
- Maternal and Child Health Nursing: May Ann B. Allera, RNDocument16 pagesMaternal and Child Health Nursing: May Ann B. Allera, RNmayal100% (1)
- 5 - Care of The Mother and The FetusDocument36 pages5 - Care of The Mother and The FetusMa Nelia P Magsino100% (2)
- 05 DystociaDocument10 pages05 DystociaRiantiara PutrizaNo ratings yet
- Module 1 NCM 107 NewDocument44 pagesModule 1 NCM 107 NewAmethystNo ratings yet
- Maternal & Child NUrsing SylabusDocument7 pagesMaternal & Child NUrsing Sylabusmarsan12No ratings yet
- Uterine ProlapseDocument11 pagesUterine ProlapseMelDred Cajes BolandoNo ratings yet
- Theories of Labor: Prepared By: Ronarica B. Diones, R.N., R.MDocument17 pagesTheories of Labor: Prepared By: Ronarica B. Diones, R.N., R.MDee BorreroNo ratings yet
- Physical Assessment of NewbornDocument39 pagesPhysical Assessment of Newbornwewix100% (3)
- Postpartum Physiology, What's Normal: Starting at Her HeadDocument26 pagesPostpartum Physiology, What's Normal: Starting at Her HeadyogurtNo ratings yet
- CASE STUDY Labor and DeliveryDocument2 pagesCASE STUDY Labor and DeliveryAprodite Sumod-ong100% (1)
- 5 P - S of LaborDocument19 pages5 P - S of LaborPerrilyn PereyNo ratings yet
- Mechanism of LaborDocument2 pagesMechanism of Laborgerold m chuaNo ratings yet
- NCM 107-109 OB Ward Clinical Instructional PlanDocument6 pagesNCM 107-109 OB Ward Clinical Instructional PlanJuriel Michael Alap100% (3)
- NCM 107 1Document5 pagesNCM 107 1Clint Mikael EulatrizNo ratings yet
- Ob MaternityDocument46 pagesOb MaternityJohanna Erazo Padilla100% (1)
- NCM 109 Resource UnitDocument51 pagesNCM 109 Resource UnitDaryl Adrian RecaidoNo ratings yet
- Labor & DeliveryDocument14 pagesLabor & DeliveryNiña Eleana FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Module NCM 107 Pre LimDocument35 pagesModule NCM 107 Pre Limjanina mykaNo ratings yet
- Myths and Beliefs Related To Pregnancy From Different Culture in The PhilippinesDocument11 pagesMyths and Beliefs Related To Pregnancy From Different Culture in The PhilippinesElla Chio Salud-Matabalao0% (1)
- AKLAN STATE UNIVERSITY MCN MODULEDocument18 pagesAKLAN STATE UNIVERSITY MCN MODULEmysterioushumane100% (2)
- Framework For Maternal and Child Health NursingDocument7 pagesFramework For Maternal and Child Health NursingJan Oliver Yares100% (1)
- Assessment of NewbornDocument26 pagesAssessment of Newbornaybee_14No ratings yet
- IntrapartumDocument17 pagesIntrapartumIris CaberteNo ratings yet
- Assessment of The Childbearing WomanDocument122 pagesAssessment of The Childbearing WomanLaurisse April Necesito100% (1)
- Incompetent CervixDocument29 pagesIncompetent CervixCyrelle Jen TorresNo ratings yet
- Uterine RuptureDocument19 pagesUterine RuptureAna Denise Quinajon0% (1)
- Nursing Management of During Stages of Labor and Delivery UpdatedDocument60 pagesNursing Management of During Stages of Labor and Delivery UpdatedSherlyn Miranda GarcesNo ratings yet
- Maternal Problems With PowerDocument2 pagesMaternal Problems With PowerAlex CvgNo ratings yet
- Components of LaborDocument57 pagesComponents of Laborangelus_eyes181996100% (1)
- ESSENTIAL NEWBORN CAREDocument5 pagesESSENTIAL NEWBORN CAREJig PirameNo ratings yet
- Dysfunctional Labor and BirthDocument167 pagesDysfunctional Labor and BirthKristel Joy Sarmiento AsuncionNo ratings yet
- Calamba Doctors' Colleges: Performance Evaluation ChecklistDocument2 pagesCalamba Doctors' Colleges: Performance Evaluation ChecklistJapsay Francisco GranadaNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Obstetrics EditedDocument11 pagesAbnormal Obstetrics EditedAbhie Gayle Erbon AbonallaNo ratings yet
- NCM-N107 Growth and DevelopmentDocument147 pagesNCM-N107 Growth and DevelopmentInsatiable CleeNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care for High-Risk Labor and DeliveryDocument170 pagesNursing Care for High-Risk Labor and DeliveryLongyapon Sheena Stephanie100% (2)
- Principles of Postpartum Nursing CareDocument2 pagesPrinciples of Postpartum Nursing CareZaire DylanNo ratings yet
- Care of Mother, Childbirth & Labor ProcessesDocument13 pagesCare of Mother, Childbirth & Labor ProcessesBardiaga JmayNo ratings yet
- NCM 107 - SL - Mat - 1Document100 pagesNCM 107 - SL - Mat - 1marilexdomagsangNo ratings yet
- Normal Labour in Obstetric2Document17 pagesNormal Labour in Obstetric2Tejasvi ChavdaNo ratings yet
- Providing Breastmilk For Premature and Ill Newborn InfantsDocument49 pagesProviding Breastmilk For Premature and Ill Newborn InfantsBayu KurniawanNo ratings yet
- Family-Centered Maternity Care: Facilitating Communication and Involvement in The Birthing Process' DR - (Prof) Meenu PaulDocument6 pagesFamily-Centered Maternity Care: Facilitating Communication and Involvement in The Birthing Process' DR - (Prof) Meenu PauleditorbijnrNo ratings yet
- Step 2 CK Usmle Questions For Ob GynDocument48 pagesStep 2 CK Usmle Questions For Ob Gyniamdonut87% (15)
- 132 HealthwiseDocument9 pages132 Healthwisemichael.staffordNo ratings yet
- Ultrasound of AdnexaDocument34 pagesUltrasound of AdnexaJazib ShahidNo ratings yet
- 05 N141 31673Document21 pages05 N141 31673priya thakurNo ratings yet
- PREGNANCY BREAST CANCER CASESDocument3 pagesPREGNANCY BREAST CANCER CASESJonny CardenasNo ratings yet
- Need To Optimise Infant Feeding CounsellingDocument30 pagesNeed To Optimise Infant Feeding CounsellingfadnesNo ratings yet
- G PpromDocument4 pagesG PpromDewa Made Sucipta PutraNo ratings yet
- NP2 RationaleDocument32 pagesNP2 RationaleCeejhaye TamangNo ratings yet
- A Clinical Evaluation of Treatment With Estriol Vaginal Cream Versus Suppository in Postmenopausal WomenDocument5 pagesA Clinical Evaluation of Treatment With Estriol Vaginal Cream Versus Suppository in Postmenopausal WomenElenita BastosNo ratings yet
- Cephalic PresentationDocument5 pagesCephalic PresentationAvaneeshNo ratings yet
- The 3 Phases of Your Menstrual Cycle ExplainedDocument3 pagesThe 3 Phases of Your Menstrual Cycle ExplainedMelai MarceloNo ratings yet
- Cervix InformationDocument4 pagesCervix InformationEdrea Aquino MendezNo ratings yet
- PuerperiumDocument26 pagesPuerperiumVignesh ThangavelNo ratings yet
- MENSTRUAL CYCLE - QuizDocument13 pagesMENSTRUAL CYCLE - QuizMaria Germamae ResosoNo ratings yet
- Prevention and Treatment of Moderate and Severe Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome NoprintDocument14 pagesPrevention and Treatment of Moderate and Severe Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome NoprintDo le QuangNo ratings yet
- Leong Et Al-2004-BJOG: An International Journal of Obstetrics & GynaecologyDocument2 pagesLeong Et Al-2004-BJOG: An International Journal of Obstetrics & GynaecologyAngie MandeoyaNo ratings yet
- Background: Placental Abruption Seen After DeliveryDocument8 pagesBackground: Placental Abruption Seen After DeliverymoigomezNo ratings yet
- COBAS 6000: E601 Reagent Inventory MONTH/YEARDocument2 pagesCOBAS 6000: E601 Reagent Inventory MONTH/YEARCharmaine Corpuz GranilNo ratings yet
- OB HesiDocument3 pagesOB HesiLeena Lapena100% (4)
- Knowledge Attitudes and Practices Regarding ModernDocument7 pagesKnowledge Attitudes and Practices Regarding Modernnaasir abdiNo ratings yet
- The Sexual SelfDocument18 pagesThe Sexual SelfAngelo Dale Derramas OndilloNo ratings yet
- Preskas Mioma Geburt DafpusDocument2 pagesPreskas Mioma Geburt DafpusNadira DanataNo ratings yet
- Labour Second StageDocument8 pagesLabour Second StageakankshaNo ratings yet
- Cmca Transes PrelimDocument33 pagesCmca Transes Prelimangelalorin.balano.cvt100% (1)
- Thyroid Dysfunction and Abnormal Uterine Bleeding: Gynecology and Women's HealthDocument7 pagesThyroid Dysfunction and Abnormal Uterine Bleeding: Gynecology and Women's HealthnandaNo ratings yet
- Problem Statement DocsDocument2 pagesProblem Statement DocsharpreetNo ratings yet
- The Dual Role of Nipple Preservation: Peer ViewpointDocument2 pagesThe Dual Role of Nipple Preservation: Peer ViewpointGustavo SalibaNo ratings yet
- Laporan Kasus Ketuban Pecah Dini + Drip OksitosinDocument8 pagesLaporan Kasus Ketuban Pecah Dini + Drip OksitosinPutra MahautamaNo ratings yet