0% found this document useful (0 votes)
475 views8 pagesSampoong Store Collapse Overview
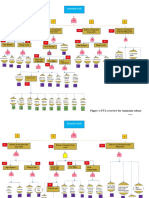
The Sampoong Department Store collapse in 1995 in Seoul, South Korea was the largest peacetime disaster in the country's history. The 5-story building collapsed, killing 501 people and injuring 937 others. An investigation found the immediate cause was structural degradation of a support column. The basic causes included a lack of engineering analysis, prioritizing profits over safety, poor management practices, and ignoring contractor warnings. Recommendations included implementing comprehensive safety programs and respecting engineering opinions to prevent future disasters.
Uploaded by
Shannon MacDonaldCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
475 views8 pagesSampoong Store Collapse Overview
The Sampoong Department Store collapse in 1995 in Seoul, South Korea was the largest peacetime disaster in the country's history. The 5-story building collapsed, killing 501 people and injuring 937 others. An investigation found the immediate cause was structural degradation of a support column. The basic causes included a lack of engineering analysis, prioritizing profits over safety, poor management practices, and ignoring contractor warnings. Recommendations included implementing comprehensive safety programs and respecting engineering opinions to prevent future disasters.
Uploaded by
Shannon MacDonaldCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd