Professional Documents
Culture Documents
WLS HSE Lifting Crane Operation Campaign DST 5 (Risza Firmansyah)
Uploaded by
Rezha KurniawanOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
WLS HSE Lifting Crane Operation Campaign DST 5 (Risza Firmansyah)
Uploaded by
Rezha KurniawanCopyright:
Available Formats
WLS HSE Lifting crane operations campaign,
DST 5
19 May 2009
TN. Ax. 73
1 Fuad ROIYAN – DWL/WLS/SMT
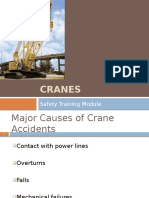
Major Causes of Crane Accidents
Contact with power lines
Overturns
Falls
Mechanical failures
Instability – unsecured load, load capacity exceeded, or ground not level or too
soft
Lack of communication - the point of operation is a distance from the crane
operator or not in full view of the operator
Lack of training
Inadequate maintenance or inspection
2 Fuad ROIYAN – DWL/WLS/SMT
Who is at Risk
Operators
Persons at Crane Site
Definitions
Crane – Consists of a rotating structure for lifting and lowering horizontally on rubber tracks or
crawler treads
Hoist - Used to lift and lower load.
Boom – An inclined spar, strut, or other long member supporting the hoisting tackle
Boom stops – A device used to limit the angle of the boom at its highest position
Brake – To slow or stop motion by friction or power
Block – Sheaves or grooved pulleys in a frame with hook, eye and strap
Jib – Extension attached to the boom point to provide added boom length for lifting specified
loads.
3 Fuad ROIYAN – DWL/WLS/SMT
Crane Hazards
Improper load rating • Working too close to
Excessive speeds power lines
• Improper exhaust
No hand signals
system
Inadequate inspection and • Shattered windows
maintenance
• No steps/guardrails
Unguarded parts walkways
Unguarded swing radius • No boom angle
indicator
• Not using outriggers
4 Fuad ROIYAN – DWL/WLS/SMT
Planning Before Start-Up
Level the crane and ensure support surface is firm and able to support
the load
Contact power line owners and determine precautions. Know the
location and voltage of overhead power lines.
Know the basic crane capacities, limitations, and job site restrictions,
such as the location of power lines, unstable soil, or high winds.
Make other personnel aware of hoisting activities.
Barricade areas within swing radius.
Ensure proper maintenance and inspections.
Determine safe areas to store materials and place machinery.
5 Fuad ROIYAN – DWL/WLS/SMT
Competent Person
The competent person must inspect all
machinery and equipment prior to each use, and
during use, to make sure it is in safe operating
condition.
If it needs fixing, take it out of service and don’t
use it until it is fixed
Load Capacity - Speed - Warnings
Make sure the crane operator can see
the:
Rated Load Capacities
Operating Speeds
Special Hazard Warning or Instruction
Load Rating Chart
6 Fuad ROIYAN – DWL/WLS/SMT
Know the Weight of the Load
Refer to shipping ticket or other documentation
Ensure lift calculations are correct
Ensure load is within load chart rating for boom length and load radius of
crane
Crane is rated by the maximum weight it will lift at a minimum radius and
minimum boom length – the further from its centerpoint, the less it will lift
Load Limiting Factors
Not level
Wind
Side loads
On its wheels
Lifting over the side
Use of extensions, jibs and other attachments
Limits of wire rope, slings and lifting devices
7 Fuad ROIYAN – DWL/WLS/SMT
Hand Signals
An illustration of
the signals must
be posted at the
job site
8 Fuad ROIYAN – DWL/WLS/SMT
What to Inspect
Remove From
Service
Correct air pressure and no leaks
Track properly inflated
Clearance for tail swing
Wire rope wear
Physical damage to crane
Loose or missing hardware, nuts,
or bolts
Fluid leaks
9 Fuad ROIYAN – DWL/WLS/SMT
Training
Operators:
must qualify on specific crane type
Must include on-the-job training
Supervisor / competent person – Rigging and Slinging
10 Fuad ROIYAN – DWL/WLS/SMT
Summary
• An unstable load, lack of communication, lack of
training, and inadequate maintenance or inspection are
major contributors to crane accidents.
• Operators or others working in the area can be
victims to “struck by" and "caught in" injuries.
• Contact with power lines causes many accidents.
• A competent person must inspect a crane regularly
to insure it is in proper order.
• Planning and training reduces accidents.
11 Fuad ROIYAN – DWL/WLS/SMT
Photos simulations when lift up
Check Valve 2” – 1502 Weco
12 Fuad ROIYAN – DWL/WLS/SMT
Commentaries
Crane operator did not have proper chair during lifting operations
Crews shall have rigger training certifications or dedicated persons for
rigging and lifting operations
Crews shall be more aware to their lifting gear conditions, the visual
checks and certifications must be perform regularly
13 Fuad ROIYAN – DWL/WLS/SMT
You might also like
- Lifting Work PresantationDocument30 pagesLifting Work PresantationIrfanadi PratomoNo ratings yet
- Crane and Hoist Safety ProgramDocument22 pagesCrane and Hoist Safety Programshahrilmr6934No ratings yet
- Crane - RiggingWorkbook PDFDocument45 pagesCrane - RiggingWorkbook PDFNguyen Duc HieuNo ratings yet
- Cranes Hoisting and RiggingDocument25 pagesCranes Hoisting and Riggingkanakarao1No ratings yet
- HSE CommunicationDocument29 pagesHSE CommunicationEllder Preye Ekiye100% (1)
- Topic 9 Accident Prevention Techniques PDFDocument14 pagesTopic 9 Accident Prevention Techniques PDFDiyana OsmanNo ratings yet
- Maritime Safety CatalogueDocument44 pagesMaritime Safety Cataloguevikrant911No ratings yet
- Flexible Pipe July 2015 WebDocument12 pagesFlexible Pipe July 2015 WebravikrsNo ratings yet
- Level 3 Health and Safety in The WorkplaceDocument5 pagesLevel 3 Health and Safety in The WorkplaceKannan JaganNo ratings yet
- Safety Alert: (E.g. Damage To Environment, Reputation, Equipment Schedule and Cost)Document5 pagesSafety Alert: (E.g. Damage To Environment, Reputation, Equipment Schedule and Cost)zaheerNo ratings yet
- Personal Protective Equipment-1Document72 pagesPersonal Protective Equipment-1Haseeb AhsanNo ratings yet
- Project ManagementDocument41 pagesProject ManagementJochie TeruelNo ratings yet
- RiggingDocument159 pagesRiggingSanthanu SukumaranNo ratings yet
- UFP - Pre-Lift Safety Checklist - CFN-1092Document2 pagesUFP - Pre-Lift Safety Checklist - CFN-1092BhaiJan59No ratings yet
- Efogen Rigging SlingingDocument52 pagesEfogen Rigging SlingingBalasuperamaniam RamanNo ratings yet
- 4 - SIL TrainingDocument23 pages4 - SIL TrainingNGUYEN HUU TUANNo ratings yet
- AssigmentDocument17 pagesAssigmentAmori GeofreyNo ratings yet
- Final Year Project 2 Presentation: Design Quail Egg Incubator For Experiments SystemDocument19 pagesFinal Year Project 2 Presentation: Design Quail Egg Incubator For Experiments SystemMohd Faiz Mohd ZinNo ratings yet
- AssigmentDocument3 pagesAssigmentBush TamamNo ratings yet
- CHESM Checklist R00 Sep18Document7 pagesCHESM Checklist R00 Sep18Nala IndrasenaNo ratings yet
- Safety TrainingDocument27 pagesSafety TrainingPradnya PatilNo ratings yet
- List of EquipmentsDocument6 pagesList of Equipmentsbittu692No ratings yet
- Workshop Technology 1: Accident PreventionDocument24 pagesWorkshop Technology 1: Accident PreventionMohsen SaidiNo ratings yet
- Hindustan Shipyard-10Document75 pagesHindustan Shipyard-10anshul21No ratings yet
- Flood SafetyDocument2 pagesFlood SafetyCatholic Charities USANo ratings yet
- Suez Oil Company: Hazard Identification and Risk AssessmentDocument15 pagesSuez Oil Company: Hazard Identification and Risk AssessmentOmar EzzatNo ratings yet
- FAA Requirements For RaftsDocument4 pagesFAA Requirements For RaftsTDHNo ratings yet
- HSE Practitioner Cari Di GoogleDocument33 pagesHSE Practitioner Cari Di GoogleHerik renaldoNo ratings yet
- Computer Communications & Networks (Swe-306) Assignment # 1 Due Date: 1, February 2018Document2 pagesComputer Communications & Networks (Swe-306) Assignment # 1 Due Date: 1, February 2018Anonymous g65DiGw0% (1)
- Risk Management ManualDocument87 pagesRisk Management ManualAndre MarsNo ratings yet
- Dupre - Travis Crane Operation and MaintenanceDocument23 pagesDupre - Travis Crane Operation and MaintenancemohammadazraiNo ratings yet
- Interpretation Solas 2005 PDFDocument280 pagesInterpretation Solas 2005 PDFChristian Rodrigo Gonzalez Cockbaine100% (1)
- E-Fact 14 - Hazards and Risks Associated With Manual Handling in The WorkplaceDocument10 pagesE-Fact 14 - Hazards and Risks Associated With Manual Handling in The WorkplaceDeby Damayanti SupardiNo ratings yet
- Do Incentives WorkDocument14 pagesDo Incentives WorkAndre MarsNo ratings yet
- Development and Validation of Three Step Risk Assessment Method For Ship Recycling Sector 2015 Safety ScienceDocument15 pagesDevelopment and Validation of Three Step Risk Assessment Method For Ship Recycling Sector 2015 Safety ScienceEvi SiswantoNo ratings yet
- Gantry Crane PDFDocument2 pagesGantry Crane PDFcityofdarwingisNo ratings yet
- DS-0036 Rev A NDT QualificationDocument2 pagesDS-0036 Rev A NDT Qualificationamaryogi100% (1)
- BOOK (21st Century Skills Library - Cool STEM Careers) Wil Mara - Wind Turbine Service Technician-Cherry Lake Publishing (2013) PDFDocument36 pagesBOOK (21st Century Skills Library - Cool STEM Careers) Wil Mara - Wind Turbine Service Technician-Cherry Lake Publishing (2013) PDFfernandochinas2253No ratings yet
- Hot Work Activity RemindersDocument24 pagesHot Work Activity RemindersKristine Danielle RamirezNo ratings yet
- Working in Shipyard IndustryDocument3 pagesWorking in Shipyard IndustryDamen YardNo ratings yet
- Offshore Transportation PaperDocument19 pagesOffshore Transportation PaperNikhilVinayNo ratings yet
- Lfting OperationDocument3 pagesLfting OperationAshok SubramaniyanNo ratings yet
- Challenges and Opportunities For Organizational BehaviourDocument16 pagesChallenges and Opportunities For Organizational BehaviourNitish BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Machine GuardingDocument54 pagesMachine GuardingAbderrahmane LarbiNo ratings yet
- Lifting and Supporting Loads, Mobile Equipment Awareness: Ashaka 16Mw CPP Project NigeriaDocument100 pagesLifting and Supporting Loads, Mobile Equipment Awareness: Ashaka 16Mw CPP Project NigeriaPhilip AdewunmiNo ratings yet
- Arc FlashDocument41 pagesArc FlashSatya PrabhatNo ratings yet
- Strong Dual Hawk Tandem Rev H 2008Document70 pagesStrong Dual Hawk Tandem Rev H 2008FaderNo ratings yet
- Offshore Petroleum Production SystemsDocument48 pagesOffshore Petroleum Production SystemsPungguh Ikhsan PNo ratings yet
- Stop BrochureDocument12 pagesStop BrochureIan MaldonadoNo ratings yet
- Safety Bulletin - Accdient During Ladder Cutting OperationDocument2 pagesSafety Bulletin - Accdient During Ladder Cutting OperationalberioNo ratings yet
- Gangway Installation ProcedureDocument8 pagesGangway Installation Procedurelon wayNo ratings yet
- Transformation Manager Job DescriptionDocument3 pagesTransformation Manager Job DescriptionworldfedksimcNo ratings yet
- OMHEC Lifting of Personnel OffshoreDocument17 pagesOMHEC Lifting of Personnel OffshoreLasse WelleNo ratings yet
- PR-1709 - Lifting and Hoisting Procedure Lift Planning ExecutionDocument31 pagesPR-1709 - Lifting and Hoisting Procedure Lift Planning ExecutionAdnanNo ratings yet
- WSHC - Landscape and Horticulture Guidelines - 16 Jan 2012Document69 pagesWSHC - Landscape and Horticulture Guidelines - 16 Jan 2012lwin_oo2435No ratings yet
- Mecca Crane CollapseDocument8 pagesMecca Crane CollapseFelix kabweNo ratings yet
- Shipyard Report PDFDocument10 pagesShipyard Report PDFvarsha raichalNo ratings yet
- EMMARDocument5 pagesEMMARNisar DeenNo ratings yet
- CranesDocument80 pagesCranesjoenediath9345No ratings yet
- Construction SafetyDocument30 pagesConstruction SafetyBharath CjNo ratings yet
- Awareness ISO 37001 - ImplementationDocument87 pagesAwareness ISO 37001 - ImplementationRezha KurniawanNo ratings yet
- Construction QHSE BudgetDocument6 pagesConstruction QHSE Budgetqhse 3dihaji100% (2)
- Home Emergency Book PDFDocument260 pagesHome Emergency Book PDFrahulmultivision100% (1)
- Accident InvestigationDocument36 pagesAccident InvestigationNauman Taj100% (3)
- WLS HSE Lifting Crane Operation Campaign DST 5 (Risza Firmansyah)Document13 pagesWLS HSE Lifting Crane Operation Campaign DST 5 (Risza Firmansyah)Rezha KurniawanNo ratings yet
- Project Title: TBA: Client: ContractorDocument5 pagesProject Title: TBA: Client: ContractorIzza HalimNo ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document38 pagesPresentation 1SeyedNo ratings yet
- Method Statement For GCBDocument6 pagesMethod Statement For GCBkamil0% (1)
- Scanreco G2 Radio Remote Control System, 20-13Document55 pagesScanreco G2 Radio Remote Control System, 20-13mauricio arias100% (4)
- Technical Description 100 150 Ton Hydramarine CraneDocument15 pagesTechnical Description 100 150 Ton Hydramarine Craneramya100% (1)
- SM Pc228us 2 Sebm015903 PDFDocument661 pagesSM Pc228us 2 Sebm015903 PDFalexandr100% (1)
- Industry Standards in Material Handling: Patrick Davison, MHI Director of StandardsDocument34 pagesIndustry Standards in Material Handling: Patrick Davison, MHI Director of StandardsMayank SoniNo ratings yet
- Ansi StanderedDocument32 pagesAnsi StanderedReda El-AwadyNo ratings yet
- Hoisting and Rigging Plan: Location: Date of Lift: Load Description: Lift Director Ordinary: Critical: Multiple CranesDocument5 pagesHoisting and Rigging Plan: Location: Date of Lift: Load Description: Lift Director Ordinary: Critical: Multiple CranesAfdalNo ratings yet
- International Standard: Cranes - Limiting and Indicating Devices - GeneralDocument6 pagesInternational Standard: Cranes - Limiting and Indicating Devices - GeneralANDYZHUANGNo ratings yet
- Rough Terrain Hydraulic Crane: Courtesy of Crane - MarketDocument12 pagesRough Terrain Hydraulic Crane: Courtesy of Crane - MarketJEAN CARLOS QUINTERO CAMPILLONo ratings yet
- BT2000 PartsDocument112 pagesBT2000 PartsHernan Reyes CarbonellNo ratings yet
- RT530E 2 Product Guide ImperialDocument16 pagesRT530E 2 Product Guide ImperialKimberly Mae DantesNo ratings yet
- 002-PDS-CON-005 Method Statement For Demoilition of Pipelines Asphalt, Concrete, Houses and FenceDocument22 pages002-PDS-CON-005 Method Statement For Demoilition of Pipelines Asphalt, Concrete, Houses and FenceMalik ZamanNo ratings yet
- JSA Steel Truss Erection and CladdingDocument4 pagesJSA Steel Truss Erection and CladdingCherry BetonioNo ratings yet
- Grove GMK 6350 - 350T PDFDocument24 pagesGrove GMK 6350 - 350T PDFMarco Torres Henrriquez50% (2)
- Crane Maintenance ChecklistDocument3 pagesCrane Maintenance ChecklistAbdul HalimNo ratings yet
- ARRIUM - Standards For Crane Anti-Derailment Final R4Document18 pagesARRIUM - Standards For Crane Anti-Derailment Final R4YOO SHIN0% (1)
- Cleveland Tram Rail Crane System PGDocument12 pagesCleveland Tram Rail Crane System PGJESUSCALVILLONo ratings yet
- Siii Dominator IIDocument227 pagesSiii Dominator IIRodrigo HambertoneNo ratings yet
- Hatch Cover and Its Types - by AfsarDocument16 pagesHatch Cover and Its Types - by AfsarMohammed AfsarNo ratings yet
- Swapnil (2016) - Design of Components Used in Hoisting Mechanism of An EOTDocument5 pagesSwapnil (2016) - Design of Components Used in Hoisting Mechanism of An EOTGogyNo ratings yet
- Manual Armado PC5500 PDFDocument104 pagesManual Armado PC5500 PDFclaudioNo ratings yet
- Tower Crane Safety Inspection Checklist Global EHSDocument1 pageTower Crane Safety Inspection Checklist Global EHSsudhansu SamantarayNo ratings yet
- Hydrotest Check ListDocument1 pageHydrotest Check ListSaut Maruli Tua SamosirNo ratings yet
- Lifting Procedure With AttachmentDocument16 pagesLifting Procedure With AttachmentIshak MalimNo ratings yet
- Progress Docking Manalagi Wanda 30-06-23Document45 pagesProgress Docking Manalagi Wanda 30-06-23cahyo putroNo ratings yet
- 03 - HIRARD Piling WorkDocument3 pages03 - HIRARD Piling WorkJames JoviNo ratings yet
- Brake Torque Application DataDocument0 pagesBrake Torque Application Dataellie210879No ratings yet
- Terex - Crawler 25t BT5092Document4 pagesTerex - Crawler 25t BT5092Taufik Singgih0% (1)