Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ATHEROSCLEROSIS
Uploaded by
Deepak0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
39 views15 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
39 views15 pagesATHEROSCLEROSIS
Uploaded by
DeepakCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 15
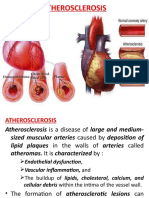
ATHEROSCLEROSIS
Atherosclerosis
The term atherosclerosis is derived from athero-(meaning
porridge) referring to the soft lipid-rich material in the centre
of atheroma, and sclerosis (scarring) referring to connective
tissue in the plaques.
Atherosclerosis is an thickening and hardening of large and
medium-sized muscular arteries, primarily due to
involvement of tunica intima and is characterised by
fibrofatty plaques or atheromas.
clinical syndromes resulting from ischaemia
due to atherosclerosis
1. Heart
(angina and myocardial infarcts or heart attacks)
2. Brain
(transient cerebral ischaemia & strokes)
3. Other sequelae are: peripheral vascular disease,
aneurysmal dilatation due to weakened arterial wall.
SMOKING
The extent and severity of atherosclerosis are much greater in smokers
than in non-smokers. Cigarette smoking is associated with higher risk
of atherosclerotic IHD and sudden cardiac death. Men who smoke a
pack of cigarettes a day are 3-5 times more likely to die of IHD than
non-smokers.
The increased risk and severity of atherosclerosis in smokers is due to
reduced level of HDL, deranged coagulation system and accumulation
of carbon monoxide in the blood that produces carboxy haemoglobin
and eventually hypoxia in the arterial wall favouring atherosclerosis.
You might also like
- Prevent and Reverse Heart DiseaseDocument95 pagesPrevent and Reverse Heart Diseaseyhanteran100% (4)
- Basic Mechanism Involved in Process of Inflammation and RepairDocument32 pagesBasic Mechanism Involved in Process of Inflammation and RepairDeepakNo ratings yet
- Review of Related LiteratureDocument23 pagesReview of Related LiteratureMark Alden PaduaNo ratings yet
- Diseases Caused by Tobacco SmokeDocument2 pagesDiseases Caused by Tobacco SmokeSara XhaferiNo ratings yet
- Acute Myocardial InfarctionDocument17 pagesAcute Myocardial InfarctionRuqowiyah TanjungNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Disorders: Definition of TermsDocument22 pagesCardiovascular Disorders: Definition of TermsCornelius OgegaNo ratings yet
- Prevalence and Risk Factors: HypertensionDocument2 pagesPrevalence and Risk Factors: HypertensionKhristine Anne FabayNo ratings yet
- Angina Pectoris Myocardial Infarction: Bahuguna, Nimisha Imd-Batch 3Document19 pagesAngina Pectoris Myocardial Infarction: Bahuguna, Nimisha Imd-Batch 3Nimisha BahugunaNo ratings yet
- Effects On Blood CoagulationDocument3 pagesEffects On Blood Coagulationevangelo22656No ratings yet
- Myocardial InfarctionDocument21 pagesMyocardial Infarctionanon_516349434No ratings yet
- 10.6 Health Issues Related To The Human Circulatory SystemDocument7 pages10.6 Health Issues Related To The Human Circulatory SystemrynNo ratings yet
- AtherosclerosisDocument23 pagesAtherosclerosisPoonam soniNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument117 pagesCardiovascular SystemHamro ChannelNo ratings yet
- StrokeDocument27 pagesStrokeSameen ArshadNo ratings yet
- Atherosclerosis and Myocardial InfractionDocument26 pagesAtherosclerosis and Myocardial InfractionElina GNo ratings yet
- Myocardial InfarctionDocument21 pagesMyocardial InfarctionasdnofalNo ratings yet
- CVS 1 PDFDocument24 pagesCVS 1 PDFafaq alismailiNo ratings yet
- Myocardial InfarctionDocument18 pagesMyocardial InfarctionYanna Habib-MangotaraNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of AtherosclerosisDocument27 pagesPathophysiology of AtherosclerosisAmira Paguyo QuilapioNo ratings yet
- Myocardial InfarctionDocument18 pagesMyocardial InfarctionMarc Lorenz DucusinNo ratings yet
- Ischemic Heart DiseaseDocument47 pagesIschemic Heart DiseaseAbood SamoudiNo ratings yet
- Myocardial InfarctionDocument25 pagesMyocardial Infarctionfam111222No ratings yet
- Learning Objectives in Cardiovascular DiseaseDocument13 pagesLearning Objectives in Cardiovascular DiseaseZul Azim AnuarNo ratings yet
- Stroke 15.1Document27 pagesStroke 15.1Salman KhanNo ratings yet
- Acute StrokeDocument13 pagesAcute StrokeJoel CanenciaNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Disease (CVD) Is Any Disease Involving The: TypesDocument9 pagesCardiovascular Disease (CVD) Is Any Disease Involving The: TypesDavidNo ratings yet
- Toate Bolile CardiovasculareDocument6 pagesToate Bolile CardiovasculareAnca CopreanNo ratings yet
- Ischaemic Heart Disease (IHD) Is Defined As Acute or Chronic Form of Cardiac Disability Arising FromDocument5 pagesIschaemic Heart Disease (IHD) Is Defined As Acute or Chronic Form of Cardiac Disability Arising FromIsak ShatikaNo ratings yet
- Hypertension: Synthesis of The Disease For Coronary Artery Disease (Book-Based) b.1. Definition of The DiseaseDocument9 pagesHypertension: Synthesis of The Disease For Coronary Artery Disease (Book-Based) b.1. Definition of The DiseaseAnnNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument13 pagesIntroductionSiyara AntonyNo ratings yet
- Ischaemic Heart Disease: EtiopathogenesisDocument12 pagesIschaemic Heart Disease: Etiopathogenesisritika shakkarwalNo ratings yet
- Coronary Artery DisaeseDocument48 pagesCoronary Artery DisaeseAzkaZulfiqarNo ratings yet
- Assignment: ON Learning Resource MaterialDocument18 pagesAssignment: ON Learning Resource MaterialMegha lakraNo ratings yet
- Heart Guide 2022Document13 pagesHeart Guide 2022AnuNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology, Medical Management, and Acute Rehabilitation of Stroke SurvivorsDocument7 pagesPathophysiology, Medical Management, and Acute Rehabilitation of Stroke SurvivorsBemon Subico NelvinNo ratings yet
- Cerebrovascular DiseaseDocument4 pagesCerebrovascular DiseasekathyfacaNo ratings yet
- Cerebrovascular Accident ReportDocument16 pagesCerebrovascular Accident ReportAngelu Gabrielle CastroNo ratings yet
- Acute Myocardial InfarctionDocument9 pagesAcute Myocardial InfarctionZachary CohenNo ratings yet
- Heart Attack (Myocardial Infarction) : 1. DefinitionDocument4 pagesHeart Attack (Myocardial Infarction) : 1. DefinitionAbdul Muhammad ThaherNo ratings yet
- Atherosclerosis Rizki WhidanarDocument20 pagesAtherosclerosis Rizki WhidanarIdham AmiryNo ratings yet
- ArteriosclerosisDocument8 pagesArteriosclerosisRhea Liza Comendador-TjernmoenNo ratings yet
- Topic 16. AtherosclerosisDocument6 pagesTopic 16. AtherosclerosisAdeleye John AdebolaNo ratings yet
- Stroke PathophysiologyDocument6 pagesStroke PathophysiologyMichelle PetismeNo ratings yet
- Has CVDDocument2 pagesHas CVDMargaret CortinasNo ratings yet
- Activity BS 1.3Document5 pagesActivity BS 1.3Camba TracyNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Diseases: Risk FactorsDocument18 pagesCardiovascular Diseases: Risk FactorsShin QuinnNo ratings yet
- 70398398Document19 pages70398398Azeke Terence AkhatorNo ratings yet
- Stroke Pa Tho PhysiologyDocument2 pagesStroke Pa Tho PhysiologyBrandoSantosNo ratings yet
- AtherosclerosisDocument1 pageAtherosclerosisTivar VictorNo ratings yet
- Ksenija, MerokokDocument32 pagesKsenija, MerokokMUHAMMAD ILHAMNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Arteriosclerosis and AtherosclerosisDocument22 pagesPathophysiology of Arteriosclerosis and Atherosclerosisjoyrena ochondraNo ratings yet
- ArtherosclerosisDocument3 pagesArtherosclerosisNewtonNo ratings yet
- Patho 2Document131 pagesPatho 2ademabdellaaleNo ratings yet
- PPISMP SEM 2 BIOLOGY Cardiovascular DiseaseDocument5 pagesPPISMP SEM 2 BIOLOGY Cardiovascular DiseaseMohamad Syafie Bin SamsirNo ratings yet
- 1 Henry McCraeDocument4 pages1 Henry McCraeAbdullah RajaNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular DiseaseDocument27 pagesCardiovascular DiseaseNuko NuraeniNo ratings yet
- Laporan Case Conference CardioDocument42 pagesLaporan Case Conference CardioDoni SetiyawanNo ratings yet
- PBL 2 - StrokeDocument14 pagesPBL 2 - StrokeKong Pei IngNo ratings yet
- Mortality RateDocument5 pagesMortality RateAlquino Heart RubioNo ratings yet
- Reverse and Prevent Heart Disease: Natural Ways to Stop and Prevent Heart Disease, Using Plant-Based Oil-Free Diets (Cure Congestive Heart Failure)From EverandReverse and Prevent Heart Disease: Natural Ways to Stop and Prevent Heart Disease, Using Plant-Based Oil-Free Diets (Cure Congestive Heart Failure)No ratings yet
- EXTRACTION PROCEDURE CloveDocument1 pageEXTRACTION PROCEDURE CloveDeepakNo ratings yet
- UGC (Min. Std. & Proc For Ph.D. Degree) Reg 2022Document6 pagesUGC (Min. Std. & Proc For Ph.D. Degree) Reg 2022DeepakNo ratings yet
- Practice SchoolDocument11 pagesPractice SchoolDeepakNo ratings yet
- Protein BindingDocument22 pagesProtein BindingDeepakNo ratings yet
- Importance, Application, Factors Affecting Dissolution Rate, Theories of Dissolution & Official Dissolution TestsDocument69 pagesImportance, Application, Factors Affecting Dissolution Rate, Theories of Dissolution & Official Dissolution TestsDeepakNo ratings yet
- Practice School Syllabus Pharmaceutics ModuleDocument2 pagesPractice School Syllabus Pharmaceutics ModuleDeepak0% (1)
- Deore Prashant Ashok Department of Pharmaceutics: Presented byDocument18 pagesDeore Prashant Ashok Department of Pharmaceutics: Presented byDeepakNo ratings yet
- Historyof PharmacyDocument32 pagesHistoryof PharmacyDeepakNo ratings yet
- pp-2 QuestionsDocument11 pagespp-2 QuestionsDeepakNo ratings yet
- Metric and Imperial Measures: Most Common Units of Measurement Length WeightDocument2 pagesMetric and Imperial Measures: Most Common Units of Measurement Length WeightDeepakNo ratings yet
- Different Approaches Toward The Enhancement of Drug Solubility: A ReviewDocument12 pagesDifferent Approaches Toward The Enhancement of Drug Solubility: A ReviewDeepakNo ratings yet
- Dosage Form UspDocument30 pagesDosage Form UspDeepakNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Ophthalmic FormulationDocument15 pagesEvaluation of Ophthalmic FormulationDeepak100% (1)
- Blow Seal ParentralDocument12 pagesBlow Seal ParentralDeepakNo ratings yet
- SOLUTIONDocument41 pagesSOLUTIONDeepakNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of ParenteralsDocument31 pagesEvaluation of ParenteralsDeepak50% (2)
- Pharmaceutical FormulationDocument60 pagesPharmaceutical FormulationDeepakNo ratings yet