0% found this document useful (0 votes)
806 views20 pagesProblem With Commutation
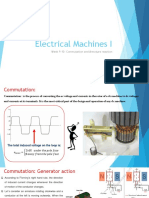
The document discusses problems with commutation in DC machines caused by armature reaction. It first provides background on DC machines and their basic structure. It then explains that commutation is the process of reversing current in conductors as they move between poles. Armature reaction occurs when the magnetic field set up by armature current affects the distribution of the main field flux, shifting the magnetic neutral plane and weakening the flux. This can cause problems during commutation like arcing and sparking as the brushes short out conductors with voltage across them. The flux weakening also reduces generator output voltage or increases motor speed.
Uploaded by
Rico Blanca AbitoCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
806 views20 pagesProblem With Commutation
The document discusses problems with commutation in DC machines caused by armature reaction. It first provides background on DC machines and their basic structure. It then explains that commutation is the process of reversing current in conductors as they move between poles. Armature reaction occurs when the magnetic field set up by armature current affects the distribution of the main field flux, shifting the magnetic neutral plane and weakening the flux. This can cause problems during commutation like arcing and sparking as the brushes short out conductors with voltage across them. The flux weakening also reduces generator output voltage or increases motor speed.
Uploaded by
Rico Blanca AbitoCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
- Introduction to DC Machines: Brief introduction to the topic of DC machines and their significance in energy conversion.
- DC Machines Overview: Defines what a DC machine is and introduces its role as an electro-mechanical energy conversion device.
- Types of DC Machines: Lists and briefly describes the two main types of DC machines: the DC generator and the DC motor.
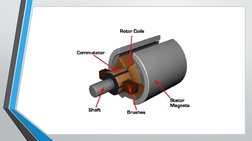
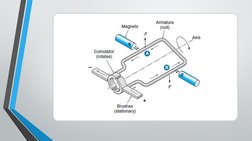
- Basic Structure of DC Machines: Details the basic components and structure of DC machines, including the stator, rotor, commutator, brushes, and shaft.
- Commutation in DC Machines: Explains the commutation process in DC machines and how current is reversed in conductors.
- Problems with Commutation: Introduces potential issues in the commutation process faced by DC machines.
- Armature Reaction: Describes the effects and consequences of armature reaction on magnetic flux and the overall operation of a DC machine.