Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ch.2 Agents of AI
Uploaded by
Official Aminho0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views20 pagesThis document defines and compares different classes of intelligent agents:
1. Simple reflex agents act based only on current percepts without considering history. Model-based reflex agents maintain an internal model of the world to act in partially observable environments.
2. Goal-based agents expand on model-based agents by using goal information to choose actions that achieve desirable states.
3. Utility-based agents further generalize by associating a "utility" or happiness measure with states to select actions with maximum expected utility.
4. Learning agents can adapt through experience to operate in unknown environments, learning to become more competent over time. They have components for learning, receiving feedback, selecting actions, and generating new experiences.
Original Description:
Original Title
Ch.2 Agents Of AI.pptx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document defines and compares different classes of intelligent agents:
1. Simple reflex agents act based only on current percepts without considering history. Model-based reflex agents maintain an internal model of the world to act in partially observable environments.
2. Goal-based agents expand on model-based agents by using goal information to choose actions that achieve desirable states.
3. Utility-based agents further generalize by associating a "utility" or happiness measure with states to select actions with maximum expected utility.
4. Learning agents can adapt through experience to operate in unknown environments, learning to become more competent over time. They have components for learning, receiving feedback, selecting actions, and generating new experiences.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views20 pagesCh.2 Agents of AI
Uploaded by
Official AminhoThis document defines and compares different classes of intelligent agents:
1. Simple reflex agents act based only on current percepts without considering history. Model-based reflex agents maintain an internal model of the world to act in partially observable environments.
2. Goal-based agents expand on model-based agents by using goal information to choose actions that achieve desirable states.
3. Utility-based agents further generalize by associating a "utility" or happiness measure with states to select actions with maximum expected utility.
4. Learning agents can adapt through experience to operate in unknown environments, learning to become more competent over time. They have components for learning, receiving feedback, selecting actions, and generating new experiences.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 20
Artificial Intelligent.
AI
Ch.2: Agents of Artificial intelligent
Or
intelligent Agents
PART 1
Lecturer: Omar Ibrahim
Definition of AI Agents
• An intelligent agent (IA) refers to an autonomous
entity which acts, directing its activity towards
achieving goals (i.e. it is an agent), upon an
environment using observation through sensors
and consequent actuators (i.e. it is intelligent)
• Intelligent agents(IA) may also learn or use
knowledge to achieve their goals
• A reflex machine, such as a thermostat, is
considered an example of an intelligent agent
CONT..
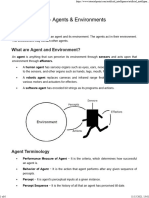
• An agent is anything that can perceive its environment
through sensors and acts upon that environment through
effectors.
• A human agent has sensory organs such as eyes, ears,
nose, tongue and skin parallel to the sensors, and other
organs such as hands, legs, mouth, for effectors.
• A robotic agent replaces cameras and infrared range
finders for the sensors, and various motors and actuators
for effectors.
• A software agent has encoded bit strings as its programs
and actions
Cont..
• The part of the agent that used to identify or
to know the perception is called sensors.
• The part of the agent taking an action is called
an Actuators.
Classes of Agents
• Russell & Norvig (2003) group agents into five
classes based on their degree of perceived
intelligence and capability:
1. Simple reflex agents
2. Model-based reflex agents
3. Goal-based agents
4. Utility-based agents
5. Learning agents
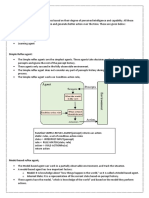
Simple reflex agents
• Simple reflex agents act only on the basis of
the current percept, ignoring the rest of the
percept history.
• The agent function is based on the condition-
action rule: "if condition, then action.
• This agent function only succeeds when the
environment is fully observable
Cont..
CONT…
• Problems with Simple reflex agents are:
Very limited intelligence.
No knowledge of non-perceptual parts of
state.
Usually too big to generate and store.
If there occurs any change in the environment,
then the collection of rules need to be
updated
2. Model-based reflex agents
• A model-based agent can handle partially
observable environments.
• Its current state is stored inside the agent
maintaining some kind of structure which
describes the part of the world which cannot be
seen.
• This knowledge about "how the world works" is
called a model of the world, hence the name
"model-based agent”
Cont..
• An agent may also use models to describe and
predict the behaviors of other agents in the
environment
• Updating the state requires information about
How the world evolves in-dependently from
the agent, and
How the agent actions affects the world.
3. Goal-based agents
• Goal-based agents further expand on the capabilities
of the model-based agents, by using "goal"
information
• Goal information describes situations that are
desirable. This allows the agent a way to choose
among multiple possibilities, selecting the one which
reaches a goal state.
• Search and planning are the subfields of artificial
intelligence devoted to finding action sequences that
achieve the agent's goals.
4. Utility-based agents
• A more general performance measure should allow
a comparison of different world states according to
exactly how happy they would make the agent. The
term utility can be used to describe how "happy"
the agent is.
• A rational utility-based agent chooses the action
that maximizes the expected utility of the action
outcomes - that is, what the agent expects to derive,
on average, given the probabilities and utilities of
each outcome
5. Learning agents
• Learning has the advantage that it allows the
agents to initially operate in unknown
environments and to become more competent
than its initial knowledge alone might allow
• A learning agent in AI is the type of agent which
can learn from its past experiences or it has
learning capabilities. It starts to act with basic
knowledge and then able to act and adapt
automatically through learning
Cont…
• A learning agent has mainly four conceptual components, which
are:
1. Learning element :It is responsible for making improvements by
learning from the environment
2. Critic: Learning element takes feedback from critic which
describes how well the agent is doing with respect to a fixed
performance standard.
3. Performance element: It is responsible for selecting external
action or chooses what action to take.
4. Problem Generator: This component is responsible for suggesting
actions that will lead to new and informative experiences
THE END
THANK YOU
You might also like
- Week 2Document5 pagesWeek 2susanabdullahi1No ratings yet
- CS302 Unit1-IDocument21 pagesCS302 Unit1-IPrakhar GargNo ratings yet
- Agents in Artificial IntelligenceDocument8 pagesAgents in Artificial Intelligenceolastig technologiesNo ratings yet
- Types of AgentsDocument2 pagesTypes of AgentsJosiah MwashitaNo ratings yet
- Study Material3Document6 pagesStudy Material3Praju ThoratNo ratings yet
- Artificial Intelligence: Unit 1-IDocument24 pagesArtificial Intelligence: Unit 1-IANKUSH NEGINo ratings yet
- AI Unit 1Document50 pagesAI Unit 1Lavanya H MNo ratings yet
- Types of Agents: Name: Sanjana Totla Rollno: 121321033027Document8 pagesTypes of Agents: Name: Sanjana Totla Rollno: 121321033027Sanjana Karthik NaiduNo ratings yet
- Types of AI Agents Artificial IntelligenceDocument4 pagesTypes of AI Agents Artificial IntelligenceΖολ αιβ100% (1)
- Types of AI AgentsDocument11 pagesTypes of AI AgentsashutoshmahisharmaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document20 pagesLecture 2SHARDUL KULKARNINo ratings yet
- AI Agents & EnvironmentsDocument18 pagesAI Agents & EnvironmentsEric LaciaNo ratings yet
- Artificial IntelligenceDocument29 pagesArtificial IntelligenceAasthaNo ratings yet
- AI AGENTS,EnVIRONMENTS by Pardon Toda , Tinotenda Maposa and Grace KuchekenyaDocument16 pagesAI AGENTS,EnVIRONMENTS by Pardon Toda , Tinotenda Maposa and Grace KuchekenyaTapiwa BaseraNo ratings yet
- Understanding Intelligent AgentsDocument28 pagesUnderstanding Intelligent Agentspacho herreraNo ratings yet
- Prof. Radha GuhaDocument27 pagesProf. Radha GuhaRadha GuhaNo ratings yet
- CS 611 SlidesDocument27 pagesCS 611 SlidesAhmad AbubakarNo ratings yet
- Agents & Environment in Ai: Submitted byDocument14 pagesAgents & Environment in Ai: Submitted byCLASS WORKNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document11 pagesLecture 1minaksheeNo ratings yet
- Chap2 AIDocument46 pagesChap2 AIshiferawyosef12No ratings yet
- Types of AI AgentsDocument3 pagesTypes of AI AgentsShoumiq DeyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Inteligent AgentDocument31 pagesChapter 2 - Inteligent AgentDawit AndargachewNo ratings yet
- Different Types of Agents and Their ExamplesDocument4 pagesDifferent Types of Agents and Their ExamplesKhim AbualasNo ratings yet
- Agents in Artificial IntelligenceDocument7 pagesAgents in Artificial IntelligenceJAYANTA GHOSHNo ratings yet
- AI Lec2-1Document24 pagesAI Lec2-1Omar SaberNo ratings yet
- By DR Narayana Swamy Ramaiah Professor, Dept of CSE SCSE, FET, JAIN Deemed To Be UniversityDocument27 pagesBy DR Narayana Swamy Ramaiah Professor, Dept of CSE SCSE, FET, JAIN Deemed To Be UniversityDr Narayana Swamy RamaiahNo ratings yet
- Intelligent Agents and Types of Agents: Artificial IntelligenceDocument22 pagesIntelligent Agents and Types of Agents: Artificial IntelligenceFind the hero in you100% (1)
- Types of Agents: What Are Agent and Environment?Document6 pagesTypes of Agents: What Are Agent and Environment?Nazmul SharifNo ratings yet
- The Structure and Types of Intelligent AgentsDocument6 pagesThe Structure and Types of Intelligent AgentsSIDDHANT JAIN 20SCSE1010186No ratings yet
- Chapter Two Intelligent Agent: ObjectiveDocument46 pagesChapter Two Intelligent Agent: ObjectiveTefera KunbushuNo ratings yet
- Agents in AI - Types and PropertiesDocument14 pagesAgents in AI - Types and PropertiesM. Talha NadeemNo ratings yet
- 2.agent Search and Game PlayingDocument35 pages2.agent Search and Game PlayingRandeep PoudelNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document21 pagesLecture 3Asif NawazNo ratings yet
- Intelligent Agent: A Variety of DefinitionsDocument6 pagesIntelligent Agent: A Variety of DefinitionsNaveen KumarNo ratings yet
- Types of AI AgentsDocument6 pagesTypes of AI AgentsSwapnil DargeNo ratings yet
- AI-Lec02bySohaibCH - UpdatedDocument21 pagesAI-Lec02bySohaibCH - UpdatedZainab LiaquatNo ratings yet
- Lecture -3 - 6Document23 pagesLecture -3 - 6spandansahil15No ratings yet
- AI - Agents & EnvironmentsDocument6 pagesAI - Agents & EnvironmentsRainrock BrillerNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Intelligent AgentDocument38 pagesChapter 2 - Intelligent AgentmuhammedNo ratings yet
- Ai 2Document35 pagesAi 2bandookNo ratings yet
- Agents in Artificial IntelligenceDocument20 pagesAgents in Artificial Intelligence517 Anjali KushvahaNo ratings yet
- m2 AgentsDocument60 pagesm2 AgentsNimraNo ratings yet
- AICH2Document38 pagesAICH2Aliyu AhmedNo ratings yet
- artificial intelligence 4Document27 pagesartificial intelligence 4Syed SamiNo ratings yet
- Ai 4Document24 pagesAi 4Kashif MehmoodNo ratings yet
- UNIT - I Agents - AIDocument63 pagesUNIT - I Agents - AIby708931No ratings yet
- Fundamentals of AI: Intelligent AgentsDocument19 pagesFundamentals of AI: Intelligent AgentsjollyggNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document29 pagesChapter 2oromafi tubeNo ratings yet
- Intelligent AgentsDocument36 pagesIntelligent AgentsSourav GangulyNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document23 pagesLecture 3SOUMYODEEP NAYAK 22BCE10547No ratings yet
- AI Chapter 2 AgentsDocument28 pagesAI Chapter 2 AgentsSheena KhannaNo ratings yet
- Agents Artificial IntelligenceDocument32 pagesAgents Artificial IntelligencemohitkgecNo ratings yet
- Wollo University KIOT Department of Software Engineering Agent Based Programming Assignment 1Document6 pagesWollo University KIOT Department of Software Engineering Agent Based Programming Assignment 1Software EngineerNo ratings yet
- CSE440_Lect_4_Agent typeDocument32 pagesCSE440_Lect_4_Agent typeSumaiya SadiaNo ratings yet
- Ai 2Document26 pagesAi 2starpapion369No ratings yet
- Unit - V: AgentsDocument44 pagesUnit - V: AgentsBhargavNo ratings yet
- Artificial Intelligence: By: Dr. Ali ArshadDocument45 pagesArtificial Intelligence: By: Dr. Ali ArshadAsma PervaizNo ratings yet
- Ai-Unit 1Document88 pagesAi-Unit 1maharajan241jfNo ratings yet
- Agents: Agent Environment Sensors ActuatorsDocument20 pagesAgents: Agent Environment Sensors ActuatorsAnuj MehtaNo ratings yet
- Blood Bank Management System PDFDocument112 pagesBlood Bank Management System PDFAnonymous DRH4iUkNo ratings yet
- ODRA Beauty Salon Management SystemDocument75 pagesODRA Beauty Salon Management SystemOfficial AminhoNo ratings yet
- Web Application Security: Abdirahman Mohamed HassanDocument30 pagesWeb Application Security: Abdirahman Mohamed HassanOfficial AminhoNo ratings yet
- Chapter One Network SecurityDocument40 pagesChapter One Network SecurityOfficial AminhoNo ratings yet
- GOLLIS University Faculty of ICT Course: Artificial Intelligent AIDocument16 pagesGOLLIS University Faculty of ICT Course: Artificial Intelligent AIOfficial AminhoNo ratings yet
- Senior ReportFINALDocument43 pagesSenior ReportFINALAnonymous eRhyuHDcDNo ratings yet
- Research Smart Shaming Chapter 1Document4 pagesResearch Smart Shaming Chapter 1MelodyNo ratings yet
- New wave theories of cognition criticismDocument40 pagesNew wave theories of cognition criticismJCNo ratings yet
- About FIRST LEGO LeagueDocument1 pageAbout FIRST LEGO LeaguelupintealNo ratings yet
- Artificial Intelligence HandbookDocument17 pagesArtificial Intelligence HandbookZaki Khan0% (1)
- Implementation of Character Education at Don Bosco Frater High School ManadoDocument11 pagesImplementation of Character Education at Don Bosco Frater High School ManadoPaulus Robert TuerahNo ratings yet
- Experiencing The Lifespan 5th Edition Belsky Test BankDocument29 pagesExperiencing The Lifespan 5th Edition Belsky Test Bankjezebelbasilm1vfe1100% (26)
- TQ For Personal DevelopmentDocument2 pagesTQ For Personal DevelopmentKen Harold CelestialNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Research Methods in Criminal Justice and Criminology Callie Marie Rennison Timothy C HartDocument24 pagesTest Bank For Research Methods in Criminal Justice and Criminology Callie Marie Rennison Timothy C HartKimColemanoayg100% (34)
- Module 3.1 Inductive and Deductive ReasoningDocument4 pagesModule 3.1 Inductive and Deductive Reasoning22-02923No ratings yet
- Assessing The Bodily-Kinesthetic Intelligence of PDocument13 pagesAssessing The Bodily-Kinesthetic Intelligence of POnderNo ratings yet
- On Memory and Reminiscence AristótelesDocument7 pagesOn Memory and Reminiscence AristótelesPatymagazoniNo ratings yet
- BBS-JIFMIM Special Issue Conference on FinTech DevelopmentsDocument37 pagesBBS-JIFMIM Special Issue Conference on FinTech DevelopmentsDr. Gaurav KumarNo ratings yet
- Results and Interpretation (NVTI)Document2 pagesResults and Interpretation (NVTI)Shruti ShrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Intelligence and Second Language LearningDocument10 pagesIntelligence and Second Language LearningVirginia Alejandra GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1,2Document56 pagesChapter 1,2Le Nguyen Kim Hoang (K17 CT)No ratings yet
- 1.approaches of TeachingDocument47 pages1.approaches of Teachingsindhu mol100% (1)
- Use of A.I in Aerospace & Defence SectorDocument6 pagesUse of A.I in Aerospace & Defence Sectormr unbelivable perfectNo ratings yet
- Iq TestDocument3 pagesIq TestMichelle Perez LucasNo ratings yet
- A.I Perspective Google CaseDocument10 pagesA.I Perspective Google CaseTANISTHA MANGARAJNo ratings yet
- Academic Reading Practice Test 57 PDFDocument12 pagesAcademic Reading Practice Test 57 PDFbinh minh maiNo ratings yet
- Tictactoe AI DocumentationDocument16 pagesTictactoe AI DocumentationKou CatarajaNo ratings yet
- Personal Development: Quarter 1 - Module 6Document24 pagesPersonal Development: Quarter 1 - Module 6Sherry-Ann TulauanNo ratings yet
- IDSSDocument79 pagesIDSSFahad FirdousNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Introduction To ResearchDocument31 pagesUnit 1 - Introduction To Researchvalentinesibs9No ratings yet
- Heredity CDPDocument7 pagesHeredity CDPRituraj ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Module-6-Ok - Docx JAN 13Document4 pagesModule-6-Ok - Docx JAN 13Stefanie Rose DomingoNo ratings yet
- Week 6 Day 1Document18 pagesWeek 6 Day 1VILZENDRICK TORRESNo ratings yet
- CITS-RPL Principles of Teaching AssignmentDocument5 pagesCITS-RPL Principles of Teaching Assignmentvineet panwarNo ratings yet
- Emotional Intelligence - Staff SenateDocument44 pagesEmotional Intelligence - Staff SenateSyrgak SamudinovNo ratings yet
- An Ideal CriticDocument3 pagesAn Ideal CriticSaleem Raza100% (4)
- LIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionFrom EverandLIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (402)
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeFrom EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeNo ratings yet
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityFrom EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (16)
- Summary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedFrom EverandSummary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (78)
- Summary of The 48 Laws of Power: by Robert GreeneFrom EverandSummary of The 48 Laws of Power: by Robert GreeneRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (233)
- Raising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsFrom EverandRaising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Dark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.From EverandDark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (110)
- By the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsFrom EverandBy the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsNo ratings yet
- The Happiness Trap: How to Stop Struggling and Start LivingFrom EverandThe Happiness Trap: How to Stop Struggling and Start LivingRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsFrom EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- The Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaFrom EverandThe Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Codependent No More: How to Stop Controlling Others and Start Caring for YourselfFrom EverandCodependent No More: How to Stop Controlling Others and Start Caring for YourselfRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (87)
- Cult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryFrom EverandCult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (44)
- Mindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessFrom EverandMindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (328)
- Summary: Limitless: Upgrade Your Brain, Learn Anything Faster, and Unlock Your Exceptional Life By Jim Kwik: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: Limitless: Upgrade Your Brain, Learn Anything Faster, and Unlock Your Exceptional Life By Jim Kwik: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (8)
- CBT Strategies: CBT Strategies for Overcoming Panic, Fear, Depression, Anxiety, Worry, and AngerFrom EverandCBT Strategies: CBT Strategies for Overcoming Panic, Fear, Depression, Anxiety, Worry, and AngerNo ratings yet
- Daniel Kahneman's "Thinking Fast and Slow": A Macat AnalysisFrom EverandDaniel Kahneman's "Thinking Fast and Slow": A Macat AnalysisRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (130)
- Rewire Your Anxious Brain: How to Use the Neuroscience of Fear to End Anxiety, Panic, and WorryFrom EverandRewire Your Anxious Brain: How to Use the Neuroscience of Fear to End Anxiety, Panic, and WorryRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (157)
- Inmersion Into The Shadown Effective Method Of Dark Psychology: How To Use The Best Persuasion Techniques To Achieve Your Best Goals And How To Protect Yourself From Being ManipulatedFrom EverandInmersion Into The Shadown Effective Method Of Dark Psychology: How To Use The Best Persuasion Techniques To Achieve Your Best Goals And How To Protect Yourself From Being ManipulatedRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Summary: It Didn't Start with You: How Inherited Family Trauma Shapes Who We Are and How to End the Cycle By Mark Wolynn: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: It Didn't Start with You: How Inherited Family Trauma Shapes Who We Are and How to End the Cycle By Mark Wolynn: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- The Garden Within: Where the War with Your Emotions Ends and Your Most Powerful Life BeginsFrom EverandThe Garden Within: Where the War with Your Emotions Ends and Your Most Powerful Life BeginsNo ratings yet
- 12 Rules for Life by Jordan B. Peterson - Book Summary: An Antidote to ChaosFrom Everand12 Rules for Life by Jordan B. Peterson - Book Summary: An Antidote to ChaosRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (207)