Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Duct Propagation or Super Refraction
Uploaded by
niji mathews0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views12 pagesOriginal Title
duct_fading_diversity
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views12 pagesDuct Propagation or Super Refraction
Uploaded by
niji mathewsCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 12
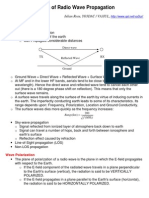
Duct propagation or super refraction
Using this method of propagtion , long distance
communication with relatively lesser attenuation is
possible in the frequency range of 300MHz to
30,000MHz .ie VHF and UHF bands.
Normally the temperature of the atmosphere falls
at the rate of 6.5oC/ km.
A normal or standard atmosphere is one where the
dielectric cont.is assumed to decrease uniformly with
height to a value of unity at a height where air density
becomes zero.
Near the earth surface, refractive index is greater
than unity.
Duct propagation or super refraction
A temperature inversion layer is formed
where the temp. increases with height rather
usual decrease of temperature at the rate of
6.6oC/km in the standard atmosphere.
It happen within 50meters of the
troposphere and leads to a rapid decrease in
refractive index with height.
This layer act as a duct or leaky waveguide
which leads the EM waves between its walls.
The high frequency waves
which enter into this duct are
continuously refracted in the
duct and reflected by the
ground.
So they propagate around
the curvature for beyond the
line of sight, even upto a
distance of 1000km.
This special refraction of EM
waves is called super refraction
and the process is called duct
propagation
The refractive index ‘n’ at a height h must be
replaced by a modified refractive index given
by
•Duct is formed only when the value of gradient
dM/dh is –ve.ie M decrease with increase in
height.
• Only waves that are travelling at small angles
w.r.t. the horizontal are trapped b/w the upper
and lower walls of the duct.
•The favourable condition for duct propagation is
that the transmitter is inside the duct
Fading
Fading is classified in terms of the duration of the
variation in signal strength. They are:
1. Rapid fluctuations:- due to multi-path interference
and they occur for a few seconds.
2. Short-term fluctuations:- due to variation in the
characteristics of the propagating medium and
they occur for a few hours.
3. Long Term fluctuations:- due to seasonal variations
in the propagation medium and they occur for a
few days
Types of Fading
Diversity Techniques
Some of the fading effect is minimizedby using AGC, but it
becomes helpless when the signal fades much below the noise
level. Such cases use diversity techniques.
You might also like
- Basics of Radio Wave PropagationDocument9 pagesBasics of Radio Wave PropagationwakyzaiNo ratings yet
- 062 - Radio Navigation - AnswersDocument86 pages062 - Radio Navigation - AnswersEASA ATPL Question Bank100% (1)
- Radio-Wave Propagation: Electromagnetic Waves (TEM) - I.EDocument78 pagesRadio-Wave Propagation: Electromagnetic Waves (TEM) - I.EGowndaManiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 01 - Basic Radio TheoryDocument28 pagesChapter 01 - Basic Radio TheoryRezwan Ahmed KhanNo ratings yet
- Space Communication: This Chapter IncludesDocument17 pagesSpace Communication: This Chapter IncludesKashyap PatelNo ratings yet
- Terrestrial PropagationDocument30 pagesTerrestrial PropagationKrishna DuttNo ratings yet
- Propagation of WavesDocument38 pagesPropagation of WavesMarhmello PadriqueNo ratings yet
- AWP Unit5Document31 pagesAWP Unit5GUNREDDY VISHNU VARDHAN REDDY100% (1)
- Mobile Radio PropagationDocument42 pagesMobile Radio PropagationShakeel HashmiNo ratings yet
- 6 Microwave Comm System PDFDocument42 pages6 Microwave Comm System PDFJeffreyBeridaNo ratings yet
- Duct Propagation Seminar 1636693816259Document17 pagesDuct Propagation Seminar 1636693816259Karunya Vardana SNo ratings yet
- Unit 2-1Document31 pagesUnit 2-1zaibahadiya19No ratings yet
- Space Wave Propagation: 16011A0458 Tejasri Kurapati JntuhDocument33 pagesSpace Wave Propagation: 16011A0458 Tejasri Kurapati JntuhKurapati tejuNo ratings yet
- 22 5 21Document26 pages22 5 21Charuruba NNo ratings yet
- Radio Waves and PropagationDocument31 pagesRadio Waves and Propagationzaibahadiya19No ratings yet
- Wireless Networks: Introduction To Wireless CommunicationDocument33 pagesWireless Networks: Introduction To Wireless CommunicationAshish PadwalNo ratings yet
- Microwave Radio Propagation: Technical Center Group NEC IndiaDocument17 pagesMicrowave Radio Propagation: Technical Center Group NEC IndiaSrikanth MahadevuniNo ratings yet
- Radio PropagationDocument12 pagesRadio PropagationAzzam AyoubNo ratings yet
- W M N (ISN 3110) : Ireless and Obile EtworksDocument31 pagesW M N (ISN 3110) : Ireless and Obile EtworksDJEFOUO FOUODJI ANGE MAGLOIRENo ratings yet
- Ice511 Term Paper ?Document11 pagesIce511 Term Paper ?Mirabel Chiebuniem ChukwumaNo ratings yet
- Lecture WMC 05a 31102022 090529amDocument19 pagesLecture WMC 05a 31102022 090529amFaizan AhmadNo ratings yet
- Wireless NetworkDocument35 pagesWireless NetworkMuhammad KhairiNo ratings yet
- Analog Communication Assignment: Submitted byDocument14 pagesAnalog Communication Assignment: Submitted byBT18ECE046 CHINTASAMSONHRUDAYNo ratings yet
- Term Paper TopicsDocument12 pagesTerm Paper TopicsAnuj RautelaNo ratings yet
- Radio TheoryDocument4 pagesRadio TheoryBing JuanizaNo ratings yet
- Wireless Channel CharacteristicsDocument4 pagesWireless Channel Characteristicsbenny_1811No ratings yet
- Physics Project Final1Document15 pagesPhysics Project Final1sohamNo ratings yet
- Tropospheric Waves and Its Applications: Gunjan Verma (U11Ec143) Kuldeep Singh (U11Ec145)Document15 pagesTropospheric Waves and Its Applications: Gunjan Verma (U11Ec143) Kuldeep Singh (U11Ec145)u11ee079No ratings yet
- Unit II AWCDocument99 pagesUnit II AWCJenath SathikbashaNo ratings yet
- Communication by Safe HandsDocument48 pagesCommunication by Safe HandsnitinNo ratings yet
- Radio Wave PropagationDocument11 pagesRadio Wave PropagationEmin KayaNo ratings yet
- AP Unit8Document15 pagesAP Unit8Abhay Shankar BharadwajNo ratings yet
- Mechanism For DiffractionDocument13 pagesMechanism For DiffractionraghvendrmNo ratings yet
- Unit - III Part-2Document23 pagesUnit - III Part-2Mohammed WaqarNo ratings yet
- Mobile Radio PropagationDocument14 pagesMobile Radio Propagationmahfuz.jkkniu13No ratings yet
- MW Basic Knowledge: - MicrowaveDocument21 pagesMW Basic Knowledge: - MicrowaverubbbitsNo ratings yet
- WaveguidesDocument40 pagesWaveguidesChristian Razel CamposNo ratings yet
- Awp U-6Document48 pagesAwp U-6Gajula Venkat SaiNo ratings yet
- Wireless TransmissionDocument22 pagesWireless TransmissionAkpevwe IsireNo ratings yet
- Multipath and FadingDocument6 pagesMultipath and FadingmbcgoudarNo ratings yet
- Skywaves: Skywaves Travel Towards The IonosphereDocument2 pagesSkywaves: Skywaves Travel Towards The IonosphereVS KRISHNA KUMARNo ratings yet
- 8th Sem Notes-1Document62 pages8th Sem Notes-1KakjajaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document34 pagesChapter 4Markos MathewosNo ratings yet
- Unit-IV: Radiation & Propagation of WaveDocument30 pagesUnit-IV: Radiation & Propagation of WaveAK 1No ratings yet
- Transferred Electron DevicesDocument42 pagesTransferred Electron DevicesSubrahmanyam GrandhiNo ratings yet
- Micowave IntroductionDocument21 pagesMicowave Introductionniji mathewsNo ratings yet
- QuizDocument2 pagesQuizZUHAD MAHMOODNo ratings yet
- Slow &fast Fading: Slow Fading Arises When The Coherence Time ofDocument19 pagesSlow &fast Fading: Slow Fading Arises When The Coherence Time ofallabakasNo ratings yet
- Radio - Wave PropagationDocument7 pagesRadio - Wave PropagationZhen PatricioNo ratings yet
- Physics - Characteristics of WavesDocument3 pagesPhysics - Characteristics of WavesMegan TaylorNo ratings yet
- A Presentation On Fading in Wireless CommunicationsDocument6 pagesA Presentation On Fading in Wireless CommunicationsLoverboy6556100% (4)
- 2.EC4012D Fading DiversityDocument23 pages2.EC4012D Fading DiversityJHANSYHARSHITHA VANKAYALAPATINo ratings yet
- MW FundamentalsDocument22 pagesMW FundamentalsPankaj Choudhary100% (1)
- OpticalDocument90 pagesOpticalsachin50% (4)
- Space Wave PropagationDocument21 pagesSpace Wave PropagationAldawi SatNo ratings yet
- Est 1Document5 pagesEst 1Paul Cedrick LlenaNo ratings yet
- TLA 2.1 - Understanding The Differences Between Three Propagation ModesDocument7 pagesTLA 2.1 - Understanding The Differences Between Three Propagation ModesSam PunoNo ratings yet
- AWP Unit6Document50 pagesAWP Unit6GUNREDDY VISHNU VARDHAN REDDYNo ratings yet
- Gunn DiodeDocument44 pagesGunn Diodeniji mathewsNo ratings yet
- Space Wave PropagationDocument10 pagesSpace Wave Propagationniji mathewsNo ratings yet
- Wave Propagation: - Propagation of Waves From One Point To Another PointDocument7 pagesWave Propagation: - Propagation of Waves From One Point To Another Pointniji mathewsNo ratings yet
- 3 Without Audio - Ionospheric Wave Propagation ppt31Document27 pages3 Without Audio - Ionospheric Wave Propagation ppt31niji mathewsNo ratings yet
- Micowave IntroductionDocument21 pagesMicowave Introductionniji mathewsNo ratings yet