0% found this document useful (0 votes)
164 views16 pagesEffective FMEA for Product Safety
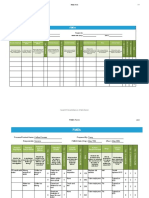
Failure Mode & Effect Analysis (FMEA) is a process that identifies potential failures in a design, manufacturing or production process. It determines the effects of failures and identifies actions to address issues with high risks. An FMEA involves identifying failure modes and their causes and effects. It determines the severity, occurrence, and detection rating of each failure and calculates a Risk Priority Number. The FMEA process aims to prevent problems and reduce costs by identifying and addressing high risk failures.
Uploaded by
OwaisCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
164 views16 pagesEffective FMEA for Product Safety
Failure Mode & Effect Analysis (FMEA) is a process that identifies potential failures in a design, manufacturing or production process. It determines the effects of failures and identifies actions to address issues with high risks. An FMEA involves identifying failure modes and their causes and effects. It determines the severity, occurrence, and detection rating of each failure and calculates a Risk Priority Number. The FMEA process aims to prevent problems and reduce costs by identifying and addressing high risk failures.
Uploaded by
OwaisCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd