Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The Corporations and Internal Stakeholders
Uploaded by
Mahad Rizwan0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views16 pagesOriginal Title
the corporations and internal stakeholders.pptx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views16 pagesThe Corporations and Internal Stakeholders
Uploaded by
Mahad RizwanCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 16
The Corporation and
Internal Stakeholders
Value-Based Moral Dimensions of
Leadership. Strategy, Structure, Culture,
And Self-Regulation
Copyright © 2003 by South-Western, a
1
division of Thomson Learning
Chapter Topics
1. Stakeholder management and value-based
organizational systems
2. A 10-step assessment of value-based
organizational systems and stakeholders
3. Leadership and strategy
4. Culture, structure, and systems
5. Corporate self-regulation: Challenges and
issues
Copyright © 2003 by South-Western, a
2
division of Thomson Learning
Stakeholder Management and Value-Based
Organizational Systems
• An organization’s enacted purpose, values, and mission
are central to its internal alignment and external
market effectiveness.
• The stakeholders management approach argues that
organizations succeed in market and nonmarket
environments through open dialogue and a duty to
assist stakeholders.
• The digital information technology revolution has
increased pressure on industries and corporations to
question to what extent ethical and stakeholder value-
based management principles and practices still work.
Copyright © 2003 by South-Western, a
3
division of Thomson Learning
Stakeholder Management and Value-Based
Organizational Systems
• The visionary built-to-last companies are premier
institutions, widely admired by their peers, and having
a long track record of making a significant impact on
the world around them.
• Not all organizations have the characteristics of built-
to-last companies, nor would all companies agree with
or support some of the ideologies, products, and
strategies of visionary firms.
– Phillip Morris
• The concept of creative destruction.
Copyright © 2003 by South-Western, a
4
division of Thomson Learning
Stakeholder Management and Value-Based
Organizational Systems
• Internal organizations are composed of systems
and stakeholders, regardless of the nature of
external environments.
• An interesting concept, and counterpart to the
creative destruction argument is creative
reconstruction.
– Dot-com survivors
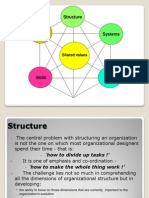
• The internal dimensions of an organization are
illustrated in the diagnostic contingency model in
Figure 4.1.
Copyright © 2003 by South-Western, a
5
division of Thomson Learning
Stakeholder Management and Value-Based
Organizational Systems
• The purpose and core ideology of organizations are
modeled by its leaders and embedded in its enterprise
strategy.
• The culture of a company is at the center spoke of the
wheel of transformation.
• The vision and strategy, people, systems, structure,
technology, and nature of work comprise the internal
operations of the organization.
• Stakeholder management theory, states that an
organization should treat its internal & external
stakeholders ethically to be effective with its
marketplace communities.
Copyright © 2003 by South-Western, a
6
division of Thomson Learning
Stakeholder Management and Value-Based
Organizational Systems
• From a stakeholder management
perspective, it is the role of an
organization’s leaders, with the support of
each professional, to ensure that the
integration and market effectiveness of a
company is based on the types of
relationship and values that embody trust,
collaboration, and a “win-win” goal for
stakeholders and stockholders.
Copyright © 2003 by South-Western, a
7
division of Thomson Learning
A 10-Step, Value-Based Stakeholder
Management Assessment
• A stakeholder management approach that is value-
based is argued to be more effective in implementing
organizational change programs that include ethics and
compliance training.
• There are many stakeholder management audits and
assessment frameworks.
• Companies can use management, human resources,
and ethics consultants to design and deliver these
types of assessments.
Copyright © 2003 by South-Western, a
8
division of Thomson Learning
A 10-Step, Value-Based Stakeholder
Management Assessment
• The 10-step assessment is as follows:
– Determine the problem or opportunity and gain top leader support
– Review and develop the vision, mission, values, and ethics code
– Use a value-based stakeholder readiness checklist
– Develop performance and responsibility measures and get feedback
– Identify stakeholder level of responsiveness and responsibility in the
corporate strategy
– Determine the organization's systems alignment
– Conduct baseline and gap analysis between current and desired
future states
– Create benchmarks
– Develop summary report with recommendations
– Review results
Copyright © 2003 by South-Western, a
9
division of Thomson Learning
Leadership And Strategy
• Leadership is a shared process, although
the values and behaviors of company
founders and CEOs often frame and set
the cultural tone for the organizations.
• A starting point for identifying a leader’s
values is the vision and mission
statement of a company.
Copyright © 2003 by South-Western, a
10
division of Thomson Learning
Leadership And Strategy
• From a stakeholder management, value-based assessment,
a CEO and other organizational leaders would demonstrate
the following skills:
– Define and lead the social and ethical, as well as the
competitive, mission of organizations
– Build and sustain relationships with stakeholders
– Talk with stakeholders, showing interest and concern for
other’s need beyond the economic and utilitarian dimensions
– Demonstrate collaborations and trust in shared decision
making and strategy sessions
– Show awareness and concerns for employees and other
stakeholders in the policies and practices of the company
Copyright © 2003 by South-Western, a
11
division of Thomson Learning
Leadership And Strategy
• An emerging body of literature and practice
describes leadership from a deeper spiritual
and value-based perspective.
• Theological and philosophical literature has
helped redefine leadership to include new
concepts and vocabulary that capture the
human and spiritual domains from which
business leaders already work.
Copyright © 2003 by South-Western, a
12
division of Thomson Learning
Leadership And Strategy
• Leadership styles:
– Manipulator
– Bureaucratic
– Professional
– Transforming
• Seven symptoms of the failure of ethical leadership:
– Ethical blindness
– Ethical muteness
– Ethical incoherence
– Ethical paralysis
– Ethical hypocrisy
– Ethical schizophrenia
– Ethical complacency
Copyright © 2003 by South-Western, a
13
division of Thomson Learning
Leadership And Strategy
• Strategy influences the goals and objectives
of the company and its stakeholders.
– Sets the overall direction of business activities
– Reflects and models activities that management
values and prioritizes
– Sets the tone and tenor of business activities
and transactions inside the organization
Copyright © 2003 by South-Western, a
14
division of Thomson Learning
Leadership And Strategy
• Corporations formulate at least four levels of
strategies:
– Enterprise
– Corporate
– Business
– Functional
• The strategy management process involves:
– Formulating goals
– Formulating strategies
– Implementing strategies
– Controlling strategies
– Evaluating strategies
– Analyzing the environment
Copyright © 2003 by South-Western, a
15
division of Thomson Learning
Culture, Structure, and Systems
• Signs of cultures in trouble or weak cultures include:
– An inward focus
– A short-term focus
– Morale and motivational problems
– Emotional outbursts
– Fragmentation and inconsistency
– Clashes among subcultures
– Ingrown subcultures
– Dominance of subculture values
– No clear values or beliefs
– Many beliefs
– Different beliefs
– Destructive or disruptive cultural heroes
– Disorganized or disruptive daily routines
Copyright © 2003 by South-Western, a
16
division of Thomson Learning
You might also like
- Chapter Four: The Corporation and Internal StakeholdersDocument18 pagesChapter Four: The Corporation and Internal Stakeholdersumar afzalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document83 pagesChapter 1jay0112varmaNo ratings yet
- Organisation Development Unit 1: Rajeev NairDocument32 pagesOrganisation Development Unit 1: Rajeev NairrajeevnairnvNo ratings yet
- Corporate Governance at UPES UniversityDocument22 pagesCorporate Governance at UPES UniversityBCom HonsNo ratings yet
- Strategy Implementation Through Organizational DesignDocument19 pagesStrategy Implementation Through Organizational Designankit274No ratings yet
- Organisational Culture Compliance and Stakeholder Management PDFDocument18 pagesOrganisational Culture Compliance and Stakeholder Management PDFjoannakamNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management (Internal Environment)Document14 pagesStrategic Management (Internal Environment)Tracy Van TangonanNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management (Internal Environment)Document14 pagesStrategic Management (Internal Environment)Tracy Van TangonanNo ratings yet
- McKinsey 7's ModelDocument21 pagesMcKinsey 7's ModeldipikarathodNo ratings yet
- Unit 3: Organization DevelopmentDocument33 pagesUnit 3: Organization DevelopmentgeenusinglaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 and 3 HRM Slides NotesDocument28 pagesChapter 2 and 3 HRM Slides NotesBlessed PanasheNo ratings yet
- Organization Development and ChangeDocument25 pagesOrganization Development and ChangeIshan AichNo ratings yet
- MHR 405: Organizational Behaviour Management: Combined Chapter NotesDocument45 pagesMHR 405: Organizational Behaviour Management: Combined Chapter NotesQamar Zaman100% (3)
- Chapter 2 Business EthicsDocument36 pagesChapter 2 Business EthicsnayabNo ratings yet
- Behavioural ImplementationDocument31 pagesBehavioural Implementationmanjusha tiruveedhulaNo ratings yet
- Corporate Governance and Ethics—An Ethical PerspectiveDocument26 pagesCorporate Governance and Ethics—An Ethical PerspectiveAkshita Chamaria LundiaNo ratings yet
- IT project management systems viewDocument8 pagesIT project management systems viewFay Fernandez-CantuangcoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 HRDocument47 pagesChapter 3 HRAnonymous s98FwgOYCNo ratings yet
- CH 03Document25 pagesCH 03Ishan AichNo ratings yet
- HRM Environmental InfluencesDocument10 pagesHRM Environmental Influencesann labraNo ratings yet
- BA115 Carpenter PPT Chapter 1Document38 pagesBA115 Carpenter PPT Chapter 1Hashani Anuttara AbeygunasekaraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Organizational Behavior TodayDocument25 pagesChapter 1 - Organizational Behavior TodayK-an SolNo ratings yet
- Planning: Strategic Management in BusinessDocument41 pagesPlanning: Strategic Management in BusinessElsen EhmedliNo ratings yet
- Unit 10Document46 pagesUnit 10kushathashreeNo ratings yet
- Attaining Behavioural ControlDocument7 pagesAttaining Behavioural ControlAarohi SinghNo ratings yet
- Organization Culture PDFDocument16 pagesOrganization Culture PDFLaxmi GurungNo ratings yet
- S1 Chap003 EngDocument14 pagesS1 Chap003 EngTeddy MaulanaNo ratings yet
- Amity School of Business Strategy ImplementationDocument36 pagesAmity School of Business Strategy ImplementationYash MittalNo ratings yet
- Strategic ManagementDocument149 pagesStrategic ManagementKALBE ABD GHANINo ratings yet
- OrganizationsDocument28 pagesOrganizationsAct VjNo ratings yet
- Unit 4Document51 pagesUnit 4Shweta SainiNo ratings yet
- HRD - OCTAPACE CultureDocument21 pagesHRD - OCTAPACE CultureRG Nawin Krishna100% (7)
- Organisational EffectivenessDocument6 pagesOrganisational EffectivenessMBA DEPT100% (1)
- Strategic ManagementDocument37 pagesStrategic ManagementKELLY KIPKOECHNo ratings yet
- Systemic Leadership Toolkit - Appendix 2Document3 pagesSystemic Leadership Toolkit - Appendix 2Triarchy PressNo ratings yet
- Summary Management & Organization: Complete Summary Management & Organization: CompleteDocument31 pagesSummary Management & Organization: Complete Summary Management & Organization: CompleteAlaa E. FaroukNo ratings yet
- SLC McKinsey7SModel LectureManuscriptDocument3 pagesSLC McKinsey7SModel LectureManuscriptMarlon P. TuizaNo ratings yet
- Strategic MGMT Mintzberg McKinsey Blue Red OceanDocument26 pagesStrategic MGMT Mintzberg McKinsey Blue Red OceanRajat ShettyNo ratings yet
- Organisational DynamicsDocument40 pagesOrganisational DynamicsUditt ChakravertyNo ratings yet
- Group Assignment For OBDocument30 pagesGroup Assignment For OBluldavidyianNo ratings yet
- OBDocument228 pagesOBetebark h/michaleNo ratings yet
- OB Chapter 1 Intro to Organizational BehaviorDocument29 pagesOB Chapter 1 Intro to Organizational BehaviorMina TarekNo ratings yet
- Organisational Behaviour: Learning ObjectivesDocument8 pagesOrganisational Behaviour: Learning ObjectivesPrashant ChandraNo ratings yet
- Organizational Behavior: Unit - 1Document201 pagesOrganizational Behavior: Unit - 1Prashansa YadavNo ratings yet
- Organization Development: Human Reource Mgt-7Document31 pagesOrganization Development: Human Reource Mgt-7Pratik PatilNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document28 pagesChapter 3Roselyn IgartaNo ratings yet
- DrSaraKhan 2661 16690 2 SHRM8Document24 pagesDrSaraKhan 2661 16690 2 SHRM8Urooj MustafaNo ratings yet
- McKinsey 7S Framework ExplainedDocument17 pagesMcKinsey 7S Framework ExplainedKanchan RaiNo ratings yet
- Creating Competitive AdvantageDocument56 pagesCreating Competitive Advantageaey de guzmanNo ratings yet
- Evolution of Management TheoriesDocument28 pagesEvolution of Management Theoriesbhagyaraja vandanapuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Corporate Culture and Leadership Keys To Effective Strategy ExecutionDocument9 pagesChapter 6 Corporate Culture and Leadership Keys To Effective Strategy Executionmelvin cunananNo ratings yet
- Structure: Shared ValuesDocument12 pagesStructure: Shared ValuesPrem TiwariNo ratings yet
- CH 1Document17 pagesCH 1Anwita MittalNo ratings yet
- Toyota's Quality Machine: How a Committed Workforce Drives ExcellenceDocument60 pagesToyota's Quality Machine: How a Committed Workforce Drives ExcellenceKohi BangNo ratings yet
- HRM and Strategy: Strategic Planning-The Evolving / Strategic Role of Human Resource ManagementDocument7 pagesHRM and Strategy: Strategic Planning-The Evolving / Strategic Role of Human Resource ManagementchandrikaNo ratings yet
- Corporate Governance TheoriesDocument8 pagesCorporate Governance TheoriesSyed NaseemNo ratings yet
- Business Strategy: Dr. Sami UllahDocument8 pagesBusiness Strategy: Dr. Sami UllahWaleed KhalidNo ratings yet
- Organization TheoryDocument131 pagesOrganization TheoryElii ManNo ratings yet
- Chapter One OTDocument17 pagesChapter One OTHika DebelaNo ratings yet
- Second LectureDocument44 pagesSecond LectureMahad RizwanNo ratings yet
- Salam, Week 3-1Document6 pagesSalam, Week 3-1Mahad RizwanNo ratings yet
- Productivity: Chapter#3Document20 pagesProductivity: Chapter#3Mahad RizwanNo ratings yet
- Buisness Ethics and Corporate Social ResponsibilityDocument22 pagesBuisness Ethics and Corporate Social ResponsibilityMahad RizwanNo ratings yet
- POM - Chapter 2 - ProductivityDocument27 pagesPOM - Chapter 2 - ProductivityMahad RizwanNo ratings yet
- EthicsDocument21 pagesEthicsMahad RizwanNo ratings yet
- Mahad Rizwan (89), Fakhar Abbas (92), Farooq Azam (90) : TeamDocument7 pagesMahad Rizwan (89), Fakhar Abbas (92), Farooq Azam (90) : TeamMahad RizwanNo ratings yet
- Ethics and Employee Rights and Discipline: Chapter 6-1Document27 pagesEthics and Employee Rights and Discipline: Chapter 6-1Mahad RizwanNo ratings yet
- History of AccountingDocument4 pagesHistory of AccountingMahad RizwanNo ratings yet
- Principles of MarketingDocument7 pagesPrinciples of MarketingMahad RizwanNo ratings yet
- Is The Data Type Used To Label Variables and Giving Any Quantitative Values, or inDocument3 pagesIs The Data Type Used To Label Variables and Giving Any Quantitative Values, or inMahad RizwanNo ratings yet
- Mahad RizwanDocument4 pagesMahad RizwanMahad RizwanNo ratings yet
- OB CHPTR 01Document36 pagesOB CHPTR 01Mahad RizwanNo ratings yet
- Customer Preferences For Restaurant Technology InnovationsDocument22 pagesCustomer Preferences For Restaurant Technology InnovationsDeepankar SinghNo ratings yet
- Benjamin Joel - American Grandmaster. Four Decades of Chess Adventures, 2007-OCR, Everyman, 270p PDFDocument270 pagesBenjamin Joel - American Grandmaster. Four Decades of Chess Adventures, 2007-OCR, Everyman, 270p PDFGabriel Henrique100% (1)
- Mid-Semester Exam ED2 2020Document11 pagesMid-Semester Exam ED2 2020Subhabrata MajumdarNo ratings yet
- BioassayDocument38 pagesBioassayMuhammad Masoom AkhtarNo ratings yet
- Advanced Topics in Requirement Engineering CSC-692Document38 pagesAdvanced Topics in Requirement Engineering CSC-692Fida VirkNo ratings yet
- Racionalidad Acotada 1Document4 pagesRacionalidad Acotada 1Hector J. RubiniNo ratings yet
- MICEDocument37 pagesMICECeleste Torino DigalNo ratings yet
- Birla Sun Life Implements Talisma CRMDocument10 pagesBirla Sun Life Implements Talisma CRMvishuvamNo ratings yet
- Arvydas Sliogeris The Thing and Art Two Essays On The Ontotopy of The Work of Art 1Document168 pagesArvydas Sliogeris The Thing and Art Two Essays On The Ontotopy of The Work of Art 1Richard OhNo ratings yet
- Holistic Retreat, Doi Saket, Chiang MaiDocument4 pagesHolistic Retreat, Doi Saket, Chiang MaiShireenNo ratings yet
- 1 Calimutan v. People - G.R. No. 152133Document1 page1 Calimutan v. People - G.R. No. 152133eiram23100% (1)
- BS en 01062-3-2008 PDFDocument12 pagesBS en 01062-3-2008 PDFjohnNo ratings yet
- Newton's Third Law and Vectors TutorialDocument9 pagesNewton's Third Law and Vectors TutorialpalparasNo ratings yet
- Explicitation and Implicitation - Omission and Addition - in ENGLISHDocument63 pagesExplicitation and Implicitation - Omission and Addition - in ENGLISHdyna bookNo ratings yet
- Transforming Enterprises Through Diversity and Inclusion - ILODocument124 pagesTransforming Enterprises Through Diversity and Inclusion - ILODaniela GalvisNo ratings yet
- Anthony Andreas Vass, Barbara Harrison Social Work Competences Core Knowledge, Values and SkillsDocument248 pagesAnthony Andreas Vass, Barbara Harrison Social Work Competences Core Knowledge, Values and SkillsAhmad Syifa100% (2)
- Henry W. Chesbrough and Andrew R. GarmanDocument8 pagesHenry W. Chesbrough and Andrew R. GarmanNeha KumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8Document3 pagesChapter 8Michelle MartinNo ratings yet
- Selling & Negotiation SkillsDocument70 pagesSelling & Negotiation SkillsMojo JOjoNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of An Effective CounselorDocument5 pagesCharacteristics of An Effective CounselorAbbas KhanNo ratings yet
- 3rd Quarter Las in Science 5Document4 pages3rd Quarter Las in Science 5Michael Edward De VillaNo ratings yet
- Selection of Hazard Evaluation Techniques PDFDocument16 pagesSelection of Hazard Evaluation Techniques PDFdediodedNo ratings yet
- Using ABAQUS to Reduce Tire Belt Edge StressesDocument10 pagesUsing ABAQUS to Reduce Tire Belt Edge StressesGautam SharmaNo ratings yet
- ED 206 Course OutlineDocument1 pageED 206 Course OutlineChe Insik RecabarNo ratings yet
- PF Lab ManualDocument72 pagesPF Lab ManualraoNo ratings yet
- STILREN Vase, White, 22 CM - IKEADocument9 pagesSTILREN Vase, White, 22 CM - IKEAAimi GhazaliNo ratings yet
- AnalogyDocument50 pagesAnalogyNathaniel Campeciño89% (9)
- Lightning Attachment Models and Maximum Shielding Failure Current: Application To Transmission LinesDocument9 pagesLightning Attachment Models and Maximum Shielding Failure Current: Application To Transmission LinespedramNo ratings yet
- MGT162 Group AssignmentDocument16 pagesMGT162 Group Assignment2022457008No ratings yet
- Oracle 1z0-986 Exam: Implementation EssentialsDocument23 pagesOracle 1z0-986 Exam: Implementation Essentialslakshmanan84No ratings yet
- Summary: The 5AM Club: Own Your Morning. Elevate Your Life. by Robin Sharma: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: The 5AM Club: Own Your Morning. Elevate Your Life. by Robin Sharma: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (22)
- The Coaching Habit: Say Less, Ask More & Change the Way You Lead ForeverFrom EverandThe Coaching Habit: Say Less, Ask More & Change the Way You Lead ForeverRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (186)
- Leadership and Self-Deception: Getting out of the BoxFrom EverandLeadership and Self-Deception: Getting out of the BoxRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (155)
- The First Minute: How to start conversations that get resultsFrom EverandThe First Minute: How to start conversations that get resultsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (57)
- Think Remarkable: 9 Paths to Transform Your Life and Make a DifferenceFrom EverandThink Remarkable: 9 Paths to Transform Your Life and Make a DifferenceNo ratings yet
- How to Lead: Wisdom from the World's Greatest CEOs, Founders, and Game ChangersFrom EverandHow to Lead: Wisdom from the World's Greatest CEOs, Founders, and Game ChangersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (95)
- The 7 Habits of Highly Effective PeopleFrom EverandThe 7 Habits of Highly Effective PeopleRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2564)
- The Millionaire Fastlane: Crack the Code to Wealth and Live Rich for a LifetimeFrom EverandThe Millionaire Fastlane: Crack the Code to Wealth and Live Rich for a LifetimeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Scaling Up: How a Few Companies Make It...and Why the Rest Don't, Rockefeller Habits 2.0From EverandScaling Up: How a Few Companies Make It...and Why the Rest Don't, Rockefeller Habits 2.0Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Billion Dollar Lessons: What You Can Learn from the Most Inexcusable Business Failures of the Last Twenty-five YearsFrom EverandBillion Dollar Lessons: What You Can Learn from the Most Inexcusable Business Failures of the Last Twenty-five YearsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (52)
- TED Talks: The Official TED Guide to Public SpeakingFrom EverandTED Talks: The Official TED Guide to Public SpeakingRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (210)
- How to Talk to Anyone at Work: 72 Little Tricks for Big Success Communicating on the JobFrom EverandHow to Talk to Anyone at Work: 72 Little Tricks for Big Success Communicating on the JobRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (36)
- Summary of Steven Bartlett's The Diary of a CEOFrom EverandSummary of Steven Bartlett's The Diary of a CEORating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Transformed: Moving to the Product Operating ModelFrom EverandTransformed: Moving to the Product Operating ModelRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- How to Win Friends and Influence People: Updated For the Next Generation of LeadersFrom EverandHow to Win Friends and Influence People: Updated For the Next Generation of LeadersRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (150)
- 24 Assets: Create a digital, scalable, valuable and fun business that will thrive in a fast changing worldFrom Everand24 Assets: Create a digital, scalable, valuable and fun business that will thrive in a fast changing worldRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (20)
- Spark: How to Lead Yourself and Others to Greater SuccessFrom EverandSpark: How to Lead Yourself and Others to Greater SuccessRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (130)
- Optimal: How to Sustain Personal and Organizational Excellence Every DayFrom EverandOptimal: How to Sustain Personal and Organizational Excellence Every DayRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- How To Win Friends And Influence PeopleFrom EverandHow To Win Friends And Influence PeopleRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (6511)
- Transformed: Moving to the Product Operating ModelFrom EverandTransformed: Moving to the Product Operating ModelRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- The Catalyst: How to Change Anyone's MindFrom EverandThe Catalyst: How to Change Anyone's MindRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (273)
- Follow The Leader: A Collection Of The Best Lectures On LeadershipFrom EverandFollow The Leader: A Collection Of The Best Lectures On LeadershipRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (122)
- No Excuses!: The Power of Self-Discipline; 21 Ways to Achieve Lasting Happiness and SuccessFrom EverandNo Excuses!: The Power of Self-Discipline; 21 Ways to Achieve Lasting Happiness and SuccessRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (453)
- The SPEED of Trust: The One Thing that Changes EverythingFrom EverandThe SPEED of Trust: The One Thing that Changes EverythingRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (93)
- Failing Forward: How to Make the Most of Your MistakesFrom EverandFailing Forward: How to Make the Most of Your MistakesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (243)
- Entreleadership: 20 Years of Practical Business Wisdom from the TrenchesFrom EverandEntreleadership: 20 Years of Practical Business Wisdom from the TrenchesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (186)
- Summary of Leaders Eat Last: Why Some Teams Pull Together and Others Don't by Simon SinekFrom EverandSummary of Leaders Eat Last: Why Some Teams Pull Together and Others Don't by Simon SinekRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (142)