Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Security Reliability of e Business
Uploaded by
Shubham Singh0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
28 views27 pagesOriginal Title
SECURITY RELIABILITY OF E BUSINESS
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
28 views27 pagesSecurity Reliability of e Business
Uploaded by
Shubham SinghCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 27
Chapter 12
Security and Reliability
of
e-Business
© Oxford University Press 2012. All rights reserved. E-Business
Learning Objectives
To understand –
• the reliability and quality considerations related to e-
business
• various e-business security requirements and
application security requirements
• the requirements of a secure e-business infrastructure
• security strategies for e-business
• technical measures to build a secure e-business
© Oxford University Press 2012. All rights reserved. E-Business
Introduction
Challenges for e-business posed by –
• Critical transactions
• Round-the-clock availability
• Integration with many other systems
E-businesses are prone to risks of security breaches as –
• Theft of IP, Viruses
• Exchange of offensive material,
• Copyright theft etc.
© Oxford University Press 2012. All rights reserved. E-Business
Need to invest in security initiatives due to –
• Rise in electronic crime and
• behavior of e-businesses
Safeguarding online businesses -
• E-safety - awareness among the users of a system of
their access rights and restrictions, and adherence to
them
• E-security - procedures that ensure the security of
electronic data and electronic systems
© Oxford University Press 2012. All rights reserved.
E-Business security Policy
E-business security policy refers to the guidelines that
clearly partition the e-business into two states –
– Secure state - system is protected from any unauthorized
access
– Non-secure state - system is vulnerable to attacks and no
controls are present
Security policies must cover all aspects of e-business
security such as –
– Confidentiality
– Integrity and Availability.
© Oxford University Press 2012. All rights reserved.
E-Business Security Policy
A typical e-business security policy should have -
• Clearly defined objectives and scope
• Details about the e-security infrastructure
• Security management programme
• Clear definitions and policies for privacy, censorship,
and accountability
• Technology and usage guidelines for access controls,
firewalls, Internet usage, and use of security
technologies
• Security audit policies and Legal policies
© Oxford University Press 2012. All rights reserved.
E-business Security Framework
E-business security framework needs to consider -
• People-related issues, which include –
• privacy policies and expectation
• Internet usage and restriction
• Trust related expectations
• Technology issues, which include –
• social issues
• Internet-related risks
• Reliability and quality issues
• Legal, technical, and organizational issues.
© Oxford University Press 2012. All rights reserved.
E-Business Security Framework
© Oxford University Press 2012. All rights reserved. E-Business
Dimensions of e-business security
The major dimensions of e-business security are -
• Integrity
• Authenticity
• Non-repudiation
• Privacy
• Availability
• Confidentiality
© Oxford University Press 2012. All rights reserved. E-Business
Integrated Security Mechanism
The integrated security mechanism has two aspects -
• Technological aspects
• Legal aspects
In addition to these, there is –
• Front-end security
• Back-end security – Database, Storage level and
Information handling related security
• Mid-tier security - Trusted OSs, component-based
security, and secured data handling
© Oxford University Press 2012. All rights reserved. E-Business
Front end Security
Front end security is provided through –
• SSL/TLS
• Firewalls
• Cryptographic Protocols
• Web-Based Security Servers
• Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS)
• Integrity Verification Tools
The issues dealt with Frontend Security -
i. Authentication ii. Authorization
iii. Availability and iv. confidentiality
© Oxford University Press 2012. All rights reserved. E-Business
Risks, Risk assessment and Risk Analysis
A Preferred approach to Risk analysis -
1.Identification and documentation of information assets of
the organization, along with the owners of the assets.
2.Ranking of the systems and assets, in terms of the
criticality, to the organization.
3.Listing of threats for each of the identified assets
4.Identification of the vulnerabilities for every identified
threat
5.Identification of impact of the exploitation of a weakness
6.Checking the probability of an event, resulting in a threat
7.Determining the level of risk that is associated with each of
these events.
© Oxford University Press 2012. All rights reserved. E-Business
Best e-security Practices Guidelines
The International Standards (ISO/IEC 27001),
established in October 2005, provide a model for
information security management.
The motivations to comply with these standards and
security certifications are –
• Protecting customer data and information
• Maintaining data integrity
• Continuity in case of disaster, and
• Protecting the organization’s reputation.
© Oxford University Press 2012. All rights reserved. E-Business
E-security Basics for Businesses
A business needs to define a trade-off between electronic
security / cost, and quality of service / privacy.
Policies to establish electronic security for business should
consider factors such as -
• Legal framework and its enforcement
• Electronic security for financial transactions and payment
systems
• Certification standard and established processes for secured
transactions
• Education and training
© Oxford University Press 2012. All rights reserved. E-Business
Legal Framework and Enforcement
The legal framework should comprise laws for –
• Electronic transactions
• E-commerce
• Payment systems
• Cyber crimes
• Infrastructure enforcement
Apart from the legal framework, there is the need for
enforcement of law within and across boundaries.
© Oxford University Press 2012. All rights reserved. E-Business
IT Act 2000
• Provides legal recognition to e-commerce and other
electronic transactions
• Defines the terms such as access, certifying authority,
Computers, as well the use of digital signatures and
electronic transactions
• Deals with electronic records and its usage
• Specifies the penalties for the breach of confidentiality,
privacy and misinterpretation of info.
• Provides guidelines for digital signatures, digital certificates,
and their validity, the power of officers in different scenarios
etc.
© Oxford University Press 2012. All rights reserved. E-Business
IT Act 2000 Cont..
IT Act 2000 defines the punishment for -
• Tampering of computer and source documents
• Hacking of computer systems
• Publishing obscene information
{ Appendix 4 provides details on IT Act with
reference to e-business }
{ Source : http://nicca.nic.in/pdf/itact2000.pdf }
© Oxford University Press 2012. All rights reserved. E-Business
Securing e-business Infrastructure
• Electronic security for financial transactions and
payment systems
• Security and e-business infrastructure
• Infrastructure availability
© Oxford University Press 2012. All rights reserved. E-Business
GLB Act
• The Gramm-Leach-Bliley (GLB) Act is a
comprehensive, federal law for security of financial
institutions
• It is aimed at maintaining integrity, security, and
confidentiality to protect the customer information
• It is composed of several parts, including the Privacy
Rule (16 CFR 313) and the Safeguards Rule (16 CFR
314)
© Oxford University Press 2012. All rights reserved. E-Business
Examples of the financial products and services,
need to be compliant with GLB Act
© Oxford University Press 2012. All rights reserved. E-Business
Objectives of the GLBA Safeguards Rule
• Ensuring the security and confidentiality of customer
information.
• Protect against any anticipated threat or hazard to the
security or integrity of such information.
• Protect against unauthorized access to genuine
information that is stored at the organization end, in
order to save the customers from any type of harm or
inconvenience.
© Oxford University Press 2012. All rights reserved. E-Business
Role of IT Security & Policy in GLB Act
• Risk assessments
• Guidelines for secure computer data
• Educational materials
• Providing security tools and software
• Providing support for security issues
• Security event response
• Enforcement of the GLBA
© Oxford University Press 2012. All rights reserved. E-Business
Technical and Remote Access Security
Guidelines
Technical and remote access security guidelines can
help businesses to secure their computer systems from
vulnerability. For example -
• Use of updated antivirus systems, All incoming mails
and communications scanned for virus and mal-ware.
• Regular assessment of all external facing devices
• A Functional security system, A proper backup System
• Remote access only if necessary, and through secured
VPN
• Password and access controls for remote access
© Oxford University Press 2012. All rights reserved. E-Business
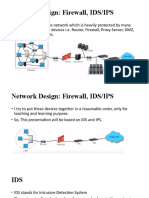
Network Level Security
• Firewalls
• Safeguarding e-business
• Information and network security policies
• Authentication Mechanism
• Intrusion detection
• Intrusion handling
• Network security
• Anticipating network attacks
© Oxford University Press 2012. All rights reserved. E-Business
Safeguarding e-business
© Oxford University Press 2012. All rights reserved. E-Business
PKI (Public Key Infrastructure) Functions
PKI is the complete infrastructure for implementing
security. A number of functions come under PKI.
Those are -
• Issue of certificates by CA
• Revoking of invalid certificates
• Storing certificates and providing trust
© Oxford University Press 2012. All rights reserved. E-Business
Ethical, Social, and Political Issues in
e-business
• Social, ethical, and political issues—severity and
understanding
• Privacy and information rights
• Intellectual property rights
• Ethical Internet Governance
• Ethical issues and protections
© Oxford University Press 2012. All rights reserved. E-Business
You might also like
- Implementing an ISO 27001 ISMSDocument110 pagesImplementing an ISO 27001 ISMSSuhendi SS100% (1)
- Prevention On and Responses To Violence Against Children Within The Juvenile Justice SystemDocument75 pagesPrevention On and Responses To Violence Against Children Within The Juvenile Justice Systemsofiabloem100% (1)
- Managing Cyber Security V1 (Level-3)Document20 pagesManaging Cyber Security V1 (Level-3)venky_akella100% (2)
- CISA - Domain 5 - Protection of Information AssetsDocument202 pagesCISA - Domain 5 - Protection of Information AssetsPremdeepakHulagbali100% (1)
- Cyber SecurityDocument23 pagesCyber SecurityYzon FabriagNo ratings yet
- Oman Presentation MDS 19th JuneDocument173 pagesOman Presentation MDS 19th Juneshiv kumarNo ratings yet
- What Is Cyber SecurityDocument56 pagesWhat Is Cyber SecurityHumayoun SaeedNo ratings yet
- Database Security: System Vulnerability and AbuseDocument7 pagesDatabase Security: System Vulnerability and AbuseAndhika Prasetya GradiyantoNo ratings yet
- Module 4b Security PDFDocument72 pagesModule 4b Security PDFAngella Chisomo MagomboNo ratings yet
- WSTG-Checklist v4.2Document29 pagesWSTG-Checklist v4.2Talo NguyenNo ratings yet
- CIA Security Model ExplainedDocument26 pagesCIA Security Model ExplainedWajiha Rehman100% (1)
- ISO27k Awareness PresentationDocument41 pagesISO27k Awareness PresentationGen VagulaNo ratings yet
- Information Security A Case Study3Document8 pagesInformation Security A Case Study3ragunathrevNo ratings yet
- Sub Dealer I Sub Dealer Name Dealer Code Dealer Namesub Dealer Msub Dealer AcDocument15 pagesSub Dealer I Sub Dealer Name Dealer Code Dealer Namesub Dealer Msub Dealer AcShubham SinghNo ratings yet
- 422 33 Powerpoint Slides Chapter 12 Security Reliability e Business Chapter 12Document5 pages422 33 Powerpoint Slides Chapter 12 Security Reliability e Business Chapter 12Aditya YadavNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 MMLSDocument33 pagesChapter 9 MMLSlelNo ratings yet
- Thwarting Attackers Defending Against Growing Security Sophistication While Managing ComplexityDocument18 pagesThwarting Attackers Defending Against Growing Security Sophistication While Managing ComplexityducuhNo ratings yet
- E-Commerce Chapter 4Document34 pagesE-Commerce Chapter 4THABISILE MBATHANo ratings yet
- Group 2 Computer SecDocument11 pagesGroup 2 Computer Secjohn andrew villanNo ratings yet
- Cyber Law & Ethics LectureDocument15 pagesCyber Law & Ethics LectureinnorajNo ratings yet
- Lesson 8Document33 pagesLesson 8Aida NatashaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To IT - Data PrivacyDocument44 pagesIntroduction To IT - Data PrivacyJulie Anne KingNo ratings yet
- AIS Chap 8Document23 pagesAIS Chap 8PhupungPrasiwiNo ratings yet
- Managerial Implications of IT/IS in Global Business: CSIT-204 Module-IVDocument19 pagesManagerial Implications of IT/IS in Global Business: CSIT-204 Module-IVBiplab BiswasNo ratings yet
- Lab 2-3 ASA FirewallDocument36 pagesLab 2-3 ASA FirewallMary Amirtha Sagayee. GNo ratings yet
- Iot Fundamentals:: Security & PrivacyDocument21 pagesIot Fundamentals:: Security & Privacyselena lopezNo ratings yet
- Cyber Security Unit 1 and 2Document95 pagesCyber Security Unit 1 and 2Veeresh NikeeNo ratings yet
- Developing Secure Information SystemDocument27 pagesDeveloping Secure Information SystemjayamalarNo ratings yet
- E Commerce Lecture2Document29 pagesE Commerce Lecture2feda jahjahNo ratings yet
- Cyber Security: Protecting Networks and Data from External ThreatsDocument9 pagesCyber Security: Protecting Networks and Data from External ThreatsSaeed FaNo ratings yet
- Securing Information SystemsDocument16 pagesSecuring Information SystemsNaveed AkbarNo ratings yet
- Chapter: 11.2 Overview of Internet Security Topic: 11.2.1 Overview of Internet SecurityDocument7 pagesChapter: 11.2 Overview of Internet Security Topic: 11.2.1 Overview of Internet SecurityETL LABSNo ratings yet
- Certificate Programme On: Cybersecurity and Data PrivacyDocument4 pagesCertificate Programme On: Cybersecurity and Data PrivacyKritika KakkarNo ratings yet
- Lecture 01Document22 pagesLecture 01Ismail MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Emerging Presentation (1) - WPS OfficeDocument16 pagesEmerging Presentation (1) - WPS OfficednzereabirukNo ratings yet
- Everything You Need To Know About Cybersecurity - THAT CYBERSECURITY DUDEDocument20 pagesEverything You Need To Know About Cybersecurity - THAT CYBERSECURITY DUDEAkhilesh JadhavNo ratings yet
- Session 6Document48 pagesSession 6thecluelessNo ratings yet
- E-Commerce SecurityDocument21 pagesE-Commerce SecurityTejasvee Tandon Jaipuria JaipurNo ratings yet
- Group 1-Network Security Policy For Cyber Surakshit Bharat June 15 KolkataDocument30 pagesGroup 1-Network Security Policy For Cyber Surakshit Bharat June 15 KolkataGattu GiridharNo ratings yet
- Web Security: Guide Name:-Mr Om Batch Number:-2 Name:-Vishnu Vamsith Yejju Roll No:-160121737204Document27 pagesWeb Security: Guide Name:-Mr Om Batch Number:-2 Name:-Vishnu Vamsith Yejju Roll No:-160121737204YAMINI SRI VISHNU VAMSITH YEJJUNo ratings yet
- Establishing a Framework for Security and ControlDocument34 pagesEstablishing a Framework for Security and ControlNoppon SETTASATIENNo ratings yet
- Cyber Security Notes on Unit 1Document97 pagesCyber Security Notes on Unit 1Krishna DeviNo ratings yet
- Unit VDocument36 pagesUnit VBijay PoudelNo ratings yet
- Ethics in Information Technology, Fourth Edition: Computer and Internet CrimeDocument22 pagesEthics in Information Technology, Fourth Edition: Computer and Internet CrimeWajiha RehmanNo ratings yet
- Ethical Issues in Computing and Information TechnologyDocument20 pagesEthical Issues in Computing and Information TechnologyJeysie ClarksonNo ratings yet
- IT Security and Management Problem 01Document30 pagesIT Security and Management Problem 01Sundeel Bin HaleemNo ratings yet
- Lab 4Document5 pagesLab 4Nguyen Dinh Quan (K15 HCM)No ratings yet
- Lesson 4 Protecting Information ResourcesDocument16 pagesLesson 4 Protecting Information ResourcesReymart SelverioNo ratings yet
- Cyber Security AdilDocument15 pagesCyber Security AdilAdilyt yttNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8 Cyber Safety 23-24Document26 pagesLecture 8 Cyber Safety 23-24Bekzat SagyndykovNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Introduction: - The Art of War, Sun TzuDocument36 pagesChapter 1 - Introduction: - The Art of War, Sun TzuAli AjamiNo ratings yet
- Unit IVDocument72 pagesUnit IVdeepakrishnanNo ratings yet
- Topic 3 - Emerging Trends and Risk ManagementDocument20 pagesTopic 3 - Emerging Trends and Risk ManagementMat RoyNo ratings yet
- Lecture Note 5new - IT Risk AssessmentDocument54 pagesLecture Note 5new - IT Risk AssessmentMndzebele SipheleleNo ratings yet
- Cisa Module 1 Part A I.S PlanningDocument42 pagesCisa Module 1 Part A I.S PlanningREJAY89No ratings yet
- BBM 7TH Note (E-Commerce)Document14 pagesBBM 7TH Note (E-Commerce)shree ram prasad sahaNo ratings yet
- Ethics in Information Technology, Fourth Edition: Ethics For IT Workers and IT UsersDocument29 pagesEthics in Information Technology, Fourth Edition: Ethics For IT Workers and IT UsersWajiha RehmanNo ratings yet
- E-Business and Its Types: ITO TDocument8 pagesE-Business and Its Types: ITO Tmqjulia_nt35063No ratings yet
- E-Business: Oxford University Press 2012. All Rights Reserved. E-BusinessDocument45 pagesE-Business: Oxford University Press 2012. All Rights Reserved. E-BusinessShubham SinghNo ratings yet
- Planning of Cyber SecurityDocument4 pagesPlanning of Cyber SecurityIfrat ZawarNo ratings yet
- IT Security Architecture & Design 1Document41 pagesIT Security Architecture & Design 1samsonoyoribwariNo ratings yet
- Info Sec ch-1Document43 pagesInfo Sec ch-1Abraham ZelekeNo ratings yet
- Accounting VoucherDocument1 pageAccounting VoucherShubham SinghNo ratings yet
- Analyzing business impacts of environmental changesDocument7 pagesAnalyzing business impacts of environmental changesShubham SinghNo ratings yet
- Rtgs Incentive - N-PB - 0.50% Veh (Wo-Erk) Car 2WL % of Achievent Till 27th Feb End of The MonthDocument2 pagesRtgs Incentive - N-PB - 0.50% Veh (Wo-Erk) Car 2WL % of Achievent Till 27th Feb End of The MonthShubham SinghNo ratings yet
- Lovely Professional University Online Assignment 1 Analyzes Business ChallengesDocument3 pagesLovely Professional University Online Assignment 1 Analyzes Business ChallengesShubham SinghNo ratings yet
- Lovely Professional University Academic Task No. 1 Mittal School of BusinessDocument3 pagesLovely Professional University Academic Task No. 1 Mittal School of BusinessShubham SinghNo ratings yet
- Lovely Professional University: Academic Task - 2 Mittal School of BusinessDocument2 pagesLovely Professional University: Academic Task - 2 Mittal School of BusinessShubham SinghNo ratings yet
- The Impact of Political Communication On Voting Behaviour: A Comparative Study in Karnataka, Kerala & Tamil NaduDocument17 pagesThe Impact of Political Communication On Voting Behaviour: A Comparative Study in Karnataka, Kerala & Tamil NaduShubham SinghNo ratings yet
- Lovely Professional University Online Assignment 1 Analyzes Business ChallengesDocument3 pagesLovely Professional University Online Assignment 1 Analyzes Business ChallengesShubham SinghNo ratings yet
- Sport Performance AnalyticsDocument9 pagesSport Performance AnalyticsAbrahamNo ratings yet
- Nigiria School DataDocument2 pagesNigiria School DataShubham SinghNo ratings yet
- MGNDocument4 pagesMGNShubham SinghNo ratings yet
- Building and Launching E-Business: Oxford University Press 2012. All Rights Reserved. E-BusinessDocument27 pagesBuilding and Launching E-Business: Oxford University Press 2012. All Rights Reserved. E-BusinessShubham SinghNo ratings yet
- Annexure-V - Cover P Age A Cademic TasksDocument8 pagesAnnexure-V - Cover P Age A Cademic TasksShubham SinghNo ratings yet
- Case Analysis of Performance Management in Football ClubDocument5 pagesCase Analysis of Performance Management in Football ClubShubham SinghNo ratings yet
- LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY ACADEMIC TASKDocument2 pagesLOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY ACADEMIC TASKChetan NarasannavarNo ratings yet
- MKT507 Ambika Sur 11900472Document12 pagesMKT507 Ambika Sur 11900472Shubham SinghNo ratings yet
- Creating E-Business Plan: Oxford University Press 2012. All Rights Reserved. E-BusinessDocument29 pagesCreating E-Business Plan: Oxford University Press 2012. All Rights Reserved. E-BusinessShubham SinghNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 9 Back End SystemDocument27 pagesChapter - 9 Back End SystemShubham SinghNo ratings yet
- Value Creation and Business Strategies in E-Age: Oxford University Press 2012. All Rights Reserved. E-BusinessDocument33 pagesValue Creation and Business Strategies in E-Age: Oxford University Press 2012. All Rights Reserved. E-BusinessShubham SinghNo ratings yet
- E-Business Applications: Oxford University Press 2012. All Rights Reserved. E-BusinessDocument21 pagesE-Business Applications: Oxford University Press 2012. All Rights Reserved. E-BusinessShubham SinghNo ratings yet
- E-Business: Oxford University Press 2012. All Rights Reserved. E-BusinessDocument45 pagesE-Business: Oxford University Press 2012. All Rights Reserved. E-BusinessShubham SinghNo ratings yet
- Knowledge Management and Business Intelligence For Strategic E-BusinessDocument21 pagesKnowledge Management and Business Intelligence For Strategic E-BusinessShubham SinghNo ratings yet
- Last Report CapDocument59 pagesLast Report CapShubham SinghNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 2 E Busines ModelsDocument41 pagesChapter - 2 E Busines ModelsShubham SinghNo ratings yet
- E-Business Competitive and Business Strategy: Oxford University Press 2012. All Rights Reserved. E-BusinessDocument27 pagesE-Business Competitive and Business Strategy: Oxford University Press 2012. All Rights Reserved. E-BusinessShubham SinghNo ratings yet
- Wrong Company for ChangeDocument2 pagesWrong Company for ChangeKristel Coleen Sumibcay100% (1)
- Research On The Relationship Between The Growth of OTT Service Market and The Change in The Structure of The Pay-TV MarketDocument49 pagesResearch On The Relationship Between The Growth of OTT Service Market and The Change in The Structure of The Pay-TV MarketShubham SinghNo ratings yet
- Case Study Analysis ReportDocument9 pagesCase Study Analysis ReportShubham SinghNo ratings yet
- Improve Password Policy with Stronger HashesDocument3 pagesImprove Password Policy with Stronger HashessnehaNo ratings yet
- International Journal of Computer Engineering and ApplicationsDocument7 pagesInternational Journal of Computer Engineering and ApplicationsrishithaNo ratings yet
- Top 30 Penetration Tester (Pentester) Interview Questions and AnswersDocument13 pagesTop 30 Penetration Tester (Pentester) Interview Questions and Answerssyed muffassir100% (1)
- Visit Braindump2go and Download Full Version 312-50v11 Exam DumpsDocument4 pagesVisit Braindump2go and Download Full Version 312-50v11 Exam DumpsLê Huyền MyNo ratings yet
- Ips and IDS - 090356Document13 pagesIps and IDS - 090356Muhammad AslamNo ratings yet
- 9 Types of Security Vulnerabilities PDFDocument5 pages9 Types of Security Vulnerabilities PDFHala DjiheneNo ratings yet
- Zero Trust Access For Dummies®, Fortinet Special Edition - Zero-Trust-Access-For-DummiesDocument49 pagesZero Trust Access For Dummies®, Fortinet Special Edition - Zero-Trust-Access-For-DummiesV DNo ratings yet
- Hindu Institute of Management: Aruna KapoorDocument10 pagesHindu Institute of Management: Aruna KapoorAruna KapoorNo ratings yet
- CRIM 4 FinalsDocument4 pagesCRIM 4 FinalsNickel ElerNo ratings yet
- IP Based Fingerprint Time & Attendance With Access Control SystemDocument1 pageIP Based Fingerprint Time & Attendance With Access Control SystemVigilantNo ratings yet
- Phishing Seminar ReportDocument27 pagesPhishing Seminar ReportsanjayNo ratings yet
- Fingerprint Tech: Identification, Authentication, Apps & SecurityDocument25 pagesFingerprint Tech: Identification, Authentication, Apps & SecurityKulwant SinghNo ratings yet
- GISEC ListDocument33 pagesGISEC Listgaju619No ratings yet
- IT ISMS WorkshopDocument18 pagesIT ISMS WorkshopIyad Ali100% (1)
- Leaked Babuk Code Ignites VMware ESXi RansomwareDocument2 pagesLeaked Babuk Code Ignites VMware ESXi Ransomwarefauzeeyah adepojuNo ratings yet
- CR300E.1-asset Security-2020Document57 pagesCR300E.1-asset Security-2020iqraNo ratings yet
- BankDocument3 pagesBankSS EntertainmentNo ratings yet
- ArcSight Connectors Supported ProductsDocument3 pagesArcSight Connectors Supported ProductsSaso KuzmanovskiNo ratings yet
- Man in The Middle AttackDocument4 pagesMan in The Middle AttackJoshuaNo ratings yet
- Digital Signature: Presented By: Mohd Yusuf Qidwai 2016CAB07Document12 pagesDigital Signature: Presented By: Mohd Yusuf Qidwai 2016CAB07Yusuf QidwaiNo ratings yet
- QuizzesDocument5 pagesQuizzesWalid BarakatNo ratings yet
- Computer Protection or SecurityDocument2 pagesComputer Protection or Securityandrei cabacunganNo ratings yet
- An Example of The RSA AlgorithmDocument4 pagesAn Example of The RSA AlgorithmstephenrajNo ratings yet
- BCN 4th and 5th Chapter NotesDocument21 pagesBCN 4th and 5th Chapter NotesM.n KNo ratings yet
- FCS Question Bank 2021-22Document4 pagesFCS Question Bank 2021-22Dhananjay SinghNo ratings yet
- SRM PresentationDocument23 pagesSRM PresentationPathan MehemudNo ratings yet
- Wireless Security Protocols WPA3 A Systematic Literature ReviewDocument13 pagesWireless Security Protocols WPA3 A Systematic Literature ReviewFresy NugrohoNo ratings yet
- Canvas Security Risk AnalysisDocument5 pagesCanvas Security Risk AnalysisHillary OdhiamboNo ratings yet