Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Oep - Ohp 180453119056,58,60,63 (7-B3)
Uploaded by
Huzeyfa ShaikhOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Oep - Ohp 180453119056,58,60,63 (7-B3)
Uploaded by
Huzeyfa ShaikhCopyright:
Available Formats
Screen clipping taken: 24-Apr-16, 3:21 PM
SVMIT-MECHANICAL ENGINEERING
OEP- OHP (2171912)
TOPIC NAME – PNEUMATIC SYSTEM ACTUATORS
ACADEMIC YEAR 2020-21
The return stroke takes place by the action of Rotary actuators:- APPLICATION
INTRODUCTION
a spring. Generally the spring is provided on 1) Gear motor: a rotary actuator
Actuators are output devices which convert the rod side of the cylinder. Loading and unloading of parts.
energy from pressurized hydraulic oil or 2) Double acting cylinder Tool exchange operation.
compressed air into the required type of action Measuring operation.
or motion. Automated & robotic welding.
Injection moulding.
In general, hydraulic or pneumatic systems are
Packaging machines.
used for gripping and/or moving operations in
industry. These operations are carried out by ADVANTAGES
using actuators.
Rotary actuators convert energy of Low cost.
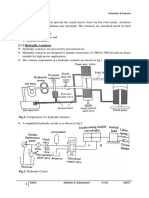
The construction of hydraulic and pneumatic The main parts of a hydraulic double acting pressurized fluid into rotary motion. Rotary High speed of moving.
linear actuators is similar. However they differ cylinder are: piston, piston rod, cylinder actuators are similar to electric motors but High reliability of work.
at their operating pressure ranges. Typical tube, and end caps. are run on hydraulic or pneumatic power. Explosion and fire safety.
pressure of hydraulic cylinders is about 100 bar These are shown in Figure The piston rod is Ecological purity.
It consists of two inter meshing gears inside
and of pneumatic system is around 10 bar. connected to piston head and the other end a housing with one gear attached to the drive DISADVANTAGES
Actuators can be classified into two types. extends out of the cylinder. shaft.
The piston divides the cylinder into two Compressibility of the air.
a) Linear actuators: These devices convert The air enters from the inlet, causes the
chambers namely the rod end side and piston Impossibility to receive uniform and constant
hydraulic/pneumatic energy into linear rotation of the meshing gear due to
end side. The seals prevent the leakage of oil speed of the working body movement.
motion. difference in the pressure and produces the
between these two chambers. Difficulties in performance at slow speed.
b) Rotary actuators: These devices convert The cylindrical tube is fitted with end caps. torque. Compressed air requires good preparation.
hydraulic/pneumatic energy into rotary The pressurized oil, air enters the cylinder The air exists from the exhaust port. Gear Limited condition use of Compressed air is
motion. chamber through the ports provided. motors tend to leak at low speed, hence are beneficial up to the definite values of pressure.
3) Cylinder end cushions generally used for medium speed
applications.
Linear actuators:-
2) Vane motor: a rotary actuator
1) Single acting cylinder
Prepared by:-
Double acting cylinders generally contain Branch:- B.E mechanical
cylinder cushions at the end of the cylinder Semester:- 7th
to slow down the movement of the piston
near the end of the stroke. Shaikh Huzayfa – 180453119056
The construction of actuating cylinder with Shaikh Mo.Tahir – 180453119058
A rotary vane motor consists of a rotor with
These cylinders produce work in one direction end cushions. Cushioning arrangement
sliding vanes in the slots provided on the Sindha Mayur – 180453119060
of motion hence they are named as single avoids the damage due to the impact Tailor Jaimin – 180453119063
rotor.
acting cylinders. occurred when a fast moving piston is
The rotor is placed eccentrically with the
The construction of a single acting cylinder. stopped by the end caps. Guided by:- Prof. Vandana Gajjar
housing. Air enters from the inlet port,
Deceleration of the piston starts when the
The compressed air pushes the piston located in rotates the rotor and thus torque is produced.
tapered plunger enters the opening in the cap
the cylindrical barrel causing the desired Air is then released from the exhaust port
and closes the main fluid exit. This restricts
motion. (outlet).
the exhaust flow from the barrel to the port.
www.postersession.com
You might also like
- Hydraulics and Pneumatics: A Technician's and Engineer's GuideFrom EverandHydraulics and Pneumatics: A Technician's and Engineer's GuideRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (8)
- MCT 2Document3 pagesMCT 2Sylesh SreehariNo ratings yet
- Pneumatic Controls and Designs: Wendell Z. BuenaobraDocument11 pagesPneumatic Controls and Designs: Wendell Z. BuenaobraJohn Paul DaliopacNo ratings yet
- Sistem Hidrolik Dan Pneumatik PerbedaanDocument17 pagesSistem Hidrolik Dan Pneumatik PerbedaanBilly Nandika Infantuzziano100% (1)
- Hydraulics vs Pneumatics: A Comparison of SystemsDocument17 pagesHydraulics vs Pneumatics: A Comparison of SystemsRizkia MunajatNo ratings yet
- Faculty of Practice: Haytham Yassin TA: Mentallah SolimanDocument28 pagesFaculty of Practice: Haytham Yassin TA: Mentallah SolimanSamar ElghalbanNo ratings yet
- Electromechanical ActuatorsDocument4 pagesElectromechanical ActuatorsMohammed Asif NNo ratings yet
- Design and Fabrication of Pneumatic Press For Various AttachmentsDocument16 pagesDesign and Fabrication of Pneumatic Press For Various AttachmentsSWAPNIL PATILNo ratings yet
- Automatic brake system for hill stationsDocument4 pagesAutomatic brake system for hill stationspampana vinayNo ratings yet
- Hydraulics and Pneumatics - NotesDocument79 pagesHydraulics and Pneumatics - NotesPuviyarasan MNo ratings yet
- Valve Actuator Selection GuideDocument3 pagesValve Actuator Selection GuideBramJanssen76100% (1)
- Design and Fabrication of Improved Pneumatic Glass Cutting MachineDocument3 pagesDesign and Fabrication of Improved Pneumatic Glass Cutting MachineHarshal PatilNo ratings yet
- SURE2011 Mech TrippNicholasDocument1 pageSURE2011 Mech TrippNicholasronald_maldonado_32No ratings yet
- Robot Actuator TypesDocument3 pagesRobot Actuator TypesDivanker SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Bosch FAQ-MD 053117 V3.pdDocument2 pagesBosch FAQ-MD 053117 V3.pdBill GinivanNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Cylinder Joints: Understanding Loads and DesignDocument16 pagesHydraulic Cylinder Joints: Understanding Loads and DesignVinaySeebaNo ratings yet
- JournalNX - Stator Stamping MachineDocument3 pagesJournalNX - Stator Stamping MachineJournalNX - a Multidisciplinary Peer Reviewed JournalNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0957415821000830 MainDocument13 pages1 s2.0 S0957415821000830 MainBrunoNo ratings yet
- Robots Drive SystemDocument28 pagesRobots Drive SystemDhalal AsmiNo ratings yet
- Electric Solenoid Gear Shifting System1Document4 pagesElectric Solenoid Gear Shifting System1International Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Choose Between Long-Stroke Sucker Rod Pumping Systems.: September 2015Document5 pagesChoose Between Long-Stroke Sucker Rod Pumping Systems.: September 2015Mohanad HussienNo ratings yet
- R&A - Module 2Document85 pagesR&A - Module 2The UltimateNo ratings yet
- The Megohmmeter For DC-10Document3 pagesThe Megohmmeter For DC-10Jay CortezNo ratings yet
- ACTUATORS: Mechanical, Electrical and Fluid Power Actuation SystemsDocument42 pagesACTUATORS: Mechanical, Electrical and Fluid Power Actuation SystemsNyandaMadili MalashiNo ratings yet
- ME8694 Hydraulics and PneumaticsDocument79 pagesME8694 Hydraulics and PneumaticselabalajiNo ratings yet
- Actuation Systems For MechatronicsDocument26 pagesActuation Systems For Mechatronicsabdulkerim seidNo ratings yet
- Robot Actuator Types and UsesDocument12 pagesRobot Actuator Types and UsesNani KumarNo ratings yet
- L-26 (SM) (Ia&c) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document18 pagesL-26 (SM) (Ia&c) ( (Ee) Nptel)Marvin BayanayNo ratings yet
- FPCLDocument24 pagesFPCLRajiv ShelakeNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document33 pagesUnit 2kssrao13No ratings yet
- Sugarcane HarvesterDocument8 pagesSugarcane HarvesterAniruddha TaraleNo ratings yet
- Pneumatic Actuator Guide - Types, Working Principles & ApplicationsDocument25 pagesPneumatic Actuator Guide - Types, Working Principles & ApplicationsHAFIZ MUGHEEZ ALI ZAHID SHEHZAD ALI100% (1)
- Actuator Selection and Sizing For Valves: October 2019Document9 pagesActuator Selection and Sizing For Valves: October 2019iJordanScribdNo ratings yet
- Eight Selection Criteria For Actuation Components - Plant EngineeringDocument12 pagesEight Selection Criteria For Actuation Components - Plant EngineeringAbhijeet RedekarNo ratings yet
- MECHATRONICS ACTUATORSDocument5 pagesMECHATRONICS ACTUATORSNavin H YadavNo ratings yet
- Closed Loop Control Systems ExplainedDocument33 pagesClosed Loop Control Systems ExplainedSgsksbskxvxk100% (1)
- Design and Implement A Semi-Automatic Clutch System For Automobiles Using DCV and The Link Mechanism To Reduce Human Effort While IncreasingDocument6 pagesDesign and Implement A Semi-Automatic Clutch System For Automobiles Using DCV and The Link Mechanism To Reduce Human Effort While IncreasingIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- Constructive-Functional Analysis of Single-Rod Double-Acting Hydraulic CylindersDocument7 pagesConstructive-Functional Analysis of Single-Rod Double-Acting Hydraulic CylindersALEXSANDRONo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1 - Actuators in Automation SystemDocument18 pagesCHAPTER 1 - Actuators in Automation SystemnurliyanaNo ratings yet
- Actuators and Drive SystemDocument58 pagesActuators and Drive Systemdanilopangatungan8No ratings yet
- Hydraulics Vs PneumaticsDocument22 pagesHydraulics Vs Pneumaticsscorpionarnold100% (1)
- 8cab & Air Conditioner System PDFDocument27 pages8cab & Air Conditioner System PDFadelmomouraNo ratings yet
- 3 ActuatorsDocument30 pages3 ActuatorsAhmad AfzaalNo ratings yet
- Experimental Study of Leakage Compensation For Actuator Speed Control in Electro Hydraulic SystemsDocument11 pagesExperimental Study of Leakage Compensation For Actuator Speed Control in Electro Hydraulic SystemsJohn WilleyNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Component ModellingDocument18 pagesHydraulic Component ModellingRajesh MalikNo ratings yet
- Development of Swashplateless Helicopter Blade Pitch Control System Using The Limited Angle Direct-Drive Motor (LADDM)Document10 pagesDevelopment of Swashplateless Helicopter Blade Pitch Control System Using The Limited Angle Direct-Drive Motor (LADDM)Juan CamiloNo ratings yet
- Ch4 Drives, Actuators and ControlDocument80 pagesCh4 Drives, Actuators and ControlcactuswillsaNo ratings yet
- 308 Hydraulic Troubleshooting Course Preview PDFDocument17 pages308 Hydraulic Troubleshooting Course Preview PDFAnonymous q9eCZHMuS0% (1)
- Robotics and Automation - Unit-2 (Part 1)Document19 pagesRobotics and Automation - Unit-2 (Part 1)jaiganeshNo ratings yet
- Application of Actuation SystemDocument5 pagesApplication of Actuation SystemKRISHNA KANT GUPTANo ratings yet
- RAULICADocument1 pageRAULICAalexis basultoNo ratings yet
- Module 3Document68 pagesModule 3sungadomsNo ratings yet
- fpcl pdfDocument24 pagesfpcl pdfRajiv ShelakeNo ratings yet
- Pneumatic Collapsible Steering Coloumn: Harsha Vardhan U, Shamanth.P.Betta, Janardhan T.S, Navaneeth G Rao, Mohith.K.SDocument4 pagesPneumatic Collapsible Steering Coloumn: Harsha Vardhan U, Shamanth.P.Betta, Janardhan T.S, Navaneeth G Rao, Mohith.K.SshethNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic and Pneumatic SystemsDocument59 pagesHydraulic and Pneumatic Systemsviahul100% (1)
- Homework2 Yasser El Mehdi DIBDocument4 pagesHomework2 Yasser El Mehdi DIBYasser DibNo ratings yet
- Piezoelectric Actuators: Vector Control Method: Basic, Modeling and Mechatronic Design of Ultrasonic DevicesFrom EverandPiezoelectric Actuators: Vector Control Method: Basic, Modeling and Mechatronic Design of Ultrasonic DevicesNo ratings yet
- Control Valves User's Manual: Model ACP - /ACNDocument100 pagesControl Valves User's Manual: Model ACP - /ACNKahl YeongNo ratings yet
- Product Bulletin Fisher 377 Trip Valve en 125044Document10 pagesProduct Bulletin Fisher 377 Trip Valve en 125044Tomás MercadoNo ratings yet
- TurboResources B737NG TEARDOWNDocument42 pagesTurboResources B737NG TEARDOWNLuisa Fernanda RodríguezNo ratings yet
- PLC System OverviewDocument30 pagesPLC System Overviewvan hangNo ratings yet
- HT-TM2200-75-E4: Rotary ActuatorDocument3 pagesHT-TM2200-75-E4: Rotary ActuatorJan Antonius DjunaediNo ratings yet
- Series W706 Ags Butterfly Valves (300 Psi/2065 Kpa) : Product DescriptionDocument6 pagesSeries W706 Ags Butterfly Valves (300 Psi/2065 Kpa) : Product DescriptionTushar LanjekarNo ratings yet
- PHL Pump CatalogueDocument6 pagesPHL Pump Catalogue30101985No ratings yet
- Cummins Qsx15-G5 Fault Code DiagnosticsDocument3 pagesCummins Qsx15-G5 Fault Code DiagnosticsJeremy MedinaNo ratings yet
- Service Training Manual Transmisión ML260 For JCBDocument84 pagesService Training Manual Transmisión ML260 For JCBDaniel Aguirre100% (1)
- TechnipFMC Long Distance Subsea ControlDocument27 pagesTechnipFMC Long Distance Subsea ControlNugroho100% (1)
- 26071-100-V2a-H701-04002 - R02 - Datasheet For MFDDocument54 pages26071-100-V2a-H701-04002 - R02 - Datasheet For MFDogyriskyNo ratings yet
- Subsea Manual PDFDocument16 pagesSubsea Manual PDFyg89No ratings yet
- Cat 4162 UkDocument256 pagesCat 4162 UkcristianNo ratings yet
- TensileDocument7 pagesTensiledayglisNo ratings yet
- UOP 2-12-5 Fired HeatersDocument45 pagesUOP 2-12-5 Fired Heaterskaboomi47100% (7)
- HP Question Bank PDFDocument8 pagesHP Question Bank PDFdurgapriyaNo ratings yet
- EMT EMD Series Multi Turn Electric Actuator en 20231213Document14 pagesEMT EMD Series Multi Turn Electric Actuator en 20231213Akram ElhamdiNo ratings yet
- Everything You Need to Know About Robot FunctionsDocument50 pagesEverything You Need to Know About Robot Functionsmk_chandruNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Hydraulics For Industry Professionals: Hydraulic Systems Volume 1Document20 pagesIntroduction To Hydraulics For Industry Professionals: Hydraulic Systems Volume 1Tushar AgarwalNo ratings yet
- CATERPILLAR - Maintenance Interval ScheduleDocument67 pagesCATERPILLAR - Maintenance Interval ScheduleVirbiir50% (2)
- Control Systems EngineeringDocument19 pagesControl Systems EngineeringAhmad RazaNo ratings yet
- Participants ManualDocument62 pagesParticipants ManualaaaaaNo ratings yet
- ALS Series: Exd Limit Switch BoxDocument4 pagesALS Series: Exd Limit Switch BoxNabeel MohammedNo ratings yet
- Handleiding Flexball 3500 Tot 4500 SeriesDocument73 pagesHandleiding Flexball 3500 Tot 4500 SerieshamzehNo ratings yet
- Level I - Ata 52 DoorsDocument40 pagesLevel I - Ata 52 Doorswagdi100% (3)
- 11 - Dynamic Decoupling of Robot Manipulators 2018Document193 pages11 - Dynamic Decoupling of Robot Manipulators 2018kurts010No ratings yet
- VtcatDocument72 pagesVtcatCalidad - TGINo ratings yet
- F-15 Flight Management System Technical ManualDocument80 pagesF-15 Flight Management System Technical ManualbrandtryanNo ratings yet
- Valves and InstrumentsDocument296 pagesValves and InstrumentsRommel Heredia TejadaNo ratings yet
- EPR SeriesDocument8 pagesEPR Seriestpelly7No ratings yet