0% found this document useful (0 votes)
186 views18 pagesOverview of Neuroglia Cells in CNS
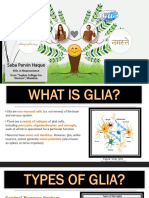
The document discusses the different types of neuroglia, or non-neuronal cells, in the nervous system. It describes six main types: oligodendrocytes, astrocytes, ependymal cells, microglia, Schwann cells, and satellite cells. Oligodendrocytes and Schwann cells form myelin sheaths around axons. Astrocytes support neurons and help form the blood-brain barrier. Ependymal cells line the ventricles. Microglia perform immune functions. Schwann cells myelinate peripheral nerves and satellite cells cover neuronal cell bodies in ganglia. Neuroglia vastly outnumber neurons and play crucial roles in the healthy functioning of the nervous system.
Uploaded by
Pro fatherCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
186 views18 pagesOverview of Neuroglia Cells in CNS
The document discusses the different types of neuroglia, or non-neuronal cells, in the nervous system. It describes six main types: oligodendrocytes, astrocytes, ependymal cells, microglia, Schwann cells, and satellite cells. Oligodendrocytes and Schwann cells form myelin sheaths around axons. Astrocytes support neurons and help form the blood-brain barrier. Ependymal cells line the ventricles. Microglia perform immune functions. Schwann cells myelinate peripheral nerves and satellite cells cover neuronal cell bodies in ganglia. Neuroglia vastly outnumber neurons and play crucial roles in the healthy functioning of the nervous system.
Uploaded by
Pro fatherCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd