0% found this document useful (0 votes)
285 views11 pagesByjus Nervous System New Notes 551687659721259
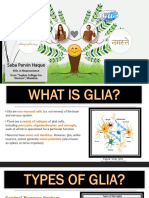
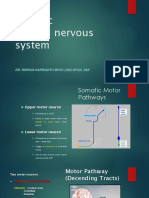
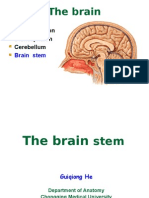
This document provides an overview of the human nervous system, detailing its components including the central nervous system (CNS) and peripheral nervous system (PNS). It describes the structure and functions of the brain, spinal cord, and neurons, highlighting their roles in processing and transmitting information throughout the body. Additionally, it covers the classification of nerve fibers and types of nerves involved in sensory and motor functions.
Uploaded by
real39130Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
285 views11 pagesByjus Nervous System New Notes 551687659721259
This document provides an overview of the human nervous system, detailing its components including the central nervous system (CNS) and peripheral nervous system (PNS). It describes the structure and functions of the brain, spinal cord, and neurons, highlighting their roles in processing and transmitting information throughout the body. Additionally, it covers the classification of nerve fibers and types of nerves involved in sensory and motor functions.
Uploaded by
real39130Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd