0% found this document useful (0 votes)
232 views24 pagesParathyroid Gland Function and Disorders
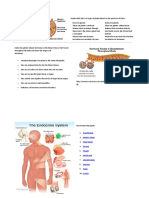
The parathyroid glands produce parathyroid hormone (PTH) which regulates calcium and phosphate levels. There are typically four parathyroid glands located behind the thyroid gland. PTH increases blood calcium levels by stimulating bone breakdown, vitamin D activation, and kidney reabsorption. It decreases kidney phosphate reabsorption. Disorders include hypoparathyroidism with low calcium and hyperparathyroidism with high calcium. Primary hyperparathyroidism is usually caused by an adenoma and results in elevated PTH and calcium levels.
Uploaded by
Leonard AcsinteCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
232 views24 pagesParathyroid Gland Function and Disorders
The parathyroid glands produce parathyroid hormone (PTH) which regulates calcium and phosphate levels. There are typically four parathyroid glands located behind the thyroid gland. PTH increases blood calcium levels by stimulating bone breakdown, vitamin D activation, and kidney reabsorption. It decreases kidney phosphate reabsorption. Disorders include hypoparathyroidism with low calcium and hyperparathyroidism with high calcium. Primary hyperparathyroidism is usually caused by an adenoma and results in elevated PTH and calcium levels.
Uploaded by
Leonard AcsinteCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd