0% found this document useful (0 votes)
65 views55 pagesThyroid Cancer and Thyroidectomy Insights
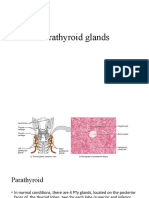
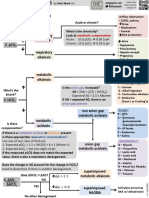
The document discusses the thyroid gland and various thyroid disorders. It covers the anatomy of the thyroid gland and its relationship to the hypothalamic-pituitary axis. It then discusses various thyroid disorders including hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism, thyroiditis, and thyroid cancer. For each disorder it provides details on causes, signs and symptoms, and in some cases images to illustrate the clinical presentation.
Uploaded by
Leonard AcsinteCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
65 views55 pagesThyroid Cancer and Thyroidectomy Insights
The document discusses the thyroid gland and various thyroid disorders. It covers the anatomy of the thyroid gland and its relationship to the hypothalamic-pituitary axis. It then discusses various thyroid disorders including hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism, thyroiditis, and thyroid cancer. For each disorder it provides details on causes, signs and symptoms, and in some cases images to illustrate the clinical presentation.
Uploaded by
Leonard AcsinteCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd