Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Elements of Fiction
Uploaded by
Ejay Lordaike Rosete Reyes0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views8 pagesOriginal Title
Elements_of_Fiction.pptx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views8 pagesElements of Fiction
Uploaded by
Ejay Lordaike Rosete ReyesCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 8
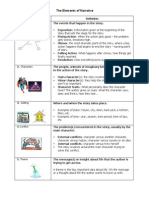
Elements of Fiction
Setting- the time and place
• Integral- settings are key to a story, it
affects the plot
• Background- settings are simply a
backdrop for the action
-Character-
• Traits- personal qualities of a Main Characters- these characters play a major
role in the story
character
• Protagonist- The main
character in a story, around
Example: friendly, suspicious, selfish, whom the events of the story’s
rude depressed. Developed through plot revolve.
a character’s speech, actions, or • Antagonist- A character or
thoughts group of characters that
represent opposition to the
main character of a story
Minor Characters- these characters play a small
role in the story
Plot- What happens in the
story, the nuts and bolts
Five Parts of plot
• 1.Introduction- The Beginning,
Characters, Setting & Problem laid out
• 2.Rising Action- Complications arise with
the problem, The Plot Thickens!
• 3.Climax- Highest point of
interest/suspense, a.k.a. the Turning Point,
the outcome is decided
• 4. Falling Actions- events that follow the
climax and end in resolution
• 5.Resolution- The ending, loose ends are
tied up, everything comes together
• Elements of Fiction
• A – Characters – who is in the story
• B – Setting – where and when the story takes place
• C –Conflict – problem
• D – Rising Action – story gets better (most of plot fits here)
• E – Climax – Highest point of interest in the story
• F – Falling Action – events that follow the climax and end in
resolution
• G – Resolution – solution to the problem
Plot Continued
• Conflict- The problem, there are four different
types, a story may have more than one.
– 1. Character v. Character – External Conflict
– 2. Character v. Nature – External Conflict
– 3. Character v. Society – External Conflict
– 4. Character v. Self – Internal Conflict
Style- How the author writes,
the techniques they use to write
• Foreshadowing- A hint to the
future, a change in setting Point of View (POV)- Who is telling
the story, three different types
• Flashback- A brief return to • First Person- Told by someone IN the
the past, a change in setting story, uses “I” and “me”
• Third Person Limited- Told by a
narrator, OUTSIDE the story, the
• Suspense- A feeling of tension narrator only knows thoughts of one
character, uses the pronouns “he”,
the author creates “she”, and “they”
• Third Person Omniscient- Told by a
narrator OUTSIDE the story, the narrator
knows what all characters are thinking,
narrator is all knowing (om=all), uses the
pronouns “he”, “she”, or “they”
Theme-
• The message about life that author is trying
to express (moral) it is a statement
• complete thought, not one word! “Love” is a
message, but “love heals all wounds” is a theme
Authors Purpose
• An author writes for many reasons. An author may give you facts
or true information about a subject. Some authors write fiction stories
or stories that are not true. They write these stories to entertain you.
Other authors may write to persuade or to try to get you to do
something.
You might also like
- Elements of FictionDocument8 pagesElements of Fictionjemilyn tungculNo ratings yet
- Elementsofastory PDFDocument23 pagesElementsofastory PDFMaffyFelicianoNo ratings yet
- Elements of A Short StoryDocument18 pagesElements of A Short StoryKyle Angelo SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Features of Narrative TextDocument20 pagesFeatures of Narrative TextAnne ChristinaNo ratings yet
- Handout CWDocument5 pagesHandout CWmaemae caparosNo ratings yet
- Elements of A Short Story and Ernest HemingwayDocument39 pagesElements of A Short Story and Ernest HemingwayΑθηνουλα ΑθηναNo ratings yet
- Features of Narrative TextDocument20 pagesFeatures of Narrative TextMicah Eunice FanoNo ratings yet
- LESSON 2 Elements of LiteratureDocument44 pagesLESSON 2 Elements of LiteratureAngel Cabrera100% (1)
- Elements of FictionDocument17 pagesElements of FictionsaadNo ratings yet
- Story ElementsDocument29 pagesStory ElementsJake Aldred CabelaNo ratings yet
- Elements of A Short StoryDocument25 pagesElements of A Short StoryDevorah Mae Filipino100% (1)
- M6. Crafting FictionDocument27 pagesM6. Crafting Fictionnada bawazierNo ratings yet
- Elements of A Story PDFDocument18 pagesElements of A Story PDF143airenNo ratings yet
- Parts of The Short StoryDocument12 pagesParts of The Short StoryRafaelDelaCruzNo ratings yet
- Elements of A Story: What You Need To Know!Document25 pagesElements of A Story: What You Need To Know!Alaa YasienNo ratings yet
- Elements of Fiction: Joanna Cheng-LorenzoDocument22 pagesElements of Fiction: Joanna Cheng-LorenzoMaria Rowena SaysonNo ratings yet
- Literary Elements1Document29 pagesLiterary Elements1jessogNo ratings yet
- Elements of A StoryDocument19 pagesElements of A StoryShiela Cervitillo-MorenoNo ratings yet
- ProseDocument23 pagesProsedian luthfiyati50% (2)
- Elements of Literature11Document38 pagesElements of Literature11Mehmet sarıNo ratings yet
- Story Writing: Short Stories Usually Focus On A Single EventDocument10 pagesStory Writing: Short Stories Usually Focus On A Single EventMina SamNo ratings yet
- Short Story - Elements of Short StoryDocument27 pagesShort Story - Elements of Short Storyapi-261452312No ratings yet
- Elements of Literature: Created by Sherice BlairDocument40 pagesElements of Literature: Created by Sherice BlairNjiaNo ratings yet
- ملخص لترتشر copyDocument12 pagesملخص لترتشر copyrawaa alshNo ratings yet
- What You Need To Know!Document102 pagesWhat You Need To Know!Kimberly Maramag100% (1)
- L1 Elements of Literature Story PDFDocument40 pagesL1 Elements of Literature Story PDFalaamohbenNo ratings yet
- Material of Story (Narrative TextsDocument30 pagesMaterial of Story (Narrative TextsAfifah 12No ratings yet
- Stylistic Analysis: - Setting - Plot - Theme - Narration - CharactersDocument27 pagesStylistic Analysis: - Setting - Plot - Theme - Narration - CharactersOlga SmochinNo ratings yet
- Literary Elements NotesDocument5 pagesLiterary Elements NotesRodel BautistaNo ratings yet
- Literary Elements Notes PDFDocument5 pagesLiterary Elements Notes PDFGacha life VideosNo ratings yet
- Elements of A StoryDocument21 pagesElements of A StoryWahyu Indah PratiwiNo ratings yet
- English Literature: Semester 2Document17 pagesEnglish Literature: Semester 2lelanieNo ratings yet
- Features of Narrative TextDocument20 pagesFeatures of Narrative TextDiana OrozcoNo ratings yet
- Elements of FictionDocument30 pagesElements of FictionLouis Gabriel BerderaNo ratings yet
- Literary Devices Elements TechniquesDocument38 pagesLiterary Devices Elements Techniquessenior high100% (2)
- Local Media2579313156156977263Document3 pagesLocal Media2579313156156977263Nerissa Juanillo TabalNo ratings yet
- Elements of A StoryDocument35 pagesElements of A StoryGlenda Perucho LlacunaNo ratings yet
- Elements of Fiction NEWDocument33 pagesElements of Fiction NEWFlorencia GarciaNo ratings yet
- The Elements of Narrative-1Document1 pageThe Elements of Narrative-1devorehumanitiesNo ratings yet
- 5 Elements of A Short Story PDFDocument16 pages5 Elements of A Short Story PDFHanahjane Atuel0% (1)
- Basic Elements of A Short StoryDocument10 pagesBasic Elements of A Short StorySHARON SOSANo ratings yet
- Lesson 3Document8 pagesLesson 3Mary Joy AliviadoNo ratings yet
- Elements of A StoryDocument22 pagesElements of A StoryIan Roy Monsanto BataanNo ratings yet
- Elements of LiteratureDocument49 pagesElements of LiteratureᴉɥɔoɯNo ratings yet
- Elements of A StoryDocument5 pagesElements of A StoryKeith Pearl Joy PrimorNo ratings yet
- Bell Ringer Define The Following Terms in Your JournalDocument100 pagesBell Ringer Define The Following Terms in Your Journaljemilyn tungculNo ratings yet
- Story Elements 2Document102 pagesStory Elements 2kaliiimuddin123No ratings yet
- Introduction To Literature: Instructor: Tran Thi Nguyet Thanh, M.ADocument45 pagesIntroduction To Literature: Instructor: Tran Thi Nguyet Thanh, M.ACuc Le Thi KimNo ratings yet
- CNF Lesson 2Document4 pagesCNF Lesson 2Shendy Acosta100% (1)
- Creative Non-Fiction 12 Literary Devices, Elements & TechniquesDocument4 pagesCreative Non-Fiction 12 Literary Devices, Elements & TechniquesShendy AcostaNo ratings yet
- Elements of Fiction NEWDocument34 pagesElements of Fiction NEWAnne FrondaNo ratings yet
- Major Genres of LiteratureDocument121 pagesMajor Genres of LiteratureAlyanna JovidoNo ratings yet
- Elements of A Short StoryDocument16 pagesElements of A Short Storyfordsantiago01No ratings yet
- Lesson 3Document37 pagesLesson 3Antonette RecopertoNo ratings yet
- Elements of FictionDocument36 pagesElements of FictionMarra CantoriaNo ratings yet
- Storyelements 2Document99 pagesStoryelements 2Lea RosalNo ratings yet
- Elements of A Story: What You Need To Know!Document27 pagesElements of A Story: What You Need To Know!Quanitum ExpressNo ratings yet
- Creating Unforgettable Characters: A Practical Guide to Character Development in Films, TV Series, Advertisements, Novels & Short StoriesFrom EverandCreating Unforgettable Characters: A Practical Guide to Character Development in Films, TV Series, Advertisements, Novels & Short StoriesRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (29)
- Guidelines For Risk Review & ManagementDocument4 pagesGuidelines For Risk Review & ManagementgauravNo ratings yet
- Additional English - 4th Semester FullDocument48 pagesAdditional English - 4th Semester FullanuNo ratings yet
- AH 0109 AlphaStarsDocument1 pageAH 0109 AlphaStarsNagesh WaghNo ratings yet
- FEMADocument51 pagesFEMAChinmay Shirsat50% (2)
- Level of GovernmentDocument17 pagesLevel of GovernmentPAULONo ratings yet
- Sturge TownDocument3 pagesSturge TownRangerNo ratings yet
- GRADE 11 - UNIT 1 - TEST 2 - ĐỀDocument3 pagesGRADE 11 - UNIT 1 - TEST 2 - ĐỀThanh ThúyNo ratings yet
- Test 1 English Ii AdvanceDocument3 pagesTest 1 English Ii AdvanceMartin Sepulveda JaraNo ratings yet
- Netflix Case NotesDocument16 pagesNetflix Case NotesSergio AcuñaNo ratings yet
- Project Report On Comparative Analysis of 4-Stroke BikesDocument72 pagesProject Report On Comparative Analysis of 4-Stroke BikesvinnetTNo ratings yet
- Dubai Mall Landside Metro Bus - Dubai Design District Zõ - DC Ó% Ó? - V - C FO Ó% Eï (Ð ( @ (Document1 pageDubai Mall Landside Metro Bus - Dubai Design District Zõ - DC Ó% Ó? - V - C FO Ó% Eï (Ð ( @ (Dubai Q&ANo ratings yet
- Family Chapter Revision GuideDocument9 pagesFamily Chapter Revision GuidePuss BootNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: How To Design A Language?Document2 pagesChapter 1: How To Design A Language?Long Dong MidoNo ratings yet
- Citizenship Articles 3Document13 pagesCitizenship Articles 3Jagadish PrasadNo ratings yet
- Balanced Scorecard Workshop: Presented By: Matt H. Evans, CPA, CMA, CFMDocument61 pagesBalanced Scorecard Workshop: Presented By: Matt H. Evans, CPA, CMA, CFMShilpa AroraNo ratings yet
- Theories of Development and Indian Economy PDFDocument119 pagesTheories of Development and Indian Economy PDFSudhanshu Bele100% (3)
- B. Arch.: Printed Pages: 1 Roll No. RAR507Document1 pageB. Arch.: Printed Pages: 1 Roll No. RAR507Vipin Kumar SharmaNo ratings yet
- Join The Following Sentences Using A Relative PronounDocument2 pagesJoin The Following Sentences Using A Relative PronounIsabel SoteleNo ratings yet
- DDI - Company Profile 2024Document9 pagesDDI - Company Profile 2024NAUFAL RUZAINNo ratings yet
- SEEBURGER WebEDI Wilo ENDocument1 pageSEEBURGER WebEDI Wilo ENmarketingNo ratings yet
- Development of Science and Technology in The PhilippinesDocument12 pagesDevelopment of Science and Technology in The PhilippinesJyra Shael L. EscanerNo ratings yet
- Divine Word University of Tacloban vs. Secretary of Labor and Employment, G. R. No. 91915, Sept. 11, 1992, 213 SCRA 759Document3 pagesDivine Word University of Tacloban vs. Secretary of Labor and Employment, G. R. No. 91915, Sept. 11, 1992, 213 SCRA 759Maria Celiña PerezNo ratings yet
- Natural Law: St. Thomas AquinasDocument50 pagesNatural Law: St. Thomas AquinasGabriel PanganibanNo ratings yet
- RP FinalDocument125 pagesRP FinalAditya SoumavaNo ratings yet
- KK Electronics Global Strategy 1. Perform SWOT Analysis For TheDocument10 pagesKK Electronics Global Strategy 1. Perform SWOT Analysis For ThesanzeetaNo ratings yet
- The Chosen by Chaim PotokDocument12 pagesThe Chosen by Chaim PotokDavid A. Malin Jr.No ratings yet
- CQM Clinical Quality MeasureDocument10 pagesCQM Clinical Quality MeasureraviNo ratings yet
- Invoice: WD Elements (WDBUZG0010BBK) 1 TB Portable External Hard Drive (Black) 1 4284 4284Document1 pageInvoice: WD Elements (WDBUZG0010BBK) 1 TB Portable External Hard Drive (Black) 1 4284 4284Amit GuptaNo ratings yet
- PM Debug InfoDocument1,221 pagesPM Debug InfoRAMIRO MNo ratings yet
- Dubai Nursery SchoolsDocument2 pagesDubai Nursery SchoolsDipti Risbud100% (1)