0% found this document useful (0 votes)
242 views10 pagesDesign Improvement: Phase I. Design and Construction Phase - Testing (Functionality) Phase - Software Code
The document describes the design, construction, testing, and repair phases of two circuit prototype projects:
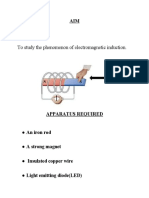
1. An automatic water level indicator and controller with 3 phases: design and construction, software coding, and testing.
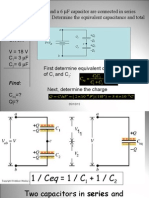
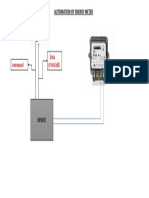
2. An SMS-based energy meter reading and control system with 4 phases: design and construction, testing device functionality, integrating a GSM module, and testing theft detection. Both projects include troubleshooting and repairing circuits if malfunctions occur.
Uploaded by
Abdifatah mohamedCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
242 views10 pagesDesign Improvement: Phase I. Design and Construction Phase - Testing (Functionality) Phase - Software Code
The document describes the design, construction, testing, and repair phases of two circuit prototype projects:
1. An automatic water level indicator and controller with 3 phases: design and construction, software coding, and testing.
2. An SMS-based energy meter reading and control system with 4 phases: design and construction, testing device functionality, integrating a GSM module, and testing theft detection. Both projects include troubleshooting and repairing circuits if malfunctions occur.
Uploaded by
Abdifatah mohamedCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 10