Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Compare and Contrast Process in Plants and Animals
Compare and Contrast Process in Plants and Animals
Uploaded by
Rjay Cruz0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views5 pagesOriginal Title
Compare and Contrast Process in Plants and Animals.pptx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views5 pagesCompare and Contrast Process in Plants and Animals
Compare and Contrast Process in Plants and Animals
Uploaded by
Rjay CruzCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 5
Compare and Contrast
Process in Plants and Animals:
Regulation of Body Fluids
Definition of terms
Internal Environmental – the fluid environment that bathes the cell (extracellular
fluids) compose of the interstitial fluid and blood.
Osmolarity – solute concentration expressed in milliosmoles per liter of
solution (mOsm/L)
Osmosis - the movement of water from a region of higher osmolarity to a
region of lower osmolarity across a selectively permeable membrane.
Osmoregulation – the regulation of water and ion balance.
Excretion - the elimination of metabolic wastes including nitrogenous wastes
produced from the breakdown of protiens, this process also helps in the
regulation of water and ion balance.
2 types of animals based on the osmolarity of their
body fluids
Osmoconformers - allow the osmolarity of their body fluids to match that of
the environment;
A. These include most marine invertebrates with the body fluids that are
generally hyperosmotic to their surroundings.
B. Because their bodies are isosmotic to seawater, they consume little or no
energy in maintaining water balance.
Osmoregulators – keep the osmolarity of vody fluids different from that of
the environment;
A. These include most marine vertebrates, birds, mammals.
B. Either their discharge water hypotonic environment of they take in water
in a hypertonic environment.
3 types of nitrogenous wastes excreted by animals;
Ammonia - the primary nitrogenous waste of aquatic invertebrates, teleosts,
and larval amphibians.
A. It is readily soluble in water but is also highly toxic
B. It can be excreted from the body only in dilute solutions.
Urea - produced by mammals, most amphibians, some reptiles, some marine
fishes, and some terrestrial invertebrates.
A. it is formed by combining ammonia with bicarbonate ion (HCO3) and
converting the product into urea.
B. Although its formation requires more energy compared to ammonia, it is
about 100,000x less toxic than ammonia.
C. Its excretion requires only about 10% as much water compared to
ammonia.
Uric acid – excreted by birds, insects and terrestrial reptiles.
A. It is relatively nontoxic but more energetically expensive to produce the urea.
B. It is largely insoluble in water and it is excreted as a semisolid paste or precipitate with very little water loss
Excretory system in invertebrates
Cell surface or
You might also like
- Lycia PDFDocument16 pagesLycia PDFjames6380100% (1)
- Nutrient Procurement and ProcessingDocument62 pagesNutrient Procurement and ProcessingClara Mae100% (2)
- Gen Chem 2 Q2 Module 2Document24 pagesGen Chem 2 Q2 Module 2Bernalene TasiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4-Compare and Contrast-Transport EtcDocument34 pagesChapter 4-Compare and Contrast-Transport EtcCristel BautistaNo ratings yet
- General Physics1: Quarter 1 - Module 1: Title: MeasurementsDocument28 pagesGeneral Physics1: Quarter 1 - Module 1: Title: MeasurementsKimberly C. Javier100% (1)
- General Chemistry 1 An Atomic View of Matter Module 5.1 PDFDocument27 pagesGeneral Chemistry 1 An Atomic View of Matter Module 5.1 PDFHello Hi0% (1)
- Disorders and Diseases That Result From The Malfunction of The Cell During The Cell CycleDocument2 pagesDisorders and Diseases That Result From The Malfunction of The Cell During The Cell CycleAmelyn Lingbawan100% (2)
- Self-Learning Package: Quantitative ResearchDocument10 pagesSelf-Learning Package: Quantitative ResearchCrysse PartisalaNo ratings yet
- Aerody Quizlet 489Document62 pagesAerody Quizlet 489Jecah Angelu S. SaquianNo ratings yet
- Regulation of Body Fluids: Compare and Contrast Process in Plants and AnimalsDocument16 pagesRegulation of Body Fluids: Compare and Contrast Process in Plants and AnimalsPaopao Macalalad100% (4)
- Regulation of Body FluidsDocument7 pagesRegulation of Body FluidsRuth FamillaranNo ratings yet
- Compare and Contrast Process in Plants and Animals PDFDocument32 pagesCompare and Contrast Process in Plants and Animals PDFLyca Gunay100% (4)
- Compare and Contrast Process in Plants and Animals GasDocument2 pagesCompare and Contrast Process in Plants and Animals GasJohn Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Plant and Animal NutritionDocument57 pagesPlant and Animal Nutritionneill arcaNo ratings yet
- NegOr Q4 GenBio2 SLKWeek2 v2Document22 pagesNegOr Q4 GenBio2 SLKWeek2 v2albazeervaNo ratings yet
- MODULE 1 & 2 - General Biology 2Document12 pagesMODULE 1 & 2 - General Biology 2John Michael LopezNo ratings yet
- Week 2 - General Chemistry 1 - LAS 1DDocument8 pagesWeek 2 - General Chemistry 1 - LAS 1Ddo san namNo ratings yet
- Colligative Properties of Non ElectrolytesDocument20 pagesColligative Properties of Non ElectrolytesHans Sicangco0% (1)
- Mechanisms That Produce Change in PopulationsDocument44 pagesMechanisms That Produce Change in PopulationsEvangelene Esquillo Sana100% (1)
- Cell Modifications That Lead To AdaptationDocument1 pageCell Modifications That Lead To AdaptationJohn Barry Ibanez80% (15)
- Gr. 12 Chemistry Module 1 NotesDocument24 pagesGr. 12 Chemistry Module 1 NotesAndrea EdwardsNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio 1 - Q1 - W1 - Las 1 PDFDocument14 pagesGen Bio 1 - Q1 - W1 - Las 1 PDFI am stupd100% (1)
- Plant and Animal Chemical and Nervous ControlDocument27 pagesPlant and Animal Chemical and Nervous ControlAlnedKirby Carijutan Mendiola100% (1)
- Biological Sciences ReflectionDocument3 pagesBiological Sciences ReflectionJames MahayagNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Molecular Model of Solids and Liquids Activity 1: Color DropDocument12 pagesKinetic Molecular Model of Solids and Liquids Activity 1: Color DropElaine Mae G. EsqueroNo ratings yet
- SolutionsDocument77 pagesSolutionsNina Grace FamosoNo ratings yet
- Fruit BatteryDocument37 pagesFruit BatteryIreena GomezNo ratings yet
- Week 3: Cell Modifications: General Biology 1Document3 pagesWeek 3: Cell Modifications: General Biology 1Florene Bhon GumapacNo ratings yet
- Technologies Diseases: Related To The Circulatory SystemDocument5 pagesTechnologies Diseases: Related To The Circulatory SystemHannahNo ratings yet
- GENERAL PHYSICS 2 - Q3 - Week 8Document19 pagesGENERAL PHYSICS 2 - Q3 - Week 8ariinnggg onichaNo ratings yet
- General Biology 2-201-270Document70 pagesGeneral Biology 2-201-270Sab IbarretaNo ratings yet
- GB2 11 q3 Mo5 wk5 Unique Characteristics of Specific Taxon Relative To Other Taxa Phylis Langakan BGDocument22 pagesGB2 11 q3 Mo5 wk5 Unique Characteristics of Specific Taxon Relative To Other Taxa Phylis Langakan BGDustin AgsaludNo ratings yet
- Physical ScienceDocument17 pagesPhysical Sciencewewe.trillanes100% (1)
- 3 Philippine National Artists in LiteratureDocument14 pages3 Philippine National Artists in LiteratureMichelleIragAlmario50% (2)
- General Biology 1 Quarter 2 WEEK 1 Module 1aDocument14 pagesGeneral Biology 1 Quarter 2 WEEK 1 Module 1aJohn Brylle UrsuaNo ratings yet
- Plant and Animal Organ Systems and Their Functions: (Nutrient Procurement and Processing, and Gas Exchange)Document28 pagesPlant and Animal Organ Systems and Their Functions: (Nutrient Procurement and Processing, and Gas Exchange)Ica A TorioNo ratings yet
- Mendelian & Modern Genetics: General Biology 2Document51 pagesMendelian & Modern Genetics: General Biology 2sannsannNo ratings yet
- Plant and Animal Organ Systems and Their Functions: General Biology 2Document25 pagesPlant and Animal Organ Systems and Their Functions: General Biology 2Ica A TorioNo ratings yet
- Gen Chem 1 Quarter 2 Week 1 2Document10 pagesGen Chem 1 Quarter 2 Week 1 2Mykhaela Louize GumbanNo ratings yet
- Chemical and Nervous ControlDocument39 pagesChemical and Nervous ControlElizabeth Alvear100% (1)
- LOOT LAS 1 Q2 Module 3Document2 pagesLOOT LAS 1 Q2 Module 3Natasha Liliane LootNo ratings yet
- Activity 1: True or False: Identify The Type of Reaction in The Following SituationsDocument3 pagesActivity 1: True or False: Identify The Type of Reaction in The Following SituationsElaine Mae G. EsqueroNo ratings yet
- Q2 - (LAS) GEN. CHEM wk4 PDFDocument4 pagesQ2 - (LAS) GEN. CHEM wk4 PDFJazer LeuterioNo ratings yet
- CH Apter Vii Calculating Formula Mass, Empirical Formula and Molecular FormulaDocument12 pagesCH Apter Vii Calculating Formula Mass, Empirical Formula and Molecular FormulaJen Karen BolidoNo ratings yet
- a3d34252160b7d0a1f1233f28322fe96Document3 pagesa3d34252160b7d0a1f1233f28322fe96Janlloyd DugoNo ratings yet
- Periodical Exam in Biology IIDocument8 pagesPeriodical Exam in Biology IINovochino CastilloNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 1 Grade 11 Book (Mine)Document5 pagesGeneral Chemistry 1 Grade 11 Book (Mine)Estela Benegildo0% (1)
- Chemical Kinetics For STEM 122Document38 pagesChemical Kinetics For STEM 122Johnnard N. BelenNo ratings yet
- What I Need To Know: 18) (2 Hours)Document73 pagesWhat I Need To Know: 18) (2 Hours)Richard BacharNo ratings yet
- MODULE 1 Gen Bio 2 PDFDocument4 pagesMODULE 1 Gen Bio 2 PDFEzekielNo ratings yet
- Bio Week 2Document7 pagesBio Week 2Elyza Joy RallosNo ratings yet
- Science Experiment ToDocument2 pagesScience Experiment ToMiguel ConcepcionNo ratings yet
- Atp-Adp CycleDocument9 pagesAtp-Adp Cyclemaria genio50% (2)
- General Chemistry 2 Q4 Module 2 1Document15 pagesGeneral Chemistry 2 Q4 Module 2 1Darwin Grande AlvaredaNo ratings yet
- LAS-Gen - Bio2 MELC 3 Q3-Week-2Document8 pagesLAS-Gen - Bio2 MELC 3 Q3-Week-2Jayma RomeNo ratings yet
- q1 General Physics Module 3Document20 pagesq1 General Physics Module 3Ciara Adrianne Tiongzon - ReyesNo ratings yet
- Understanding Culture Module 2Document8 pagesUnderstanding Culture Module 2Ennyliejor YusayNo ratings yet
- Reviewer For PhysicsDocument3 pagesReviewer For PhysicsRegina Victoria Ortega100% (1)
- General Biology 2 - AngieDocument9 pagesGeneral Biology 2 - AngiePrincess Mejarito MahilomNo ratings yet
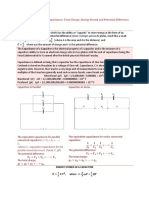
- Determining Equivalent CapacitanceDocument3 pagesDetermining Equivalent CapacitanceJulianna CristinaNo ratings yet
- 7.osmoregulation and Excretion in Invertebrates - FinalDocument58 pages7.osmoregulation and Excretion in Invertebrates - FinalAhmed Oraby81% (16)
- Chapter 8 BioDocument19 pagesChapter 8 Biosgangwar2005sgNo ratings yet
- Business Proposal: "Sago-Gulamanicious andDocument9 pagesBusiness Proposal: "Sago-Gulamanicious andRjay CruzNo ratings yet
- Mangrove Species Diversity Assessment in Barangay TinotoDocument11 pagesMangrove Species Diversity Assessment in Barangay TinotoRjay CruzNo ratings yet
- Active TransportDocument14 pagesActive TransportRjay CruzNo ratings yet
- Academic Field Trip in PalawanDocument31 pagesAcademic Field Trip in PalawanRjay CruzNo ratings yet
- Eduardo Torejos JR.: ObjectiveDocument2 pagesEduardo Torejos JR.: ObjectiveRjay CruzNo ratings yet
- Active - Passive Voice-FinaleDocument25 pagesActive - Passive Voice-FinaleRjay CruzNo ratings yet
- Main Beautiful Spot: HistoryDocument4 pagesMain Beautiful Spot: HistoryRjay CruzNo ratings yet
- Percent ConcentrationDocument14 pagesPercent ConcentrationRjay CruzNo ratings yet
- Effect of Air Inlet Hole Diameter of Venturi TubeDocument5 pagesEffect of Air Inlet Hole Diameter of Venturi TubeYesid Tapiero MartínezNo ratings yet
- Environmental Impact Assessment Study An PDFDocument13 pagesEnvironmental Impact Assessment Study An PDFburhanNo ratings yet
- PWA-RPD-CON-FM-1917 Maintenance Certificate Checklist R08Document2 pagesPWA-RPD-CON-FM-1917 Maintenance Certificate Checklist R08AbdelmonȜm MohNo ratings yet
- Physics of Soil Water and WatershedsDocument4 pagesPhysics of Soil Water and Watershedschrisr310No ratings yet
- DredgingDocument4 pagesDredgingرعد العكيليNo ratings yet
- R oDocument15 pagesR oPrabhat JhaNo ratings yet
- WEEK 2 - Level 0 - Jar TestDocument2 pagesWEEK 2 - Level 0 - Jar TestWHfamilyNo ratings yet
- Material Safety Data Sheet: Abzorbit Premium AbsorbentDocument2 pagesMaterial Safety Data Sheet: Abzorbit Premium AbsorbentKen DuncanNo ratings yet
- Ex Aluminum PDFDocument1 pageEx Aluminum PDFRENE HERNANDEZNo ratings yet
- Webinar Part 1Document48 pagesWebinar Part 1Annalou PialaNo ratings yet
- HJRS 0517 RND 01-Layout1Document1 pageHJRS 0517 RND 01-Layout1WAN ADLI WAN SHARIFUDZILLAHNo ratings yet
- G Force DX IOMDocument40 pagesG Force DX IOMRenzo RosasNo ratings yet
- Key Concepts: TotalDocument18 pagesKey Concepts: TotalSachin Kumar67% (3)
- ENGR10004 Engineering Technology and Society Semester 1, 2022Document12 pagesENGR10004 Engineering Technology and Society Semester 1, 2022Eric HeNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment: Water Systems: DescriptionDocument3 pagesRisk Assessment: Water Systems: DescriptionPablo CartesNo ratings yet
- Basic Information of The Project and ProponentDocument1 pageBasic Information of The Project and ProponentJoshua AssinNo ratings yet
- San Francisco Wastewater TreatmentDocument4 pagesSan Francisco Wastewater TreatmentseriouscallerzonlyNo ratings yet
- Waste WaterDocument106 pagesWaste WaterLing Li100% (1)
- Geography Coursework Debden BrookDocument8 pagesGeography Coursework Debden Brookafiwhyber100% (2)
- Viking Foam Manual 001Document24 pagesViking Foam Manual 001Trần VânNo ratings yet
- Construction Method StatementDocument35 pagesConstruction Method StatementHoang ThiNo ratings yet
- Reading Test 21 3Document5 pagesReading Test 21 3Hồ NhiNo ratings yet
- Geological Survey of Great Britain - L The Country Around Holmfirth and GlossopDocument233 pagesGeological Survey of Great Britain - L The Country Around Holmfirth and GlossopCraig BurtonNo ratings yet
- Colwood Creek Microhydro Proposal (2021)Document18 pagesColwood Creek Microhydro Proposal (2021)Jessica TruongNo ratings yet
- Combustion Analysis Basics LectureDocument32 pagesCombustion Analysis Basics LectureClaudineNo ratings yet
- AspirinDocument4 pagesAspiringenelleestremos100% (1)
- 05 Srs Eng Ref Rev 1Document16 pages05 Srs Eng Ref Rev 1Christian BarNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document13 pagesModule 1Jercy Ann TorresNo ratings yet