Professional Documents
Culture Documents
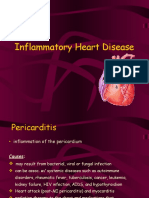
PERICARDITIS
Uploaded by
Lydia Lopz Msnrncd0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views17 pagesChest
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentChest
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views17 pagesPERICARDITIS
Uploaded by
Lydia Lopz MsnrncdChest
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 17
PERICARDITIS
Acute Pericarditis
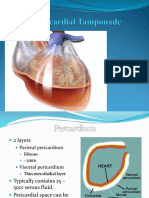
• Inflammation of the sac
surrounding the heart
• Area becomes rough &
scarred
Etiology
1. Bacteria, viruses, fungal organisms
2. Dressler’s syndrome [Post-MI]
3. Post-pericardiotomy syndrome [PPS]
4. Acute exacerbation of systemic connective
tissue
5. Previous trauma or cardiac surgery
6. Radiation
Assessment/Noticing:
Manifestations/Presentation
• Substernal precordial pain: radiating
to L neck, shoulder or neck
• Grating, oppressive pain: made worse
by breathing [on inspiration], coughing
& swallowing [Dysphagia]
• Pain worse: supine position: relieved:
Sitting up & leaning forward
• Pericardial friction rub: L lower
sternal border
Assessment/Noticing: Presentation:
Diagnostics
• WBC: Elevated
• Fever [infectious cause]
• Blood cultures
• EKG: ST elevation [all leads]; Afib
• Echo: pericardial effusion
• S/S cardiac tamponade
Proposed Diagnostic Criteria
• Presence of 2 of the following:
• Pericardial chest pain
• Pericardial rub presence
• New ST elevation or PR-segment depression
• New or worsening pericardial effusion
Chronic Constrictive Pericarditis
• Results from inflammation • Presentation
causing fibrous thickening of • R-side HF incl. dyspnea,
pericardium exertional fatigue, orthopnea
• Elevated systemic venous
• Causes
pressures w/JVD
• Radiation, TB, Trauma, renal • Hepatic engorgement [ascites]
failure [uremia] or metastatic • Dependent edema
cancer Diagnostics
• Pericardium: rigid, thick • Echo/CT: pericardial thickening
preventing filling of ventricles
leading to cardiac failure
Interventions
• Promote comfort
• Encouraging rest
• Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs [NSAIDS]
• Corticosteroid Rx: if NSAIDS ineffective & no
infection exists
• Positioning: Upright; leaning slightly forward
• No relief within 24-48 hours: notify provider
• Colchicine 0.5 mg PO twice/day x3 months
Interventions
• Treat specific cause of pericarditis
• Bacterial: AB & pericardial drainage
• Chronic
• Radiation or chemo: malignant disease
• Hemodialysis: uremia from renal disease
• Pericardiectomy [Chronic]: definitive treatment
• Monitor for pericardial effusion
• Risk for Cardiac tamponade
Pleural Effusion
Cardiac Tamponade
• Emergency; Notify if suspected
• Accumulation of fluid, blood [20-50
mL] or exudates between the two
layers of the pericardium
• Results in compression of cardiac
muscle
• Most serious complication of
pericarditis
• Causes
• MI, RV biopsy, trauma to ches, cardiac
bypass surgery
Assessment/Presentation/Manifestations
• ___________Cardiac output
• Central venous pressures: ____________
• Blood Pressure: ______________
• Heart sounds: Muffled or distant
• Narrow pulse pressure: difference b/w SBP & DBP
• JVD; clear BS on auscultation
• Paradoxical pulse [pulsus paradoxus: SBP 10 mm
Hg or more higher on expiration than inspiration
• Decreased HR, dyspnea, fatigue
Pericardiocentesis
• Removes fluid, blood and relieve pressure
from around the heart
• Procedure under echocardiography,
fluoroscopic and hemodynamic
monitoring:
• 16-18 g needle into pericardial space
• Pericardial drain temporarily placed
• Monitor pulmonary artery wedge and R
atrial pressures
• Send pericardial fluid to lab for c/s,
cytology
Nursing Safety Priority: Action Alert
• Post procedure
• Close monitoring for recurrence of tamponade
• Be prepared to provide adequate fluid volume
to increase CO ad prepare for emergency
sternotomy if tamponade recurs
Pericardial Window
• Surgical removal of portion of
pericardium and create a
'window' to continuously drain
the excess fluid into pleural
space
You might also like
- Pericardialdiseases 190121084846Document65 pagesPericardialdiseases 190121084846Insta GrammerNo ratings yet
- Pericardial Diseases - Raghad DghaishDocument32 pagesPericardial Diseases - Raghad Dghaish180045No ratings yet
- Inflammatory Disorders PDFDocument41 pagesInflammatory Disorders PDFMoon KillerNo ratings yet
- BSC Nursing: Medical Surgical Nursing - I Unit V - Disorders of The Cardio Vascular SystemDocument36 pagesBSC Nursing: Medical Surgical Nursing - I Unit V - Disorders of The Cardio Vascular SystemPoova RagavanNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Tamponade: Mrs. D.Melba Sahaya Sweety.D M.SC Nursing GimsarDocument23 pagesCardiac Tamponade: Mrs. D.Melba Sahaya Sweety.D M.SC Nursing GimsarD. Melba S.S ChinnaNo ratings yet
- Pericardium PDFDocument50 pagesPericardium PDFRawabi rawabi1997No ratings yet
- Pericardial DX Endocarditis MyocarditisDocument74 pagesPericardial DX Endocarditis MyocarditisJefry SNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Tamponade (Suryani)Document72 pagesCardiac Tamponade (Suryani)Hamdani UsmanNo ratings yet
- PericarditisDocument120 pagesPericarditisCalin Popa100% (1)
- Heart Failure: DR Edial SanifDocument45 pagesHeart Failure: DR Edial SanifiikNo ratings yet
- Pemicu 6 Eko Blok KGDDocument128 pagesPemicu 6 Eko Blok KGDEko SiswantoNo ratings yet
- Pericardial EffusionDocument35 pagesPericardial EffusionRizky Amalia WakanoNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Cardiology: Infective Endocarditis Rheumatic Heart Disease Endomyocardial FibrosisDocument52 pagesPediatric Cardiology: Infective Endocarditis Rheumatic Heart Disease Endomyocardial FibrosisEffah FestusNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Tamponade & Pericardial DiseasesDocument15 pagesCardiac Tamponade & Pericardial DiseasesSamiha HassanNo ratings yet
- Infective Endocarditis: Akriti DahalDocument79 pagesInfective Endocarditis: Akriti DahalAkriti100% (1)
- Curs Bolile PericarduluiDocument85 pagesCurs Bolile PericarduluiAndreea ElenaNo ratings yet
- Cardiac PathophysiologyDocument83 pagesCardiac PathophysiologyJauhar Anindita SariNo ratings yet
- Etiology: Clinical FeaturesDocument2 pagesEtiology: Clinical FeaturesAmalNo ratings yet
- PericarditisDocument52 pagesPericarditissanjivdasNo ratings yet
- New HematologyOncology FAE2016Document108 pagesNew HematologyOncology FAE2016omarNo ratings yet
- PERICARDITISDocument11 pagesPERICARDITISsalman hNo ratings yet
- V. Complications of CVDDocument26 pagesV. Complications of CVDJan Federick BantayNo ratings yet
- PericarditisDocument11 pagesPericarditisinyanji.barasaNo ratings yet
- Pericardial DX Endocarditis MyocarditisDocument63 pagesPericardial DX Endocarditis MyocarditisIrfan Ners MaulanaNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Disorders 2Document78 pagesCardiovascular Disorders 2Erlinda SagadsadNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular DiseasesDocument4 pagesCardiovascular DiseasesAshley Nicole LimNo ratings yet
- Pericardial DiseseasDocument38 pagesPericardial Diseseasmameekasim75No ratings yet
- CHF Concept and Physiology Ikm 6.9.19Document31 pagesCHF Concept and Physiology Ikm 6.9.19AfifulichwanNo ratings yet
- Cardiac TemponadeDocument18 pagesCardiac TemponadeDIVYA GANGWAR100% (1)
- LECTURE 8 - Early Detection and Management in Cardiac TamponadeDocument34 pagesLECTURE 8 - Early Detection and Management in Cardiac TamponadeWiwing SetionoNo ratings yet
- Cardiology Review SessionDocument139 pagesCardiology Review SessionNour LakisNo ratings yet
- Disease of Pericardium: DR Peter R KisengeDocument21 pagesDisease of Pericardium: DR Peter R KisengeamosNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis Gangguan KardiovaskulerDocument41 pagesDiagnosis Gangguan KardiovaskulerFifit SiePutry BintaNgnya KudaciNo ratings yet
- Guest Lecturer PMC CHF - 2021Document43 pagesGuest Lecturer PMC CHF - 2021Cindy DeliaNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Test 2Document28 pagesPediatric Test 2Nurse JonesNo ratings yet
- Heart Failure: DR Kaem Shir AliDocument24 pagesHeart Failure: DR Kaem Shir AliMwanja MosesNo ratings yet
- Pericarditis 65 SlidesDocument65 pagesPericarditis 65 SlidesAtifBhoreNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Pericardial DiseaseDocument36 pagesPathophysiology of Pericardial DiseaseivaniNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Disease in Pregnancy1Document23 pagesCardiac Disease in Pregnancy1Homeground entertainmentNo ratings yet
- CARDIOMYOPATHIESDocument80 pagesCARDIOMYOPATHIESNadun MethwadaneNo ratings yet
- Emergencies in Renal Failure and Dialysis PatientsDocument46 pagesEmergencies in Renal Failure and Dialysis PatientsDeepak JoshiNo ratings yet
- Acynotic DiseaseDocument55 pagesAcynotic DiseaseTesfamichael AbathunNo ratings yet
- Cardiac TamponadeDocument29 pagesCardiac Tamponadeanimesh pandaNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis and Management of Shock: Dr. Nurkhalis, SPJP, FihaDocument49 pagesDiagnosis and Management of Shock: Dr. Nurkhalis, SPJP, FihaSiti rahmawatiNo ratings yet
- Inflammatory Heart DiseaseDocument35 pagesInflammatory Heart DiseaseM RazzaqNo ratings yet
- Pericarditis: Dr. Alfredo Gonzales SaavedraDocument38 pagesPericarditis: Dr. Alfredo Gonzales SaavedraSandy Burgos CabanillasNo ratings yet
- Cardiac TamponadeDocument2 pagesCardiac TamponadechoobiNo ratings yet
- Ischemic Heart Diseases: Clinical Session: Prof. Ahmed Tamara, MD Dr. Mahmoud Baraka, MDDocument28 pagesIschemic Heart Diseases: Clinical Session: Prof. Ahmed Tamara, MD Dr. Mahmoud Baraka, MDNouran AliNo ratings yet
- Bimbingan Dokter Muda Heart FailureDocument57 pagesBimbingan Dokter Muda Heart FailurerachmaniabudiatiNo ratings yet
- Disorders of The Peripheral Vascular SystemDocument17 pagesDisorders of The Peripheral Vascular SystemDardarConstantinoNo ratings yet
- Cardiac PathophysiologyDocument33 pagesCardiac Pathophysiologyapi-76740522No ratings yet
- (Nelson Hour) Acquired Heart DiseasesDocument26 pages(Nelson Hour) Acquired Heart DiseasesJustin Ng SincoNo ratings yet
- Congestive Heart FailureDocument39 pagesCongestive Heart FailureEthiopia TekdemNo ratings yet
- Heart Failure Lecture 6Document39 pagesHeart Failure Lecture 6Nithin SureshNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Diseases and Cardiac Surgery: by Dr. Tehreem Nasir MBBS, RMPDocument26 pagesCardiac Diseases and Cardiac Surgery: by Dr. Tehreem Nasir MBBS, RMPAhmed SaeedNo ratings yet
- Cardiogenic Shock: BY Dr. M L Patel MD Associate Professor Deptt. of MedicineDocument19 pagesCardiogenic Shock: BY Dr. M L Patel MD Associate Professor Deptt. of MedicineDurgesh PushkarNo ratings yet
- Diseases of The PericardiumDocument28 pagesDiseases of The PericardiumHero StoreNo ratings yet
- The Ideal Heart Healthy Diet Cookbook; The Superb Diet Guide To Lower Your Blood Pressure And Cholesterol Levels With Nutritious Low Sodium Low Fat RecipesFrom EverandThe Ideal Heart Healthy Diet Cookbook; The Superb Diet Guide To Lower Your Blood Pressure And Cholesterol Levels With Nutritious Low Sodium Low Fat RecipesNo ratings yet
- Medicine in Brief: Name the Disease in Haiku, Tanka and ArtFrom EverandMedicine in Brief: Name the Disease in Haiku, Tanka and ArtRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Cardiac Care and COVID-19: Perspectives in Medical PracticeFrom EverandCardiac Care and COVID-19: Perspectives in Medical PracticeNo ratings yet
- Analgesics NonpopioidsDocument20 pagesAnalgesics NonpopioidsLydia Lopz MsnrncdNo ratings yet
- Vaccines ImmunizationsDocument31 pagesVaccines ImmunizationsLydia Lopz MsnrncdNo ratings yet
- Lyme DisorderLLDocument14 pagesLyme DisorderLLLydia Lopz MsnrncdNo ratings yet
- Gout FIBRODocument16 pagesGout FIBROLydia Lopz MsnrncdNo ratings yet
- Neuro AssessmentDocument42 pagesNeuro AssessmentLydia Lopz MsnrncdNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular AssessmentsreviewDocument34 pagesCardiovascular AssessmentsreviewLydia Lopz MsnrncdNo ratings yet
- Scribble Pad: Drugs Used To Treat Parkinson'sDocument24 pagesScribble Pad: Drugs Used To Treat Parkinson'sLydia Lopz MsnrncdNo ratings yet
- Meningitis SVDocument15 pagesMeningitis SVLydia Lopz MsnrncdNo ratings yet
- Bowel Disorder DRUGS: 29: Prof. Lopez NUR 210: PharmacologyDocument22 pagesBowel Disorder DRUGS: 29: Prof. Lopez NUR 210: PharmacologyLydia Lopz MsnrncdNo ratings yet
- Lyme DisorderLLDocument14 pagesLyme DisorderLLLydia Lopz MsnrncdNo ratings yet
- Vitamins & Minerals & HerbalsDocument27 pagesVitamins & Minerals & HerbalsLydia Lopz MsnrncdNo ratings yet
- Encephalitis 3Document9 pagesEncephalitis 3Lydia Lopz MsnrncdNo ratings yet
- Enteral Feeding II SVDocument15 pagesEnteral Feeding II SVLydia Lopz MsnrncdNo ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal Trauma FracturesDocument47 pagesMusculoskeletal Trauma FracturesLydia Lopz MsnrncdNo ratings yet
- Sprains, Strains, Dislocations & Subluxations, Carpal Tunnel & Other Related InjuriesDocument26 pagesSprains, Strains, Dislocations & Subluxations, Carpal Tunnel & Other Related InjuriesLydia Lopz MsnrncdNo ratings yet
- Hematological AssessmentSV522Document17 pagesHematological AssessmentSV522Lydia Lopz MsnrncdNo ratings yet
- OsteoarthritisDocument28 pagesOsteoarthritisLydia Lopz MsnrncdNo ratings yet
- Seizure DisordersDocument38 pagesSeizure DisordersLydia Lopz MsnrncdNo ratings yet
- Pictorial Images of Thoracic DeformitiesSVDocument13 pagesPictorial Images of Thoracic DeformitiesSVLydia Lopz MsnrncdNo ratings yet
- Sample Problem Calculated: #2: 2. Order: Zovirax 250 MG IV Available: Read Label Ans: 5 MLDocument4 pagesSample Problem Calculated: #2: 2. Order: Zovirax 250 MG IV Available: Read Label Ans: 5 MLLydia Lopz MsnrncdNo ratings yet
- Nursing DiagnosisDocument48 pagesNursing DiagnosisLydia Lopz MsnrncdNo ratings yet
- Group 4 Tuberculosis Case Study 2Document16 pagesGroup 4 Tuberculosis Case Study 2Lydia Lopz MsnrncdNo ratings yet
- PCR Testing Centers in The PhilippinesDocument36 pagesPCR Testing Centers in The Philippineskhrayzie bhoneNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Pharmacology AntibioticDocument15 pagesIntroduction To Pharmacology AntibioticZaira Reine SantosNo ratings yet
- Health Care Law OutlineDocument17 pagesHealth Care Law OutlineMegan Lindsay Ruffin100% (1)
- Absorption of Drugs From Extravascular RoutesDocument11 pagesAbsorption of Drugs From Extravascular RoutesraviNo ratings yet
- Syndrome of Inappropriate Antidiuretic Hormone Secretion SIADHDocument14 pagesSyndrome of Inappropriate Antidiuretic Hormone Secretion SIADHbhatubim100% (1)
- Manual Resp Carat 2Document96 pagesManual Resp Carat 2jan gutiNo ratings yet
- Blueprints Obstetrics and Gynecology 5th Edition MCQDocument30 pagesBlueprints Obstetrics and Gynecology 5th Edition MCQsinglez100% (1)
- Kochi Claim FormDocument4 pagesKochi Claim FormRadhika ShenoiNo ratings yet
- National List of Essential Medicines Nepal 2021Document72 pagesNational List of Essential Medicines Nepal 2021Sugandhi SahNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of The Pain Resource Nurse Role - A Resource For Improving Pediatric Pain ManagementDocument8 pagesEvaluation of The Pain Resource Nurse Role - A Resource For Improving Pediatric Pain ManagementWahyu WidiyantoNo ratings yet
- Shaping The Future - Recent Advances of 3D Printing in Drug and Heatlhcare PDFDocument15 pagesShaping The Future - Recent Advances of 3D Printing in Drug and Heatlhcare PDFyuvinta kalimsaNo ratings yet
- Hipaa FillableDocument2 pagesHipaa FillableRameezNatrajanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12Document16 pagesChapter 12Ruthleen May Simeon100% (1)
- PPSC FaysalDocument24 pagesPPSC FaysalJoseph Jackson100% (3)
- NCM 113 Community Health Nursing IiDocument4 pagesNCM 113 Community Health Nursing IiRenee CamilleNo ratings yet
- Quick Reference Guide: Supported byDocument25 pagesQuick Reference Guide: Supported byJanine HorsthNo ratings yet
- Death Wish ListDocument6 pagesDeath Wish ListphilippatstonNo ratings yet
- Infection Control Management Plan: PurposeDocument6 pagesInfection Control Management Plan: PurposeRekhaNo ratings yet
- 2020 WHO Global Tuberculosis ReportDocument232 pages2020 WHO Global Tuberculosis Reportsana shakeelNo ratings yet
- Essays Expository TextsDocument5 pagesEssays Expository TextsEddie BaezNo ratings yet
- Hypersexual DisorderDocument8 pagesHypersexual DisorderAndra ComanNo ratings yet
- FFMedicalDevicesRules2017Notifiedon16 01 2018Document93 pagesFFMedicalDevicesRules2017Notifiedon16 01 2018Anonymous dukfCrCBdnNo ratings yet
- (Serbian Journal of Dermatology and Venereology) National Guidelines For The Treatment of Atopic DermatitisDocument25 pages(Serbian Journal of Dermatology and Venereology) National Guidelines For The Treatment of Atopic DermatitisFebtri IRnawitaNo ratings yet
- Malignant Diseases of The CervixDocument128 pagesMalignant Diseases of The Cervixnicewan0% (1)
- VRP One Page Handout 3-11-10Document1 pageVRP One Page Handout 3-11-10Jennifer TankersleyNo ratings yet
- Rectal Prolapse PDFDocument92 pagesRectal Prolapse PDFadel santos100% (2)
- Placenta PreviaDocument2 pagesPlacenta PreviaIrish Joy S. DecrepitoNo ratings yet
- Tech TriageDocument50 pagesTech TriagefadiNo ratings yet
- NSTPDocument2 pagesNSTPBernadette ArrojoNo ratings yet
- Pedoman Nasional Pengendalian TuberkulosisDocument111 pagesPedoman Nasional Pengendalian TuberkulosisYusriNo ratings yet