0% found this document useful (0 votes)
99 views8 pagesUnderstanding CT Scans and Technology
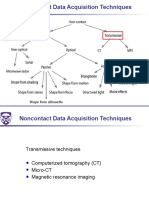
CT scans use X-rays and a computer to create detailed cross-sectional images of the body. Multiple X-ray measurements are taken from different angles and processed with a computer to produce tomographic images without requiring surgery. CT scans provide more detail than regular X-rays and can show the internal structure of organs, bones, and tissues. The technique involves aiming a narrow X-ray beam around the body to generate signals that are computed to produce slices and cross-sectional images.
Uploaded by
Nehar YusophCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
99 views8 pagesUnderstanding CT Scans and Technology
CT scans use X-rays and a computer to create detailed cross-sectional images of the body. Multiple X-ray measurements are taken from different angles and processed with a computer to produce tomographic images without requiring surgery. CT scans provide more detail than regular X-rays and can show the internal structure of organs, bones, and tissues. The technique involves aiming a narrow X-ray beam around the body to generate signals that are computed to produce slices and cross-sectional images.
Uploaded by
Nehar YusophCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd