Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Bee Performance Management Systems Compared
Uploaded by
Jigar PatelOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Bee Performance Management Systems Compared
Uploaded by
Jigar PatelCopyright:
Available Formats
Performance
Management
Balanced Score Card
LOGO
Bees Inc.
Two beekeepers(BeeX & BeeY), each with a bee hive
Customers loved their honey, demand increased
Management of Bees Inc. assigned both beekeepers
to increase honey production
Bees Inc. (BeeX)
BeeX established a performance
management approach that measured
“The number of flowers each bee visited”
Bees Inc. (BeeY)
BeeY measured two aspects of bees
performance
The amount of nectar each bee brought back to the
hive
The amount of honey the beehive produced
Performance Management
Performance management reminds us
that being busy is not the same as
producing results. It reminds us that
training, strong commitment and lots of
hard
Work alone are not results. The major
contribution of performance management
is its focus on achieving results
Performance management redirects our
efforts away from busyness toward
effectiveness.
Performance
Performance is often defined simply in
output terms – the achievement of
quantified objectives. But performance is
a matter not only of what people achieve
but how they achieve it.
High performance results from
appropriate behavior, especially
discretionary behavior, and the effective
use of the required knowledge, skills and
competencies.
Performance Management
Performance means both behaviors and results.
Behaviors emanate from the performer and
transform performance from abstraction to action.
Not just the instruments for results, behaviors are
also outcomes in their own right – the product of
mental and physical effort applied to tasks – and can
be judged apart from results.’
This definition of performance leads to the
conclusion that when managing performance both
inputs (behavior) and outputs (results) need to be
considered.
It is not a question of simply considering the
achievement of targets as used to happen in
management-by-objectives schemes.
Competence factors need to be included in the
process.
This is the so-called ‘mixed model’ of performance
management, which covers the achievement of
expected levels of competence as well as objective
setting and review.
Performance Measurement Systems
Limitations of Financial Control Systems:
Relying solely on financial measurements is
inadequate.
It may encourage short term actions that are not
in company’s long term interests
Bausch & Lomb (1993)
Some divisional presidents under pressure to
produce bottom line results adopt tactics which
maximized short term bonuses but harmed
company in long term.
“Under pressure to beat sales target in 1993,
B&L managers shipped products that doctor
never ordered and forced distributors to take up
two years of unwanted inventory, while assuring
many that they wouldn’t have to pay till they
sold the lenses.
(Source: BusinessWeek)
Balanced Scorecard
Balanced Scorecard is a tool developed
by Robert S. Kaplan and David P. Norton.
“The Balanced Scorecard translates an
organization's mission and strategy into a
comprehensive set of performance
measures that provides the framework
for a strategic measurement and
management system.”
Balanced Scorecard – Why?
• Important to have a plan, set goals, and
measure your success
• Having a plan is more important than the
specific tool you use
• “Holistic” approach that extends beyond
financials measures and incorporates
other priorities
• Linking strategic institutional plans and
priorities
Objectives of Balanced Scorecard
Consistently deliver superb customer
experience
Optimize resource utilization and be
accountable and financial stewards
Achieve operational excellence in our
internal processes
Organization must consistently strive for
learning and growth
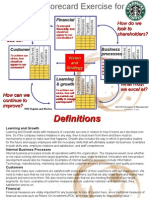
Balanced Scorecard
Financial Perspective
How do we appear to our
How should we stakeholders?
appear to our Goals
customers? What financial outcomes do we
Measures need to generate?
Are they satisfied?
Organizational Learning
Customer Perspective
Perspective
Goals
Vision and Goals
Measures
Strategy Measures
Are we able to sustain
Process/Product innovation, change and
What business processes improvement?
must we excel at to satisfy Perspective
How will we maintain our
our customers?
ability to meet customer
Are these processes expectations?
Goals
effective (i.e., adding value
for customers)? Measures
Are they efficient?
Customer Perspective
How do customers see us?
ECI (Electronic Circuits Incorporated, , a
semi conductor company) established
general goals for customer performance
Get standard products to the market sooner
Improve customers’ time to market
Become customers supplier of choice
through partnerships
Develop innovative product tailored to
customer needs
Customer Perspective
Goals Measures
New Products Percentage of sales from new
products
Percentage of sales from
proprietary products
Responsive Supply On – Time Delivery (as defined by
Customer)
Preferred Suppliers Share of key accounts’ purchases
Ranking by key accounts
Customer partnerships Number of cooperative
engineering efforts
Financial Perspective
How do we look to our shareholders
ECIs Goals
To Survive
To Succeed
To Prosper
Financial Perspective
Goals Measures
Survive Cash Flow
Succeed Quarterly sales growth and
operating income by division
Prosper Increased market share and ROE
Internal Business Perspective
What must we excel at?
Managers at ECI identified the following:
Submicron technology was critical to its
market position
Have to focus on manufacturing excellence
Design productivity
New product introduction
Internal Business Perspective
Goals Measures
Technology Capability Manufacturing geometry versus
competition
Manufacturing Excellence Cycle Time, Unit Cost, Yield
Design productivity Silicon efficiency, engineering
efficiency
New product introduction Actual introduction schedule
versus plan
Innovation & Learning Perspective
Intense global competition requires that
companies make Continual improvement
ECIs innovation measures focus on the
company’s ability to develop and
introduce standard products rapidly, the
products that the company expects will
be the bulk of its future sales
Innovation and Learning
Goals Measures
Technology leadership Time to develop next generation
Manufacturing learning Process time to maturity
Product focus Percentage of products that equal
80% of sales
Time to market New product introduction versus
competition
Thank You
You might also like
- Why Do Strategic Plans Fail?Document33 pagesWhy Do Strategic Plans Fail?Shilpi KhuranaNo ratings yet
- Balanced ScorecardDocument72 pagesBalanced ScorecardBalaji Sekar100% (1)
- Non-Financial Performance MeasuresDocument41 pagesNon-Financial Performance MeasuresSandeep SonawaneNo ratings yet
- Balanced ScorecardDocument13 pagesBalanced ScorecardRamalingam ChandrasekharanNo ratings yet
- Balance Scorecard of TcsDocument17 pagesBalance Scorecard of TcsKrishna Chaitanya100% (2)
- Performance Measurement Week 5: Chapter 11Document43 pagesPerformance Measurement Week 5: Chapter 11cheesywedges20No ratings yet
- Module 5 Strategy Evaluation - Implementation and BSCDocument25 pagesModule 5 Strategy Evaluation - Implementation and BSCSidharth ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- BSC - Strategic Focus OrgDocument16 pagesBSC - Strategic Focus OrgmorinNo ratings yet
- The Balanced Scorecard (Review and Analysis of Kaplan and Norton's Book)From EverandThe Balanced Scorecard (Review and Analysis of Kaplan and Norton's Book)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- BFT 509 Accounting for Business Performance Measurement SystemDocument22 pagesBFT 509 Accounting for Business Performance Measurement SystemtcsNo ratings yet
- Hafiz AhsanDocument10 pagesHafiz AhsanjosephNo ratings yet
- Strategic Performance Measurement Balanced ScorecardDocument33 pagesStrategic Performance Measurement Balanced ScorecardJanes VuNo ratings yet
- Measuring Supply Chain PerformanceDocument25 pagesMeasuring Supply Chain PerformanceSumit ChaherNo ratings yet
- Balance ScorecardDocument25 pagesBalance ScorecardJia BarrientosNo ratings yet
- Balanced Scorecard GuideDocument38 pagesBalanced Scorecard Guideedward100% (1)
- Bahan Ajar SCM 13Document18 pagesBahan Ajar SCM 13Budy AriyantoNo ratings yet
- Using the Balanced Scorecard for Improving Quality in EducationDocument13 pagesUsing the Balanced Scorecard for Improving Quality in EducationHowaidaNo ratings yet
- Balanced Score Card & Giving FeedbackDocument35 pagesBalanced Score Card & Giving FeedbacksupriyanairNo ratings yet
- Balanced ScorecardDocument32 pagesBalanced Scorecardfaney singh100% (3)
- Module 4 Balanced ScorecardDocument35 pagesModule 4 Balanced ScorecardWendryNo ratings yet
- SOPDocument44 pagesSOPDian SugiartoNo ratings yet
- Workshop Tips & Trik "Lolos" UJI KompetensiDocument44 pagesWorkshop Tips & Trik "Lolos" UJI KompetensiGatot HarmonoNo ratings yet
- 4.7.2020 Strategic Management Lecture OneDocument45 pages4.7.2020 Strategic Management Lecture OneSohel MahmudNo ratings yet
- Balance Score Card IntroductionDocument24 pagesBalance Score Card Introductionsushant_sNo ratings yet
- Balanced Scorecard: The BS PhilosophyDocument6 pagesBalanced Scorecard: The BS PhilosophyFarNo ratings yet
- BSC and Pms Abhay 205Document42 pagesBSC and Pms Abhay 205Misganaw GishenNo ratings yet
- Business Process Mapping: How to improve customer experience and increase profitability in a post-COVID worldFrom EverandBusiness Process Mapping: How to improve customer experience and increase profitability in a post-COVID worldNo ratings yet
- Week 8a Business Strategy - Implementing StrategyDocument21 pagesWeek 8a Business Strategy - Implementing StrategyAlejandro CardonaNo ratings yet
- Balanced Scorecard 2Document45 pagesBalanced Scorecard 2Balaji Sekar100% (1)
- Presentasi Balanced ScorecardDocument43 pagesPresentasi Balanced Scorecardvivi vidya100% (1)
- The Balanced ScorecardDocument13 pagesThe Balanced Scorecardssb_74100% (2)
- Balanced Scorecard: Your Company NameDocument32 pagesBalanced Scorecard: Your Company NameSheika SuhailNo ratings yet
- Chapter-12: Evaluation of Strategies and Performance MeasurementDocument15 pagesChapter-12: Evaluation of Strategies and Performance MeasurementTamim All HasanNo ratings yet
- Topic Five - Strategies in ActionDocument9 pagesTopic Five - Strategies in ActionZeytun GodanaNo ratings yet
- Performance Management, Evaluation, and Data AnalysisDocument18 pagesPerformance Management, Evaluation, and Data AnalysiscandraNo ratings yet
- Brief Introduction On Balanced Scorecard Concept For Strategic AlignmentDocument25 pagesBrief Introduction On Balanced Scorecard Concept For Strategic AlignmentAjay GuptaNo ratings yet
- Models of Improving Operations: Chapter EightDocument35 pagesModels of Improving Operations: Chapter EightAbdiNo ratings yet
- B Konsep Manajemen KeperawatanDocument3 pagesB Konsep Manajemen KeperawatanRohmatullahNo ratings yet
- Strategic Balanced Management ScorecardDocument34 pagesStrategic Balanced Management ScorecardKumar ManojNo ratings yet
- Week 8a Business Strategy - Implementing StrategyDocument21 pagesWeek 8a Business Strategy - Implementing StrategyAlejandro CardonaNo ratings yet
- WEEK 8A BUSINESS STRATEGY - Implementing StrategyDocument21 pagesWEEK 8A BUSINESS STRATEGY - Implementing StrategyAlejandro CardonaNo ratings yet
- Managing Corporate Performance with Balanced ScorecardDocument83 pagesManaging Corporate Performance with Balanced ScorecardT Ferdinand S Lumbantobing100% (1)
- Balance Scorecard - An Effective ToolDocument27 pagesBalance Scorecard - An Effective ToolParimal JariwalaNo ratings yet
- Sir M Visvesvaraya Institute of Management StudiesDocument32 pagesSir M Visvesvaraya Institute of Management StudiesMonil VisariyaNo ratings yet
- One Page Plan ExampleDocument7 pagesOne Page Plan ExampleBhinitha Chandrasagaran100% (2)
- Balanced Scorecard ExplainedDocument33 pagesBalanced Scorecard Explainedshahzad2689100% (2)
- Chapter 4Document4 pagesChapter 4Mixx MineNo ratings yet
- Balanced Scorecard GuideDocument19 pagesBalanced Scorecard GuidejhafjfNo ratings yet
- The Balanced Scorecard: Turn your data into a roadmap to successFrom EverandThe Balanced Scorecard: Turn your data into a roadmap to successRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (4)
- KPI: Individual Performance To Make Organization GreatDocument28 pagesKPI: Individual Performance To Make Organization GreatMetoo ChyNo ratings yet
- Functional Strategy ImplementationDocument41 pagesFunctional Strategy ImplementationEriNo ratings yet
- 1lecture One SMDocument41 pages1lecture One SMবুঝ বালকNo ratings yet
- Tutorial PMS Non-Financial MeasuresDocument10 pagesTutorial PMS Non-Financial MeasuresAisyah ShahidanNo ratings yet
- Session 2-Charting A Company's DirectionDocument34 pagesSession 2-Charting A Company's DirectionJosephine MargarettaNo ratings yet
- Engineering Marketing Plan by SlidesgoDocument41 pagesEngineering Marketing Plan by SlidesgoJohansonNo ratings yet
- Balanced Scorecard Measures Drive PerformanceDocument15 pagesBalanced Scorecard Measures Drive PerformanceSampat MishraNo ratings yet
- Operations Management For Hospitality ManagemenDocument41 pagesOperations Management For Hospitality ManagemenAngelo Chistian OreñadaNo ratings yet
- SCM - 16 - Performance MeasurementDocument28 pagesSCM - 16 - Performance MeasurementVishesh khandelwalNo ratings yet
- 2023 SMA Lecture 10Document47 pages2023 SMA Lecture 10Haniie NguyenNo ratings yet
- Strategic Map and Balanced Score Card With Case StudyDocument25 pagesStrategic Map and Balanced Score Card With Case StudySyamly Sathyan100% (7)
- Balanced Scorecard-Enabled Project ManagementDocument40 pagesBalanced Scorecard-Enabled Project ManagementEdson Andres Valencia SuazaNo ratings yet
- KPMG & INFOSYS BALANCE SCORECARDSDocument18 pagesKPMG & INFOSYS BALANCE SCORECARDSAditya Rahmaniac100% (1)
- Microsoft Balanced Scorecard Framework5Document33 pagesMicrosoft Balanced Scorecard Framework5abcdeNo ratings yet
- The Balanced Scorecard: A Tool To Implement StrategyDocument39 pagesThe Balanced Scorecard: A Tool To Implement StrategyAilene QuintoNo ratings yet
- Assignment HR Audit SKMDocument6 pagesAssignment HR Audit SKMAiman BegNo ratings yet
- BALANCED SCORECARD - SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT TOOL-dikonversi PDFDocument9 pagesBALANCED SCORECARD - SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT TOOL-dikonversi PDFisabellaNo ratings yet
- Corporate Performance Management: An OverviewDocument42 pagesCorporate Performance Management: An OverviewgoomezNo ratings yet
- Elearning For Building & Managing The Balanced Scorecard Course ManualDocument133 pagesElearning For Building & Managing The Balanced Scorecard Course ManualFlorin Marius PopaNo ratings yet
- Balanced Scorecard Exercise Lecture 5Document5 pagesBalanced Scorecard Exercise Lecture 5MktgProf50% (2)
- Comparison of Strategic Planning Models and FrameworksDocument14 pagesComparison of Strategic Planning Models and FrameworksRiz DeenNo ratings yet
- Activity-Based Costing (ABC) ExplainedDocument5 pagesActivity-Based Costing (ABC) ExplainedTiffy LouiseNo ratings yet
- 10 18400-Tekderg 977849-1905248Document28 pages10 18400-Tekderg 977849-1905248sushil.tripathiNo ratings yet
- Management Advisory Services Strategic Cost Management: MAS - 1.2.7 Integrated Review & Refresher Course R.D.BalocatingDocument3 pagesManagement Advisory Services Strategic Cost Management: MAS - 1.2.7 Integrated Review & Refresher Course R.D.BalocatingVanessa Arizo ValenciaNo ratings yet
- Balance Scorecard ReviewDocument72 pagesBalance Scorecard Reviewapi-3781744100% (1)
- Effectiveness and Efficiency-MBA 631Document22 pagesEffectiveness and Efficiency-MBA 631Manasseh Abimaje100% (1)
- Balanced Scorecard and Benchmarking StrategiesDocument12 pagesBalanced Scorecard and Benchmarking StrategiesGaurav Sharma100% (1)
- Strategic Planning ModelDocument55 pagesStrategic Planning ModelShamkant KomarpantNo ratings yet
- BBP Ford Final - SkyDocument18 pagesBBP Ford Final - SkyAvula Shravan YadavNo ratings yet
- Principles of Total Quality ManagementDocument17 pagesPrinciples of Total Quality Managementsinghashish5444No ratings yet
- Managing Markets Strategically: Professor Noel CaponDocument53 pagesManaging Markets Strategically: Professor Noel CaponMoidin AfsanNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Managerial Accounting 10th Edition by HiltonDocument19 pagesSolution Manual For Managerial Accounting 10th Edition by Hiltona46078460233% (3)
- U T B S A: A G E: Sing HE Alance Corecard Pproach Roup XerciseDocument7 pagesU T B S A: A G E: Sing HE Alance Corecard Pproach Roup XerciseAlena MatskevichNo ratings yet
- BSC - Balanced Scorecard and IT GovernanceDocument4 pagesBSC - Balanced Scorecard and IT GovernanceriyasbasheerNo ratings yet
- Kenyon StoresDocument123 pagesKenyon StoresSourav AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Syllabus Mata Kuliah Strategic Cost ManagementDocument5 pagesSyllabus Mata Kuliah Strategic Cost ManagementLarasati LarasNo ratings yet
- Reyes Fitness Centers Inc - IMDocument22 pagesReyes Fitness Centers Inc - IMMohammad Rafiq100% (1)
- Introduction to Cost AccountingDocument10 pagesIntroduction to Cost AccountingaiswiftNo ratings yet