0% found this document useful (0 votes)
823 views15 pagesWorld System Theory & Neo-Marxism Explained
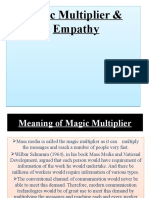
World systems theory posits that the global economy consists of core countries that dominate and exploit peripheral countries for resources and labor. This leads to unequal development and benefits core nations. Dependency theory built on this by arguing developing nations are structurally different and need indigenous models rather than following the path of industrialized nations. Immanuel Wallerstein further developed world systems analysis to argue a capitalist world economy emerged in the 16th century, indirectly resulting in unequal development as Europe gained control over most of the global economy. Neo-Marxist theories critique and build on Marxism to analyze ongoing exploitation and unequal power dynamics in the global capitalist system.
Uploaded by
Gauri GargCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
823 views15 pagesWorld System Theory & Neo-Marxism Explained
World systems theory posits that the global economy consists of core countries that dominate and exploit peripheral countries for resources and labor. This leads to unequal development and benefits core nations. Dependency theory built on this by arguing developing nations are structurally different and need indigenous models rather than following the path of industrialized nations. Immanuel Wallerstein further developed world systems analysis to argue a capitalist world economy emerged in the 16th century, indirectly resulting in unequal development as Europe gained control over most of the global economy. Neo-Marxist theories critique and build on Marxism to analyze ongoing exploitation and unequal power dynamics in the global capitalist system.
Uploaded by
Gauri GargCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
- Non-linear: World System Theory
- Non-linear: World System Theory, Neo Marxist Theory
- Neo Marxist Theory