0% found this document useful (0 votes)
615 views20 pagesFour Conic Sections: Cone Intersecting A Plane
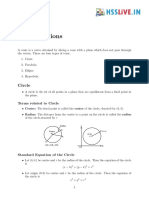
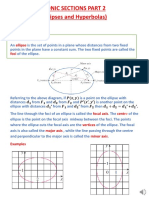
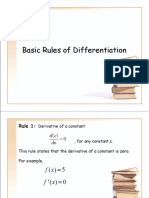
This document discusses the four conic sections - parabolas, ellipses, hyperbolas, and circles - formed by intersecting a plane with a cone. It provides definitions and key properties of each type of conic section, including their equations in standard form and how to identify their components like foci, vertices, axes and asymptotes. Examples of each with accompanying problems are presented to illustrate how to find equations, graph the shapes, and identify conic sections from equations.
Uploaded by
Wendell ReyesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
615 views20 pagesFour Conic Sections: Cone Intersecting A Plane
This document discusses the four conic sections - parabolas, ellipses, hyperbolas, and circles - formed by intersecting a plane with a cone. It provides definitions and key properties of each type of conic section, including their equations in standard form and how to identify their components like foci, vertices, axes and asymptotes. Examples of each with accompanying problems are presented to illustrate how to find equations, graph the shapes, and identify conic sections from equations.
Uploaded by
Wendell ReyesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd