0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1K views11 pagesCognitive-Code Learning: Carlos Bello Laurent Flórez
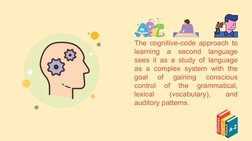
The cognitive-code approach sees language learning as gaining conscious control over grammatical, lexical, and auditory patterns through cognitive processing. It emphasizes helping students reflect on their experiences, explore connections between ideas, and justify their thinking. While it revived an emphasis on grammar and cognitive effort in learning, weaknesses include a lack of specific teaching methods and use of authentic materials.
Uploaded by
dulce crissCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1K views11 pagesCognitive-Code Learning: Carlos Bello Laurent Flórez
The cognitive-code approach sees language learning as gaining conscious control over grammatical, lexical, and auditory patterns through cognitive processing. It emphasizes helping students reflect on their experiences, explore connections between ideas, and justify their thinking. While it revived an emphasis on grammar and cognitive effort in learning, weaknesses include a lack of specific teaching methods and use of authentic materials.
Uploaded by
dulce crissCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
- Cognitive-Code Learning Overview
- Approach vs. Method
- Teacher’s Role
- Student’s Role
- Examples of Cognitive Learning Strategies
- Strength of the Cognitive-Code Learning Theory
- Weaknesses of Cognitive-Code Learning Theory
- Learning from Home