Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Types of Nouns and Adjectives Explained
Uploaded by
Prayoga Saputra Sugiarto0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views14 pagesOriginal Title
Noun and adjective
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views14 pagesTypes of Nouns and Adjectives Explained
Uploaded by
Prayoga Saputra SugiartoCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 14
After completing this material the students
are able to:
Explain the definition of noun and types of
noun
Identify the types of noun in a song text
What is a Noun?
A noun is a word used to name a person,
animal, place, thing, and abstract idea.
Nouns are usually the first words which small
children learn. Example:
Late last year our neighbors bought a goat.
Portia White was an opera singer.
There are many different types of nouns.The
proper noun, the common noun, the
concrete noun, the abstract noun, the
countable noun, the non-countable noun
(also called the mass noun), and the
collective noun. You should note that a noun
will belong to more than one type: it will be
proper or common, abstract or concrete,
and countable or non-countable or
collective.
You always write a proper noun with a capital
letter, since the noun represents the name of a
specific person, place, or thing. The names of
days of the week, months, historical documents,
institutions, organizations, religions, the holy
texts. A proper noun is the opposite of a
common noun
In each of the following sentences, the proper
nouns are :
-Many people dread Monday mornings.
-Abraham appears in the Talmud and in the Koran.
A common noun is a noun referring to a
person, place, or thing in a general sense
usually, you should write it with a capital
letter only when it begins a sentence.
-In each of the following sentences, the
common nouns are:
According to the sign, the nearest town is 60
miles away.
All the gardens in the neighborhood were
invaded by beetles this Summer.
A concrete noun is a noun which names
anything (or anyone) that you can perceive
through your physical senses: touch, sight,
taste, hearing, or smell. A concrete noun is
the opposite of a abstract noun.
-The highlighted words in the following
sentences are all concrete nouns:
The judge handed the files to the clerk.
Whenever they take the dog to the beach, it
spends hours chasing waves.
An abstract noun is a noun which names
anything which you can not perceive through
your five physical senses. The highlighted
words in the following sentences are all
abstract nouns:
Buying the fire extinguisher was an
afterthought.
Tillie is amused by people who are nostalgic
about childhood.
Justice often seems to slip out of our grasp.
A countable noun (or count noun) is a noun
with both a singular and a plural form, and it
names anything (or anyone) that you can
count. Countable nouns are the opposite of
non-countable nouns and collective nouns.
-In each of the following sentences, the
highlighted words are countable nouns:
We painted the table red and the chairs
blue.
Since he inherited his aunt's library, Jerome
spends every weekend indexing his books.
A non-countable noun (or mass noun) is a
noun which does not have a plural form, and
which refers to something that you could (or
would) not usually count.
-The highlighted words in the following
sentences are non-countable nouns:
Joseph Priestly discovered oxygen.
The word "oxygen" cannot normally be made
plural.
Oxygen is essential to human life.
A collective noun is a noun naming a group of
things, animals, or persons. You could count
the individual members of the group, but you
usually think of the group as a whole is
generally as one unit. Example: a class of
students,an army of soldiers, a zoo of wild
animals.
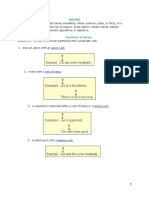
An adjective modifies a noun or a pronoun by
describing, identifying, or quantifying words.
An adjective usually precedes the noun or
the pronoun which it modifies.
In the following examples, the highlighted
words are adjectives:
The truck-shaped balloon floated over the
treetops.
Mrs. Morrison papered her kitchen walls with
hideous wall paper.
The coal mines are dark and dank.
A possessive adjective ("my," "your," "his,"
"her," "its," "our," "their") is similar or
identical to a possessive pronoun; however,
it is used as an adjective and modifies a noun
or a noun phrase, as in the following
sentences:
I can't complete my assignment because I
don't have the textbook.
The demonstrative adjectives "this," "these,"
"that," "those," and "what" are identical to the
demonstrative pronouns, but are used as
adjectives to modify nouns or noun phrases, as
in the following sentences:
When the librarian tripped over that cord, she
dropped a pile of books.
In this sentence, the demonstrative adjective
"that" modifies the noun "cord" and the noun
phrase "that cord" is the object of the
preposition "over."
This apartment needs to be fumigated.
An indefinite adjective is similar to an
indefinite pronoun, except that it modifies a
noun, pronoun, or noun phrase, as in the
following sentences:
Many people believe that corporations are
under-taxed.
The indefinite adjective "many" modifies the
noun "people" and the noun phrase "many
people" is the subject of the sentence.
I will send you any mail that arrives after you
have moved to Sudbury.
You might also like
- What is a Noun? Types of Nouns ExplainedDocument5 pagesWhat is a Noun? Types of Nouns ExplainedAllen Cornelius YongNo ratings yet
- GrammarDocument13 pagesGrammarWong AgungNo ratings yet
- The Grammar Bible: Everything You Always Wanted to Know About Grammar but Didn't Know Whom to AskFrom EverandThe Grammar Bible: Everything You Always Wanted to Know About Grammar but Didn't Know Whom to AskRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (25)
- Assignment On NounsDocument14 pagesAssignment On NounsRobert Encila100% (7)
- Parts of SpeechDocument11 pagesParts of SpeechAyesha AsifNo ratings yet
- What Is A NounDocument17 pagesWhat Is A NounDin Lin WongNo ratings yet
- The Noun ExplainedDocument4 pagesThe Noun Explainedveruncik1991No ratings yet
- Guide to Nouns, Their Types and FunctionsDocument28 pagesGuide to Nouns, Their Types and FunctionsLady Amor Telompros PeroteNo ratings yet
- What Is A Noun2Document20 pagesWhat Is A Noun2Awaludin MohamadNo ratings yet
- Nouns: Noun of AddressDocument41 pagesNouns: Noun of AddressGekchieng YeoNo ratings yet
- Topic 5Document33 pagesTopic 5Patri CardielNo ratings yet
- Everything You Need to Know About NounsDocument5 pagesEverything You Need to Know About NounsIbnu ShinaNo ratings yet
- Types of Nouns: Common, Proper, Concrete, Abstract, Countable, Non-Countable & CollectiveDocument4 pagesTypes of Nouns: Common, Proper, Concrete, Abstract, Countable, Non-Countable & CollectiveNicole Erika LopezNo ratings yet
- Parts of Speech GuideDocument15 pagesParts of Speech GuideBEO.Teacher ChuNo ratings yet
- Learn Noun and Pronoun Types (39Document7 pagesLearn Noun and Pronoun Types (39Praja Putra Galuh ChiliandraNo ratings yet
- As2022 23:pgd:nounsDocument27 pagesAs2022 23:pgd:nounsKashvii SinghaniaNo ratings yet
- KKP Elp The LatestDocument45 pagesKKP Elp The LatestKulas KungNo ratings yet
- Campus Life GrammarDocument10 pagesCampus Life Grammarsanti setiyaningsihNo ratings yet
- Seminarski Rad Engleski JezikDocument19 pagesSeminarski Rad Engleski JezikTamara Tasha MarkovicNo ratings yet
- Common Parts of SpeechDocument4 pagesCommon Parts of SpeechxBluEx100% (1)
- Types of NounsDocument5 pagesTypes of NounsnarutothunderjetNo ratings yet
- Types of Nouns Explained in DetailDocument7 pagesTypes of Nouns Explained in Detailshara santosNo ratings yet
- Waj3102 ELP1 JUN 2011Document150 pagesWaj3102 ELP1 JUN 2011Jennifer WebbNo ratings yet
- WEEK 1 The 8 Parts of Speech-1Document26 pagesWEEK 1 The 8 Parts of Speech-1Aya MeftiNo ratings yet
- PARTS OF SPEECH ProjectDocument13 pagesPARTS OF SPEECH ProjectSãéèďNo ratings yet
- Parts of Speech: Click To Edit Master Subtitle StyleDocument25 pagesParts of Speech: Click To Edit Master Subtitle StyleTitih Ratih RidwanNo ratings yet
- Part of Speech: Written by Heather MacfadyenDocument17 pagesPart of Speech: Written by Heather MacfadyenanneNo ratings yet
- Parts of SpeechDocument17 pagesParts of SpeechJuank_14_12No ratings yet
- Parts of SpeechDocument45 pagesParts of SpeechVitaManiezt100% (3)
- Curso de Gramatica InglesDocument66 pagesCurso de Gramatica InglesJean Pierre Lara MartinezNo ratings yet
- Parts of SpeeckDocument13 pagesParts of SpeeckMarietta SzabóováNo ratings yet
- Confusing Words, Including Heteronyms; Or Why English is Difficult to LearnFrom EverandConfusing Words, Including Heteronyms; Or Why English is Difficult to LearnNo ratings yet
- Identifying Nouns in SentencesDocument4 pagesIdentifying Nouns in SentencesKryzl Rey del FierroNo ratings yet
- Kind of Noun Pronoun AdjectiveDocument26 pagesKind of Noun Pronoun Adjectivegian riskiNo ratings yet
- 2 Forum InglesDocument4 pages2 Forum InglesRaimundo AfonsoNo ratings yet
- Types of Nouns ExplainedDocument9 pagesTypes of Nouns ExplainedbobswapNo ratings yet
- 8 Parts of Speech ExplainedDocument15 pages8 Parts of Speech ExplainedTechnical InformationNo ratings yet
- Rticles Eterminers AND UantifiersDocument11 pagesRticles Eterminers AND UantifiersAnamaria BlajanNo ratings yet
- Noun Determiners: Discussant: Camposano, Rhodalyn P Year&Section: BSED-English 1st - ADocument6 pagesNoun Determiners: Discussant: Camposano, Rhodalyn P Year&Section: BSED-English 1st - AGewie Shane Blanco SumayopNo ratings yet
- English Grammar: Parts of SpeechDocument12 pagesEnglish Grammar: Parts of SpeechInfotainment and Entertainment Videos & MoviesNo ratings yet
- Parts of Speech GomezDocument25 pagesParts of Speech GomezsingcosweindinglasaNo ratings yet
- Types of Nouns: Demonstrative PronounsDocument12 pagesTypes of Nouns: Demonstrative Pronounsanon_132777102No ratings yet
- ESSENTIAL ENGLISH GRAMMAR GUIDEDocument32 pagesESSENTIAL ENGLISH GRAMMAR GUIDEhalconfenixNo ratings yet
- Intermediate C Noun and Noun PhraseDocument9 pagesIntermediate C Noun and Noun PhraseFauss ForeverNo ratings yet
- Noun Study in Detail TypesDocument11 pagesNoun Study in Detail Typessofyankhan336No ratings yet
- What Is A PronounDocument9 pagesWhat Is A PronounFanera JefferyNo ratings yet
- Learn the Key Parts of Speech: Nouns, Pronouns, AdjectivesDocument2 pagesLearn the Key Parts of Speech: Nouns, Pronouns, AdjectivesShahzad BhuttaNo ratings yet
- The Noun: Morphological CompositionDocument12 pagesThe Noun: Morphological CompositionJoane MassaNo ratings yet
- The Definite and Indefinite Articles: Uses and FunctionsDocument7 pagesThe Definite and Indefinite Articles: Uses and FunctionsMariana PerussiaNo ratings yet
- ESOL parts of speech guideDocument18 pagesESOL parts of speech guideSharib SheraziNo ratings yet
- Word ClassificationDocument28 pagesWord ClassificationmiftaNo ratings yet
- Part of SpeechDocument25 pagesPart of SpeecharumdiyasNo ratings yet
- Noun of Address: Nouns (Or Non-Count Nouns), Which Name Something That Can't Be Counted (Water, AirDocument16 pagesNoun of Address: Nouns (Or Non-Count Nouns), Which Name Something That Can't Be Counted (Water, Airmsaadshuib757390No ratings yet
- Common NounsDocument17 pagesCommon NounsAnne WongNo ratings yet
- What Is A NounDocument33 pagesWhat Is A NounBiee BarbNo ratings yet
- SpeechDocument15 pagesSpeechMahboob RiazNo ratings yet
- Such As Business in Business MeetingDocument15 pagesSuch As Business in Business MeetingPhoebe Cates Tayanes ViscaynoNo ratings yet
- What Is A NounDocument22 pagesWhat Is A NounSylvia GintingNo ratings yet
- Nouns: Action VerbDocument15 pagesNouns: Action VerbJerica PalomariaNo ratings yet
- Nouns Can Be Proper Nouns or Common NounsDocument18 pagesNouns Can Be Proper Nouns or Common NounsSi Aby ReyesNo ratings yet
- Lê,+U.T.+K+ 2015 .+Writing+level+3.+ENG+217+-+2020S+-+TEXTDocument69 pagesLê,+U.T.+K+ 2015 .+Writing+level+3.+ENG+217+-+2020S+-+TEXTMy Võ Hoàng0% (1)
- Understanding Subject, Object and Possessive PronounsDocument2 pagesUnderstanding Subject, Object and Possessive PronounsJung WooyoungNo ratings yet
- The Aromânians: An Ethnos and Language With A 2000-Year History - Nikolai KyurkchievDocument16 pagesThe Aromânians: An Ethnos and Language With A 2000-Year History - Nikolai Kyurkchievvaler_crushuveanlu100% (2)
- Ingles Unidad 2Document34 pagesIngles Unidad 2Alex Alvarez Ramirez50% (4)
- Prepositions and phrasal verbsDocument25 pagesPrepositions and phrasal verbsЛюдмила Писаренко33% (3)
- ACT English Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesACT English Cheat SheetElza Amir FawzyNo ratings yet
- Ahw1 Sot U2 PDFDocument2 pagesAhw1 Sot U2 PDFHector EvangNo ratings yet
- Modern Chinese Textbook 1a Simplified CharactersDocument26 pagesModern Chinese Textbook 1a Simplified CharactersRenee CaiNo ratings yet
- Module Eng7Document8 pagesModule Eng7Sfa Mabini BatangasNo ratings yet
- Collins Easy Learning Grammar & Punctuation (In Colour) PDFDocument162 pagesCollins Easy Learning Grammar & Punctuation (In Colour) PDFwalteremm100% (3)
- ТЕСТ ЗА ПРОВЕРКА А1.1Document3 pagesТЕСТ ЗА ПРОВЕРКА А1.1StelaNo ratings yet
- 01 PronounDocument5 pages01 PronounJumriah AnandaNo ratings yet
- Grammar Book 1Document121 pagesGrammar Book 1Sri RamayantiNo ratings yet
- The Syntax and Morphology of Honorification in NahuatlDocument40 pagesThe Syntax and Morphology of Honorification in NahuatlEduardo PonceNo ratings yet
- Structure Iii - C - ModuleDocument145 pagesStructure Iii - C - ModuleFarrah Dhiba HernindyaNo ratings yet
- PronounsDocument11 pagesPronounsosiris_isis297No ratings yet
- CBR Bahasa Inggris Martua EriksonDocument17 pagesCBR Bahasa Inggris Martua EriksonErikson SilabanNo ratings yet
- Santo Domingo Bilingual School Eleventh Grade ExerciseDocument41 pagesSanto Domingo Bilingual School Eleventh Grade ExerciseLiliana LopezNo ratings yet
- Subject and Object Pronouns. Possessive AdjectivesDocument1 pageSubject and Object Pronouns. Possessive AdjectivesNora NaserNo ratings yet
- Mbetrix Skill I - 29Document44 pagesMbetrix Skill I - 29mbetrix100% (5)
- Grammar For TeachersDocument66 pagesGrammar For Teachersapi-3765132100% (2)
- Possessive Nouns: by Lyka P. Ladon Beed Iii-2Document24 pagesPossessive Nouns: by Lyka P. Ladon Beed Iii-2Lyka LadonNo ratings yet
- PARTS OF SPEECH-WPS OfficeDocument18 pagesPARTS OF SPEECH-WPS OfficeGine Bert Fariñas Palabrica100% (2)
- North African Story Vocabulary LessonDocument2 pagesNorth African Story Vocabulary Lessonjuan manuelNo ratings yet
- English GrammarDocument122 pagesEnglish GrammarE5251888100% (5)
- SEDABook Beginner NewEdition Dec20Document76 pagesSEDABook Beginner NewEdition Dec20Cleiton XavierNo ratings yet
- To Access A Library of Interactive ESL Lessons Complete With Teacher Notes, Lesson Summaries, Homework and Games, Visit Us atDocument22 pagesTo Access A Library of Interactive ESL Lessons Complete With Teacher Notes, Lesson Summaries, Homework and Games, Visit Us atMilena MilchovaNo ratings yet
- English stress and rhythm patternsDocument3 pagesEnglish stress and rhythm patternsiammiguelsalacNo ratings yet
- Peace Corps Marshallese Language Training ManualDocument96 pagesPeace Corps Marshallese Language Training ManualHamid LeNo ratings yet
- A Complete Grammar of EsperantoDocument448 pagesA Complete Grammar of EsperantoCatalin VoinescuNo ratings yet