Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ASHWIN RAM (Cology Dept) MPAT SEMINAR 1
Uploaded by
ASHWIN RAM0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views33 pagesOriginal Title
ASHWIN RAM(cology dept) MPAT SEMINAR 1
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views33 pagesASHWIN RAM (Cology Dept) MPAT SEMINAR 1
Uploaded by
ASHWIN RAMCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 33
MODERN
PHARMACEUTICAL
ANALYTICAL TECHNIQUE
SEMINAR-1
COUPLING CONSTANT AND ITS
APPLICATION
Submitted to, Presented by,
Dr.A.RAJASEKARAN ASHWIN RAM R
PRINCIPAL & PROFESSOR Master of pharmacy
DEPT OF PHARMACEUTICAL ANALYSIS
Pharmacology Department
KMCH COLLEGE OF PHARMACY
KMCH COLLEGE OF PHARMACY
11/29/2021 MPAT COUPLING CONSTANT 1
CONTENT
Spectroscopy
NMR
Spin -spin coupling
Coupling constant
Factors affecting coupling constant
Applications
11/29/2021 MPAT COUPLING CONSTANT 2
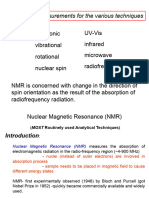
SPECTROSCOPY
DEFENITION:
• It is the study of sample with
respect to interaction of
Electromagnetic
Radiation(EMR).
• EMR: cosmic rays, gamma rays,
X-rays, UV rays, visible rays,
infrared radiation,
Micro waves, radio ways.
11/29/2021 MPAT COUPLING CONSTANT 3
NUCLEAR MAGNETIC RESONANCE
SPECTROSCOPY(NMR)
DEFENITION:
NMR is the study of determining the content
and purity of the sample as well as its
molecular structure by recording the
interaction of Radio frequency (Rf) with the
nuclei of molecules placed in a strong external
applied magnetic field (Ho).
11/29/2021 MPAT COUPLING CONSTANT 4
SPIN-SPIN COUPLING
DEFENITION:
The interaction between the spins of
neighbouring nuclei, non equivalent NMR
active nuclei(spin quantum number should be
more than zero) in a molecule may cause the
splitting of lines in the NMR spectrum. This is
known as spin-spin coupling.
11/29/2021 MPAT COUPLING CONSTANT 5
E.g. consider 1,1,2- tribromomethane(CHBr2-CH2Br)
which is having only two types of proton, therefore
its NMR spectrum may be have only 2 absorption
peaks but in actual practice the NMR spectrum
shows as many as 5 peaks in total.
11/29/2021 MPAT COUPLING CONSTANT 6
• The number of signals in NMR spectrum is
equal to number of type of protons present in
the given molecules. There being one signal
each for every set of equivalent protons.
• In the above example the NMR spectra
shows the presence of many more peaks than
the number of types of proton present in the
molecule.
11/29/2021 MPAT COUPLING CONSTANT 7
• This means that the individual signal which we
expect from a set of equivalent protons must
be appearing not as a single peak but as a
group of peak. This is called splitting of NMR
signal.
11/29/2021 MPAT COUPLING CONSTANT 8
PASCALS TRIANGLE
• The pascals triangle is a graphical device used
to determine the ratio of heights of lines in a
split NMR peak.
• The number of peaks which N into which a
proton signal is split up is equal to 1 more
than the number of Vicinal protons(n)[proton
attached to the adjacent carbon atom].
• N=n+1
11/29/2021 MPAT COUPLING CONSTANT 9
11/29/2021 MPAT COUPLING CONSTANT 10
11/29/2021 MPAT COUPLING CONSTANT 11
COUPLING CONSTANT
• The distance between the centre of two adjacent peaks in a
given multiplet is usually constant and is called as coupling
constant.
• The distance between two peaks for the resonance of one
nucleus split by another is a measure of how strongly the
nuclear spins influence each other.
• It is measured in Hertz (Hz) or in cycles per second (cps). It is
denoted by symbol “J”.
• The values of J generally lies upto 20 hertz.
11/29/2021 MPAT COUPLING CONSTANT 12
• For a pair of mutually coupled protons the
coupling constant due to splitting by one
proton has the same value as the coupling
constant due to splitting by second proton
11/29/2021 MPAT COUPLING CONSTANT 13
• Unlike the chemical shifts, the values of J are
independent of externally applied magnetic
field and depends only upon the molecular
structure. This is because the strength of the
magnetic moment of the neighbouring
proton, which is the responsible for spin-spin
coupling.
11/29/2021 MPAT COUPLING CONSTANT 14
FACTORS AFFECTING COUPLING CONSTANT
Various factor affecting:
1.Geminal coupling
2.vicinal coupling
3.Long range coupling
4. Aromatic group
11/29/2021 MPAT COUPLING CONSTANT 15
GEMINAL COUPLING
• The values of J varies upto 20 Hz.
• In case of geminal proton, the proton are
attached to the same carbon atoms where the
protons are in different environment i.e they
are not chemically equivalent.
• Here the values of J depending upon the bond
angle and overall structure of the molecule.
11/29/2021 MPAT COUPLING CONSTANT 16
• i.e. the bond angle is directly proportional to
the coupling constant. If the bond angle
increases the coupling constant also increases.
11/29/2021 MPAT COUPLING CONSTANT 17
• e.g.: Methane (109o) = (-12Hz)
Ethylene (> 117o) = (-2.5Hz).
BOND ANGLE J VA L U E
105O -25Hz
109O -12Hz
125O 0
>125O p o s i ti v e v a l u e
11/29/2021 MPAT COUPLING CONSTANT 18
VICINAL COUPLING
• The values J varies from 2-18Hz.
• The vicinal coupling, the protons are attached
to the adjacent carbon atoms, they are non
equivalent to each other.
11/29/2021 MPAT COUPLING CONSTANT 19
• Here the values of J are depending on the
dihedral angle (φ),valence angle(θ),bond
length of carbon and effect of electro
negative atom.
11/29/2021 MPAT COUPLING CONSTANT 20
• The dihedral angle is given by karplus
equation.
• KARPLUS EQUATION:
For 0-90o J = 8.5 Cos2 φ – 0.28
For 90-180o J = 9.5 Cos2 φ – 0.28
DIHEDRAL ANGLE J VALUE
0 or 180o positive value
90o 0 or negative value
11/29/2021 MPAT COUPLING CONSTANT 21
11/29/2021 MPAT COUPLING CONSTANT 22
For e.g.
1. Freely rotating proton i.e. proton with anti-
conformation have J = 5-12 Hz, while proton
with gauche conformation have J = 2-14Hz.
Eg: propane = 6.5 (Hz) (anti)
propane = 7.2 Hz (gauche)
11/29/2021 MPAT COUPLING CONSTANT 23
2. In Restricted rotating protons, due to double
bond is involved the cis form have J = 6-14Hz ,
trans form J = 11-18Hz.
Eg: ethyl chloride (cis) J = 10 Hz
(trans)J = 15 Hz
11/29/2021 MPAT COUPLING CONSTANT 24
LONG RANGE COUPLING
• Generally no coupling is observed the distance
between the two absorbing nuclei is more than
three covalent bond is called long range coupling.
• In some case appreciable coupling observed with
the help of high resolution spectrometer.
• In pi bond system appreciable coupling are
frequently observed even the protons are
separated by four or five bonds.
• Eg: 2,3 dimethyl butanoicacid = -1.2Hz
butene = -2.3Hz
11/29/2021 MPAT COUPLING CONSTANT 25
AROMATIC COUPLING
• Coupling constant is depends on whether the
coupling proton are present in ortho, meta,
para position.
• The range of coupling constant varies for
ortho = 7-10Hz para = 0-1Hz
meta = 1-3Hz
11/29/2021 MPAT COUPLING CONSTANT 26
OTHER FACTORS
• The substitution of deuterium for hydrogen
also affects the coupling constant.
• Substituent effect
1. The increase in electronegative atom or
group which withdraw sigma electrons
increase the value of coupling constant.
2. Similarly the coupling constant decreases
when the electronegative atom withdraw pi
electrons.
11/29/2021 MPAT COUPLING CONSTANT 27
HOW TO CALCULATE COUPLING CONSTANT
• In NMR spectrum where the peaks are in ppm(parts
per million).
• To calculate the coupling constant we need to convert
the ppm to Hz.
• Step 1: Determine the difference betweeen the two
adjacent peaks in ppm
• Step 2: multiply the value with the magnetic strength
we applied.
• By following these step coupling constant can be
calculated.
11/29/2021 MPAT COUPLING CONSTANT 28
• Eg: here the externely applied magnetic field
in 500Hz
11/29/2021 MPAT COUPLING CONSTANT 29
APPLICATIONS
• coupling constant are very useful for
discussing the structure and nature of
chemical bonding through which it gives an
exact skeleton of compound.
• J value contains information of relative bond
length and angles.
• It helps in determine the cis and trans form of
the compound.
11/29/2021 MPAT COUPLING CONSTANT 30
• It also gives informtion regarding the presence
of proton in ortho ,meta and para position in
an aromatic compound.
• The J-coupling can be used as a sole criterion
for novel synthetic analogs to identify the
right stereochemistry.
• couplings are typically used in combination
with chemical shifts to trace the bond
connectivity in small molecules and proteins.
11/29/2021 MPAT COUPLING CONSTANT 31
• Coupling constant are very much useful in
conformational analysis of the compound.
(Conformational analysis is the study of
kinetic and thermodynamic properties of
molecules.)
11/29/2021 MPAT COUPLING CONSTANT 32
REFERENCE
• Spectroscopy(Atomic and molecular) by
GERDEEP.R.CHATWALL.
• Organic spectroscopy by WILLIAM KEMP.
• JOURNAL OF MOLECULAR STRUCTURE.
11/29/2021 MPAT COUPLING CONSTANT 33
You might also like
- Nuclear Magnetic ResonanceDocument34 pagesNuclear Magnetic ResonanceD.N.S DE ZOYSANo ratings yet
- UNIT IV NMR Mass - WatermarkDocument23 pagesUNIT IV NMR Mass - WatermarkvickyNo ratings yet
- CHEM 430 NMR Spectroscopy Chapter 4Document95 pagesCHEM 430 NMR Spectroscopy Chapter 4Ravi GolNo ratings yet
- 2D NMR Spectroscopy - 1-D and 2-D NMR, Noesy and Cosy, Hetcor, INADEQUATE TechniquesDocument21 pages2D NMR Spectroscopy - 1-D and 2-D NMR, Noesy and Cosy, Hetcor, INADEQUATE TechniquesАрсений БекишевNo ratings yet
- 2DNMRSpectroscopy AdvancedspectralanalysisDocument21 pages2DNMRSpectroscopy Advancedspectralanalysisابراهيم الاسطىNo ratings yet
- NMR 2Document27 pagesNMR 2Nitish KumarNo ratings yet
- 12622094Document34 pages12622094hw6hbvqwtpNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry NMR ChapterDocument57 pagesOrganic Chemistry NMR ChapterHafidz ArkanNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Magnetic Resonance SpectrosDocument8 pagesNuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectrosanirbanmanna88320No ratings yet
- Spin-Spin Splitting and J Value: AssignmentDocument9 pagesSpin-Spin Splitting and J Value: AssignmentMcsf18M052-GULFAM RAZANo ratings yet
- NMR Mes 112Document48 pagesNMR Mes 112Sourav Rajput ThakurNo ratings yet
- NMR Spectroscopy ExplainedDocument101 pagesNMR Spectroscopy ExplainedMustapha ImadudeenNo ratings yet
- NMR Spectroscopy: Afsath. B Mpharm1 Year Pharmacognosy and Phytochemistry Malik Deenar College of PharmacyDocument23 pagesNMR Spectroscopy: Afsath. B Mpharm1 Year Pharmacognosy and Phytochemistry Malik Deenar College of PharmacychinmayeeNo ratings yet
- NMR interpretation key to structure determinationDocument16 pagesNMR interpretation key to structure determinationChandni SahaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Analysis NMRDocument5 pagesChemical Analysis NMROmar AbdulahNo ratings yet
- Chemistry PresentationDocument22 pagesChemistry PresentationJatin KalraNo ratings yet
- NMR PostalDocument10 pagesNMR PostalParth ShahNo ratings yet
- Solid State NMRDocument11 pagesSolid State NMRscancian2000No ratings yet
- Chapter 13 NMR SpectrosDocument61 pagesChapter 13 NMR SpectroshazemNo ratings yet
- CMS Physics Analysis SummaryDocument16 pagesCMS Physics Analysis SummaryEdgar Mauricio Loza RamírezNo ratings yet
- NMR Spectroscopy Lect. 2Document23 pagesNMR Spectroscopy Lect. 2khamisnassor2016No ratings yet
- Dissertation NMRDocument5 pagesDissertation NMRFindSomeoneToWriteMyCollegePaperUK100% (1)
- Chemical ShiftDocument10 pagesChemical Shifthema maliniNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Magnetic Resonance SpectrosDocument32 pagesNuclear Magnetic Resonance SpectrosChiranjeevi TulluriNo ratings yet
- NMR 7.Document36 pagesNMR 7.Imran KhanNo ratings yet
- Raphex Answers 2008 PDFDocument32 pagesRaphex Answers 2008 PDFcarlosqueiroz7669No ratings yet
- NMRDocument17 pagesNMRSourabhNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy See The Following WebsiteDocument58 pagesNuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy See The Following WebsiteSunnyd1013No ratings yet
- Information NMRspectroDocument8 pagesInformation NMRspectroMATHANKUMAR.SNo ratings yet
- NQR and EPR SpectrosDocument57 pagesNQR and EPR SpectrosPG ChemistryNo ratings yet
- 5.Nmr Class LatestDocument81 pages5.Nmr Class Latestdimitra shenoyNo ratings yet
- 15 P18CHC309 2020110401224341Document19 pages15 P18CHC309 2020110401224341hw6hbvqwtpNo ratings yet
- Clim Ente 2004Document4 pagesClim Ente 2004ArifNo ratings yet
- Sem-III - Unit - IV (NQR and Epr Spectroscopy)Document46 pagesSem-III - Unit - IV (NQR and Epr Spectroscopy)PG ChemistryNo ratings yet
- 5.2 Teacher's Notes QDocument19 pages5.2 Teacher's Notes QCormac WhiteNo ratings yet
- NMR Spectroscopy ExplainedDocument50 pagesNMR Spectroscopy Explainedpharmacologist786No ratings yet
- Who, Apr 2011Document5 pagesWho, Apr 2011emediageNo ratings yet
- CHM 3402 Experiment 8Document11 pagesCHM 3402 Experiment 8Uma Villashini GunasekaranNo ratings yet
- H NMRDocument34 pagesH NMRbsmalah11alroxnamNo ratings yet
- Dr. K.S. Dubey: Head of Chemistry DeptDocument57 pagesDr. K.S. Dubey: Head of Chemistry DeptprinceNo ratings yet
- NMR Lectures (Dr. G. B. Shah)(1)Document40 pagesNMR Lectures (Dr. G. B. Shah)(1)usamaNo ratings yet
- What Is NMRDocument9 pagesWhat Is NMRNishant SharmaNo ratings yet
- NMR GoodDocument52 pagesNMR GoodSiju N. Antony100% (1)
- Quantum-Chemistry of Zeolite AcidityDocument14 pagesQuantum-Chemistry of Zeolite AciditymanojrnpNo ratings yet
- Informe 2 AnalisisDocument17 pagesInforme 2 AnalisisCarla ParraNo ratings yet
- 3B AnalysisDocument19 pages3B AnalysisRida Nadeem SheikhNo ratings yet
- NMR Caracterization - 2022-2023Document21 pagesNMR Caracterization - 2022-2023Paula ArmendárizNo ratings yet
- Nonradiative Decay of Excited Molecules Near a Metal SurfaceDocument6 pagesNonradiative Decay of Excited Molecules Near a Metal SurfaceHeo Toàn TậpNo ratings yet
- Organic NMR Spectroscopy ExplainedDocument57 pagesOrganic NMR Spectroscopy ExplainedAthina MardhaNo ratings yet
- Organic NMR Spectroscopy ExplainedDocument57 pagesOrganic NMR Spectroscopy ExplainedNovalina Berliana Sibarani100% (1)
- 13C NMR Spectroscopy of Coumarin DerivativesDocument18 pages13C NMR Spectroscopy of Coumarin DerivativesGeorge MoshiashviliNo ratings yet
- NMR and EsrDocument52 pagesNMR and EsrSenthil Sethu FvfcNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Field and Symmetry Effects in Small Quantum Dots: R. G. NazmitdinovDocument44 pagesMagnetic Field and Symmetry Effects in Small Quantum Dots: R. G. NazmitdinovNoir LagNo ratings yet
- Lecture 25 - RG - NMR - Chemical Shift - 7.10.2014Document30 pagesLecture 25 - RG - NMR - Chemical Shift - 7.10.2014Sampada DesaiNo ratings yet
- Applications of H, C, F and P - NMR Spectroscopy in The Structural Assessment of Inorganic CompoundsDocument25 pagesApplications of H, C, F and P - NMR Spectroscopy in The Structural Assessment of Inorganic CompoundsSaurav PaulNo ratings yet
- Chemical ShiftDocument13 pagesChemical ShiftGitanjali SahuNo ratings yet
- 1H NMR SpectrosDocument41 pages1H NMR SpectrosTushar NaikNo ratings yet
- The Stopping and Ranges of Ions in Matter: Handbook of Stopping Cross-Sections for Energetic Ions in All ElementsFrom EverandThe Stopping and Ranges of Ions in Matter: Handbook of Stopping Cross-Sections for Energetic Ions in All ElementsNo ratings yet
- Negative Mass and Negative Refractive Index in Atom Nuclei - Nuclear Wave Equation - Gravitational and Inertial Control: Part 2: Gravitational and Inertial Control, #2From EverandNegative Mass and Negative Refractive Index in Atom Nuclei - Nuclear Wave Equation - Gravitational and Inertial Control: Part 2: Gravitational and Inertial Control, #2No ratings yet
- Electron Paramagnetic Resonance in Modern Carbon-Based NanomaterialsFrom EverandElectron Paramagnetic Resonance in Modern Carbon-Based NanomaterialsNo ratings yet
- Arduino and BH1750 SensorDocument4 pagesArduino and BH1750 SensorrealaffiliateNo ratings yet
- Review Assessment: Test Quiz FE1005 Materials ScienceDocument3 pagesReview Assessment: Test Quiz FE1005 Materials Scienceqwert1243No ratings yet
- Heat and mass transfer worksheet assignmentsDocument5 pagesHeat and mass transfer worksheet assignmentsBISRAT YIHUNNo ratings yet
- Motion Physics Grade 11 AssignmentDocument4 pagesMotion Physics Grade 11 Assignmentmn m,n m, bm43% (7)
- ISO - 24213 - Avaliação de SpringbackDocument18 pagesISO - 24213 - Avaliação de Springback0511018No ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE™: Chemistry 0620/43Document11 pagesCambridge IGCSE™: Chemistry 0620/43krishaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Positron and PositroniumDocument30 pagesChapter 3 Positron and PositroniumKhalid AhmedNo ratings yet
- Non - Rectangular Components: Prepared By: D.M.ODocument5 pagesNon - Rectangular Components: Prepared By: D.M.OCiero John MarkNo ratings yet
- Reference Books FDocument7 pagesReference Books FAamerNo ratings yet
- Physics FormulasDocument108 pagesPhysics FormulasArsalan Ahmed Usmani100% (3)
- Cast Iron: History and Application: AbstractDocument12 pagesCast Iron: History and Application: Abstract13311A0341 S SHIVA SAI KIRANNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan LightDocument12 pagesLesson Plan LightRhisia RaborNo ratings yet
- DryLube Brochure 11358 enDocument28 pagesDryLube Brochure 11358 enIslam FawzyNo ratings yet
- Safety Factor of Statically Loaded Weld JointDocument2 pagesSafety Factor of Statically Loaded Weld JointMoonzeNo ratings yet
- Achromatic Prisms and LensesDocument4 pagesAchromatic Prisms and LensesModyKing99No ratings yet
- TP114HEP Reexaminations FewerLocations HigherConfidenceDocument14 pagesTP114HEP Reexaminations FewerLocations HigherConfidenceKurt CobainNo ratings yet
- LabreportphysicdDocument4 pagesLabreportphysicdapi-263436863No ratings yet
- Ochsner 2008 Carbon Dioxide Heat Pipe in ConjuncDocument6 pagesOchsner 2008 Carbon Dioxide Heat Pipe in ConjuncHugo PeresNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15 Oscillations Version 2Document28 pagesChapter 15 Oscillations Version 2nabeelNo ratings yet
- Design of Steel BeamsDocument25 pagesDesign of Steel Beamsronaldnyirenda2230No ratings yet
- Shower: Group Members: Masturah Binti T.Peter@ Mustafa Dianna Binti Maxy Hannah Fairuz Binti HamdanDocument8 pagesShower: Group Members: Masturah Binti T.Peter@ Mustafa Dianna Binti Maxy Hannah Fairuz Binti HamdanNajib TowyNo ratings yet
- Mit18086 Navierstokes.mDocument3 pagesMit18086 Navierstokes.mAnkit AnuragNo ratings yet
- Neet Major Test Plan - 2023-2024Document3 pagesNeet Major Test Plan - 2023-2024santhoshsivoNo ratings yet
- Malixi Integrated School Science Exam Covers Gas Laws, BiomoleculesDocument4 pagesMalixi Integrated School Science Exam Covers Gas Laws, Biomoleculeszayd87% (38)
- Class XII Chemistry Surface Chemistry Chapter NotesDocument18 pagesClass XII Chemistry Surface Chemistry Chapter Notessanjit mukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Conformal Field Theory Interpretation of Black Hole Quasi-Normal ModesDocument4 pagesConformal Field Theory Interpretation of Black Hole Quasi-Normal ModesLeonardo BossiNo ratings yet
- Ec6 Eurocode-6 - Lateral-Resistance - 19 - 01 - 091 PDFDocument8 pagesEc6 Eurocode-6 - Lateral-Resistance - 19 - 01 - 091 PDFHeris DoggaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 21 Sound Wave REVISIONDocument4 pagesChapter 21 Sound Wave REVISIONYilea1111111No ratings yet
- Freshwater Acidification - WikipediaDocument4 pagesFreshwater Acidification - Wikipediatsvmpm1765No ratings yet
- Fletcher, A. and J. Davis. How EOR Can Be Transformed by Nanotechnology. in SPE Improved Oil Recovery Symposium. 2010. Society of Petroleum Engineers.Document16 pagesFletcher, A. and J. Davis. How EOR Can Be Transformed by Nanotechnology. in SPE Improved Oil Recovery Symposium. 2010. Society of Petroleum Engineers.David MoedanoNo ratings yet