Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Agile: Axel Christian Santos Bloomfield
Uploaded by
Axel Christian Santos Bloomfield0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views18 pagesOriginal Title
Agile Class 4
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views18 pagesAgile: Axel Christian Santos Bloomfield
Uploaded by
Axel Christian Santos BloomfieldCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 18
agile
Axel Christian Santos Bloomfie
Agenda
1. What is Spiral model?
2. Uses of the Spiral Model
3. Spiral Model Phases
4. Steps of the Spiral Model
5. Pros & Cons
What is Spiral Model?
Spiral Model
The spiral model is a systems development
lifecycle (SDLC) method used for risk
management that combines the iterative
development process model with elements of the
Waterfall model. The spiral model is used by
software engineers and is favored for large,
expensive and complicated projects.
Uses of the Spiral Model
Uses of the spiral model
• Projects in which frequent releases are necessary;
• Projects in which changes may be required at any time
• Long term projects that are not feasible due to altered economic
priorities
• Medium to high risk projects
• When creation of a prototype is applicable
• Projects in which cost and risk analysis is important
• Projects that would benefit from the creation of a prototype
• Projects with unclear or complex requirements.
Spiral Model Phases
Spiral Model phases
Planning (Identify Objectives)
Phases begin in the quadrant dedicated to
the identification and understanding of
requirements. The overall goal of the phase
should be determined and all objectives
should be elaborated and analyzed. It is
important to also identify alternative
solutions in case the attempted version fails
to perform.
It includes estimating the cost, schedule and
resources for the iteration. It also involves
understanding the system requirements for
continuous communication between the
system analyst and the customer
Risk Analysis
Next, risk analysis should be performed
on all possible solutions in order to find
any faults or vulnerabilities -- such as
running over the budget or areas within
the software that could be open to
cyber attacks.
Each risk should then be resolved
using the most efficient strategy.
Identification of potential risk is done
while risk mitigation strategy is planned
and finalized
Engineering
In the next quadrant, the prototype is built
and tested. This step includes: architectural
design, design of modules, physical product
design and the final design. It takes the
proposal that has been created in the first
two quadrants and turns it into software
that can be utilized.
It includes testing, coding and deploying
software at the customer site
Review and Evaluate
Finally, in the fourth quadrant, the test
results of the newest version are
evaluated. This analysis allows
programmers to stop and understand what
worked and didn’t work before progressing
with a new build. At the end of this
quadrant, planning for the next phase
begins and the cycle repeats. At the end of
the whole spiral, the software is finally
deployed in its respective market.
Evaluation of software by the customer.
Also, includes identifying and monitoring
risks such as schedule slippage and cost
overrun
Steps of Spiral Model
Steps of the Spiral Model
1. The new system requirements are defined in as 1. The entire project can be aborted if the risk is
much detail as possible. This usually involves deemed too great. Risk factors might involve
interviewing a number of users representing all development cost overruns, operating-cost
the external or internal users and other aspects miscalculation and other factors that could result
of the existing system. in a less-than-satisfactory final product.
2. A preliminary design is created for the new 2. The existing prototype is evaluated in the same
system. manner as was the previous prototype, and, if
3. A first prototype of the new system is constructed necessary, another prototype is developed from it
from the preliminary design. This is usually a according to the fourfold procedure outlined
scaled-down system, and represents an above.
approximation of the characteristics of the final 3. The preceding steps are iterated until the
product. customer is satisfied that the refined prototype
4. A second prototype is evolved by a fourfold represents the final product desired.
procedure: (1) evaluating the first prototype in 4. The final system is constructed, based on the
terms of its strengths, weaknesses, and risks; (2) refined prototype.
defining the requirements of the second 5. The final system is thoroughly evaluated and
prototype; (3) planning and designing the second tested. Routine maintenance is carried out on a
prototype; (4) constructing and testing the second continuing basis to prevent large-scale failures
prototype. and to minimize downtime.
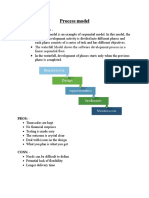
Pros & Cons
Pros of Spiral Model
• Additional functionality or changes can
be done at a later stage
• Cost estimation becomes easy as the
prototype building is done in small
fragments
• Continuous or repeated development
helps in risk management
• Development is fast and features are
added in a systematic way in Spiral
development
• There is always a space for customer
feedback
Cons of Spiral Model
• Risk of not meeting the schedule or budget
• Spiral development works best for large
projects only also demands risk assessment
expertise
• For its smooth operation spiral model
protocol needs to be followed strictly
• Documentation is more as it has
intermediate phases
• Spiral software development is not
advisable for smaller project, it might cost
them a lot
Questions?
You might also like
- Installation Checklist For SPV Module: Sterling and Wilson Document No.: SW-SEPC-ICL-PV-002, Rev: 01Document2 pagesInstallation Checklist For SPV Module: Sterling and Wilson Document No.: SW-SEPC-ICL-PV-002, Rev: 01Adithi RNo ratings yet
- Advantages of Spiral ModelDocument7 pagesAdvantages of Spiral ModelGallowbraidNo ratings yet
- SDLC METHDOLOGIES SpiralDocument3 pagesSDLC METHDOLOGIES SpiralYesu RajNo ratings yet
- Software Model or Architecture Analysis: SDLC MethodologyDocument4 pagesSoftware Model or Architecture Analysis: SDLC Methodologykalcode35No ratings yet
- System ModelsDocument18 pagesSystem ModelsgurugksNo ratings yet
- Software Development Life: Cycle (SDLC)Document34 pagesSoftware Development Life: Cycle (SDLC)JohnNo ratings yet
- Spiral and Evolutionary ModelDocument12 pagesSpiral and Evolutionary ModelSidharath PathaniaNo ratings yet
- Prototype and Spiral ModelDocument6 pagesPrototype and Spiral ModelrajeshNo ratings yet
- All in One AssignmentDocument46 pagesAll in One AssignmentNirmalNo ratings yet
- Introduction - The Spiral ModelDocument7 pagesIntroduction - The Spiral ModelAaron LeeNo ratings yet
- Spiral ModelDocument2 pagesSpiral ModelMNaveedsdkNo ratings yet
- What Is The Spiral Development Model?Document11 pagesWhat Is The Spiral Development Model?ShilpaNo ratings yet
- Software EngineeringDocument25 pagesSoftware Engineeringmarv hartiganNo ratings yet
- SpiralDocument3 pagesSpiralPraveen KumarNo ratings yet
- Process Mode1Document9 pagesProcess Mode1PRINCE HINGRAJIYANo ratings yet
- Wa0031Document184 pagesWa0031priya moreNo ratings yet
- Testing PDFDocument15 pagesTesting PDFSenthil RajendranNo ratings yet
- Ra2011026010080 Week1 AssignmentDocument8 pagesRa2011026010080 Week1 AssignmentShaik IrfanNo ratings yet
- 2.introduction To System Analysis and DesignDocument27 pages2.introduction To System Analysis and DesignGeethma RamanayakaNo ratings yet
- Abhijeet Savkar Software TestingDocument41 pagesAbhijeet Savkar Software TestingAbhijeet SavkarNo ratings yet
- Software Development Life CyclesDocument9 pagesSoftware Development Life CycleskbindhujaNo ratings yet
- Software Engg Week 3 LectureDocument19 pagesSoftware Engg Week 3 Lectureabdul wahabNo ratings yet
- Process ModelDocument4 pagesProcess ModelParvathi GoudNo ratings yet
- CH - 2 Overview of Software TestingDocument30 pagesCH - 2 Overview of Software TestingUmesh MahajanNo ratings yet
- System Development Models:: AdvantagesDocument5 pagesSystem Development Models:: Advantageschowmow0% (1)
- Unit Ii - Project Life Cycle and Effort Estimation 2.1 Software Process and Process ModelsDocument19 pagesUnit Ii - Project Life Cycle and Effort Estimation 2.1 Software Process and Process Models123No ratings yet
- Software Development ModelsDocument5 pagesSoftware Development ModelsVikasNo ratings yet
- Falls e Lecture 6Document17 pagesFalls e Lecture 6Azaz Ali ShahNo ratings yet
- CHP 2 (Project Management)Document12 pagesCHP 2 (Project Management)Parth A ShahNo ratings yet
- AbbreviationDocument16 pagesAbbreviationAsha ShashiniNo ratings yet
- SOFTWARE DEVELOPMENT LIFE CYCLE For MoodleDocument9 pagesSOFTWARE DEVELOPMENT LIFE CYCLE For MoodleFrancis MwanikiNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - Software Process ModelsDocument7 pagesModule 1 - Software Process ModelsfebinstNo ratings yet
- U-2 CCS-404 G Software Project ParadigmasDocument40 pagesU-2 CCS-404 G Software Project Paradigmasmithilesh bidkarNo ratings yet
- Prototyping Model - Evolution and Spiral ModelsDocument5 pagesPrototyping Model - Evolution and Spiral ModelsVijay KrishnaNo ratings yet
- What Is The Spiral Model Mthandy AssignmentDocument6 pagesWhat Is The Spiral Model Mthandy AssignmentPeace Runyararo MutenderiNo ratings yet
- SPM Unit 2 NotesDocument18 pagesSPM Unit 2 NotesUtkarsh BhadauriaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document35 pagesUnit 2lavanya2webNo ratings yet
- Software Life Cycle ModelsDocument15 pagesSoftware Life Cycle Modelsumang patelNo ratings yet
- (Lilaram Anjane) Software TestingDocument41 pages(Lilaram Anjane) Software TestingAnonymous QECOCzrNo ratings yet
- Traditional SW DevDocument13 pagesTraditional SW DevWeb Best WabiiNo ratings yet
- Week 03Document6 pagesWeek 03O.M. CreationsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 SummaryDocument9 pagesChapter 2 Summaryبندر الرشيدNo ratings yet
- SDLCDocument14 pagesSDLCHimanshu AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Unit2 (I)Document10 pagesUnit2 (I)2130154006No ratings yet
- Unit-3, Lecture-9: Course ID: BBA-210Document15 pagesUnit-3, Lecture-9: Course ID: BBA-210Vanshika GirdharNo ratings yet
- The Spiral ModelDocument5 pagesThe Spiral ModelMary Ann RebloraNo ratings yet
- 3.1 The Evolutionary Process Models: Software Engineering Third ClassDocument8 pages3.1 The Evolutionary Process Models: Software Engineering Third ClassAmit ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Software Engineering: Process ModelsDocument19 pagesSoftware Engineering: Process ModelsOrhan rumiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2.2 Software Processes Software EngineeringDocument20 pagesChapter 2.2 Software Processes Software Engineeringmansoorsherzad217No ratings yet
- ASM LifecycleDocument9 pagesASM LifecycleLe Van Dung (BTECHCM)No ratings yet
- Unit Ii Project Life Cycle and Effort Estimation: IT8075-Software Project Management Department of IT 2021-2022Document35 pagesUnit Ii Project Life Cycle and Effort Estimation: IT8075-Software Project Management Department of IT 2021-2022zoeNo ratings yet
- Software Process ModelsDocument10 pagesSoftware Process ModelsDexter KamalNo ratings yet
- SE AssignmentDocument6 pagesSE AssignmentAshok ThakraniNo ratings yet
- Introduction To SE BSNLDocument60 pagesIntroduction To SE BSNLSudhakar SelvamNo ratings yet
- Clark SpiralDocument24 pagesClark Spiralfarhat514No ratings yet
- Software Engineering NotesDocument25 pagesSoftware Engineering Notesitsch2392No ratings yet
- INFORMATION MANAGEMENT Unit 2Document35 pagesINFORMATION MANAGEMENT Unit 2Thirumal AzhaganNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Process ModelsDocument13 pagesUnit 1 Process ModelsdkjvhkjfkjsdbfkwebfkjNo ratings yet
- Experiment-1: Aim - TheoryDocument14 pagesExperiment-1: Aim - TheoryGurpreet Kaur DhaliwalNo ratings yet
- Cost Estimation in Agile Software Development: Utilizing Functional Size Measurement MethodsFrom EverandCost Estimation in Agile Software Development: Utilizing Functional Size Measurement MethodsNo ratings yet
- Software Testing Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be Asked: Job Interview Questions SeriesFrom EverandSoftware Testing Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be Asked: Job Interview Questions SeriesNo ratings yet
- ManifestFileUpload Template IncludeCasePack IncludeExpirationDateGBODocument11 pagesManifestFileUpload Template IncludeCasePack IncludeExpirationDateGBOAxel Christian Santos BloomfieldNo ratings yet
- ManifestFileUpload Template IncludeCasePack IncludeExpirationDateGBODocument11 pagesManifestFileUpload Template IncludeCasePack IncludeExpirationDateGBOAxel Christian Santos BloomfieldNo ratings yet
- ManifestFileUpload Template IncludeCasePack IncludeExpirationDateGBODocument11 pagesManifestFileUpload Template IncludeCasePack IncludeExpirationDateGBOAxel Christian Santos BloomfieldNo ratings yet
- ManifestFileUpload Template IncludeCasePack IncludeExpirationDateGBODocument11 pagesManifestFileUpload Template IncludeCasePack IncludeExpirationDateGBOAxel Christian Santos BloomfieldNo ratings yet
- Agile: Axel Christian Santos BloomfieldDocument15 pagesAgile: Axel Christian Santos BloomfieldAxel Christian Santos BloomfieldNo ratings yet
- Agile: Axel Christian Santos BloomfieldDocument17 pagesAgile: Axel Christian Santos BloomfieldAxel Christian Santos BloomfieldNo ratings yet
- Agile: Axel Christian Santos BloomfieldDocument16 pagesAgile: Axel Christian Santos BloomfieldAxel Christian Santos BloomfieldNo ratings yet
- Agile: Axel Christian Santos BloomfieldDocument20 pagesAgile: Axel Christian Santos BloomfieldAxel Christian Santos BloomfieldNo ratings yet
- Agile: Axel Christian Santos BloomfieldDocument15 pagesAgile: Axel Christian Santos BloomfieldAxel Christian Santos BloomfieldNo ratings yet
- Agile: Axel Christian Santos BloomfieldDocument17 pagesAgile: Axel Christian Santos BloomfieldAxel Christian Santos BloomfieldNo ratings yet
- Agile: Axel Christian Santos BloomfieldDocument16 pagesAgile: Axel Christian Santos BloomfieldAxel Christian Santos BloomfieldNo ratings yet
- Agile: Axel Christian Santos BloomfieldDocument18 pagesAgile: Axel Christian Santos BloomfieldAxel Christian Santos BloomfieldNo ratings yet
- Agile: Axel Christian Santos BloomfieldDocument20 pagesAgile: Axel Christian Santos BloomfieldAxel Christian Santos BloomfieldNo ratings yet
- Oinarrizko Hezkuntza. Curriculum DekretuaDocument961 pagesOinarrizko Hezkuntza. Curriculum DekretualeirelurNo ratings yet
- 70-532 Exam Dumps With PDF and VCE Download (1-20) PDFDocument25 pages70-532 Exam Dumps With PDF and VCE Download (1-20) PDFTanveer Kumbari100% (1)
- Academic Task 3 ACC507Document2 pagesAcademic Task 3 ACC507shivam kumar patelNo ratings yet
- Deep Learning in Cardiology: Paschalis Bizopoulos, and Dimitrios KoutsourisDocument27 pagesDeep Learning in Cardiology: Paschalis Bizopoulos, and Dimitrios KoutsourisWided MiledNo ratings yet
- Trimec EM LockDocument15 pagesTrimec EM LockManoj GandhiNo ratings yet
- Cheat Sheet Crear RFC en ISM v1.2Document10 pagesCheat Sheet Crear RFC en ISM v1.2kingsoftNo ratings yet
- Controller Option (M416) PC 120912Document8 pagesController Option (M416) PC 120912Dawood AhmedNo ratings yet
- Adidas Cycling Jersey - With Formotion Technology - Baju Sepeda Adidas Limited Item - DetikForumDocument300 pagesAdidas Cycling Jersey - With Formotion Technology - Baju Sepeda Adidas Limited Item - DetikForumAditya Tudhing PermanaNo ratings yet
- Serial Communication 8051 MicrocontrollerDocument27 pagesSerial Communication 8051 Microcontrollersivaeeinfo100% (1)
- Exam 1D0-735: Javascript Specialist V2.0Document5 pagesExam 1D0-735: Javascript Specialist V2.0Leo MartinesNo ratings yet
- Communication Aids and Communication TechnologiesDocument21 pagesCommunication Aids and Communication TechnologiesGONZALES, Nichole Kate, J.No ratings yet
- Kotlin in Action - FunctionalDocument5 pagesKotlin in Action - FunctionaljobaxyraNo ratings yet
- Electronic Transaction Act 2063: NITC/Ministry of Environment, Science and Technology)Document29 pagesElectronic Transaction Act 2063: NITC/Ministry of Environment, Science and Technology)setup vpnNo ratings yet
- HowTo Calibration ES-1000 v1Document8 pagesHowTo Calibration ES-1000 v1trunghieu02ck1No ratings yet
- PC Controls and Key Bindings in Assassin's Creed Odyssey - ShacknewsDocument6 pagesPC Controls and Key Bindings in Assassin's Creed Odyssey - ShacknewsEleytheriou TaxiarchisNo ratings yet
- Oracle® Database Express Edition: Getting Started Guide 11g Release 2 (11.2)Document16 pagesOracle® Database Express Edition: Getting Started Guide 11g Release 2 (11.2)Yuli NurcahyantiNo ratings yet
- Mesa DMX (Manual)Document12 pagesMesa DMX (Manual)Sérgio Paulo MúsicoNo ratings yet
- Instagram Study: Simply Measured Q4 2014Document15 pagesInstagram Study: Simply Measured Q4 2014gaboss63No ratings yet
- Web & Mobile Security Lab 20CSP-338: Bachelor Degree of EngineeringDocument11 pagesWeb & Mobile Security Lab 20CSP-338: Bachelor Degree of EngineeringWar LockNo ratings yet
- Factual Reading Text: English Literature Class CDocument27 pagesFactual Reading Text: English Literature Class CHasan SholahuddinNo ratings yet
- OptiX OSN Series General Configura LapDocument33 pagesOptiX OSN Series General Configura LapElfatih HashimNo ratings yet
- Xxx 팀 Aaa Bbb Ccc DddDocument23 pagesXxx 팀 Aaa Bbb Ccc DddLeo VegaNo ratings yet
- What Is Functional Dependency?: Re Exivity: If Y Is A Subset of X, Then X Y Holds by Re Exivity RuleDocument17 pagesWhat Is Functional Dependency?: Re Exivity: If Y Is A Subset of X, Then X Y Holds by Re Exivity RuleDivya SinghNo ratings yet
- SlideShop Ideal Customer ProfileDocument17 pagesSlideShop Ideal Customer Profiletelulikur 23No ratings yet
- SumoDocument21 pagesSumoWalid JiNo ratings yet
- Fortigate 200F Series: Data SheetDocument6 pagesFortigate 200F Series: Data SheetEliranNo ratings yet
- 1323-Texto Do Artigo-2359-1-10-20160601 PDFDocument10 pages1323-Texto Do Artigo-2359-1-10-20160601 PDFIrina AlexandraNo ratings yet
- IAT-I Question Paper With Solution of 18CS71 Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Oct-2022-Dr. Paras Nath SinghDocument7 pagesIAT-I Question Paper With Solution of 18CS71 Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Oct-2022-Dr. Paras Nath SinghBrundaja D NNo ratings yet
- Muting Light Curtain DOC V21 enDocument59 pagesMuting Light Curtain DOC V21 enCayetano CaceresNo ratings yet