Professional Documents
Culture Documents
New Chapter 3
New Chapter 3
Uploaded by
nayef a0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views16 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views16 pagesNew Chapter 3
New Chapter 3
Uploaded by
nayef aCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 16
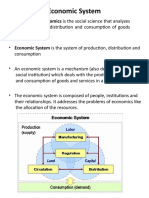
CHAPTER 3
FREE ENTERPRISE ECONOMY
• Free Enterprise Economy: An Economic
system in which privately owned businesses
have the freedom to operate for a profit with
limited government intervention
• A free enterprise economy has both capitalism
and free markets.
• Characteristics of a capitalistic free enterprise
economy include economic freedom, voluntary
exchange, private property rights, the profit
motive, and competition.
• Economic freedom allows you to choose your
occupation, employer, and job location.
• Economic freedom is a characteristic of
capitalism.
• People can buy what they want and choose
their own occupation, employer, and job
location.
• Businesses can hire the workers of their
choice and produce what they want; they
are free to risk success or failure.
• Capitalism allows voluntary exchange
between buyers and sellers.
• Private property rights allow people to own
and control possessions, which gives them the
incentive to work, save, and invest.
• The profit motive is largely responsible for
the growth of a free enterprise system.
• Competition benefits both consumers and the
economy.
Benefits of Free Enterprise
• Individual freedom is closely related to
economic freedom.
• Market economies produce a huge variety of
goods.
• Market economies adjust daily, mainly
through the ever-changing prices of goods and
services.
• Intense competition in a free market
capitalist economy promotes economic
progress in the form of a continuing supply
of newer and better products.
• When more and better products are
produced in a free market capitalistic
system, wealth is created.
Disadvantages
• Periods of uneven economic growth are one of
the disadvantages of free enterprise capitalism.
• In free enterprise capitalism, the gaps between
rich and poor citizens seem to increase.
• In free enterprise economies, suppliers tend to
combine to avoid competition, which results in
fewer participants on the supply side of the
market.
• Businesses such as corporations have most of
the same rights as individuals, but they also
have many responsibilities as a result of
government-imposed regulations.
Economic freedom, voluntary exchange, private
property rights,competition, profit motive
Role of Entrepreneur
• Entrepreneurs are important because they are willing to take
risks to start new businesses, so they become the catalyst of
the free enterprise economy.
• Most entrepreneurs fail, but some survive and a few even
become wealthy.
• Successful entrepreneurs attract other firms to the industry,
eventually leading to new products, greater competition,
more production, higher quality, and lower prices.
Role of Consumer
• Consumers ultimately determine WHAT to
produce.
• The term consumer sovereignty reflects the idea
that the consumer rules the market.
• Consumers play an important role in the
American free enterprise economy because their
spending helps determine what is, and is not,
produced.
Role of the Government
• Government has become involved in the
American free enterprise system because its
citizens want it that way.
• The government passes laws to help protect
citizens from false advertising, unsafe food
and drugs, environmental hazards, and unsafe
products.
• All levels of government provide goods and
services for citizens, including education,
highways, public welfare, and many others.
• The government regulates economic activity to
help preserve competition in the marketplace.
• The government spends more than all private
businesses combined, so it has become a huge
consumer in the marketplace.
Mixed Economy
• In a mixed or modified free enterprise economy, people
and businesses carry out their economic affairs freely, but are
subject to some government intervention and regulation.
• The question of how much government involvement is
necessary is one of the great unsolved questions of our times.
• The American system is a mixed or modified free enterprise
economy because the majority of the people want it that way.
You might also like
- Capitalism, Socialism, and Mixed Economy-Ppt-1Document24 pagesCapitalism, Socialism, and Mixed Economy-Ppt-1nandini swami100% (1)
- Marketing Mix MCQ'sDocument6 pagesMarketing Mix MCQ'sMehmood Alam100% (3)
- DPB1023 Unit 1 Introduction To MicroeconomicsDocument49 pagesDPB1023 Unit 1 Introduction To MicroeconomicsnikazidaNo ratings yet
- Economic System: Planned EconomyDocument8 pagesEconomic System: Planned EconomyHossain Mohammad Abin100% (2)
- Economy - Its Meaning and TypesDocument22 pagesEconomy - Its Meaning and TypesBA LLB Section BNo ratings yet
- (Chapter 2) Understanding Economics and How It Affects BusinessDocument6 pages(Chapter 2) Understanding Economics and How It Affects BusinessTommyArnzenNo ratings yet
- Summary of Milton Friedman's Capitalism and FreedomFrom EverandSummary of Milton Friedman's Capitalism and FreedomRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Internship Report On Ananash TravelDocument41 pagesInternship Report On Ananash Travelnehasaboo64% (14)
- CE 406 Lecture 04 Economic SystemsDocument40 pagesCE 406 Lecture 04 Economic SystemsMuhammad Talha HassanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document3 pagesChapter 3bohlale.mosalaNo ratings yet
- Market EconomyDocument22 pagesMarket Economycastrence히아신스 leeyhanzie hyacinthNo ratings yet
- Capitalism - Book by Khalid Mehmood CheemaDocument19 pagesCapitalism - Book by Khalid Mehmood CheemaDavid PicassoNo ratings yet
- Economic MethodDocument14 pagesEconomic MethodSakibNo ratings yet
- Economics Lecture 2Document55 pagesEconomics Lecture 2Arvind GiritharagopalanNo ratings yet
- Economics Basic Economic System & Basic Economic ProblemsDocument5 pagesEconomics Basic Economic System & Basic Economic Problemsjoshuavictoria186No ratings yet
- Wa0005.Document24 pagesWa0005.Abdirahman Ahmed mohamudNo ratings yet
- Disadvantage of CapitalismDocument2 pagesDisadvantage of CapitalismRonnel Angelo TrevinioNo ratings yet
- Economic System and The Flow of Economic ActivityDocument8 pagesEconomic System and The Flow of Economic ActivityRosalyn Rongap BañariaNo ratings yet
- Capitalismsocialismmixedeconomy 110903012113 Phpapp02Document24 pagesCapitalismsocialismmixedeconomy 110903012113 Phpapp02shahirmuzawarNo ratings yet
- Capitalist SystemDocument18 pagesCapitalist Systemswati madadNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Business Environmetnt and Legal AspectsDocument46 pagesUnit 2 Business Environmetnt and Legal AspectsSatyam JadonNo ratings yet
- Session 16: Understanding Economics and How Its Affects BusinessDocument36 pagesSession 16: Understanding Economics and How Its Affects BusinessJennifer CarliseNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document2 pagesChapter 3suyeebnayeemNo ratings yet
- Basic Economics ProblemsDocument51 pagesBasic Economics Problemsgarciarjb000No ratings yet
- (Economics) : Managing Within The Dynamic Business Environment: Taking Risks and Making ProfitsDocument42 pages(Economics) : Managing Within The Dynamic Business Environment: Taking Risks and Making ProfitsRafayet Omar ShuvoNo ratings yet
- 1.7 - Economic SystemDocument31 pages1.7 - Economic Systemcrishantip2No ratings yet
- 5 Types of EconomyDocument7 pages5 Types of Economypulak506rblxNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Market EconomyDocument14 pagesCharacteristics of Market EconomyHimanshu ChawlaNo ratings yet
- EcosystemDocument25 pagesEcosystemtwiceNo ratings yet
- Allocation of Resources: 1) What To Produce?Document4 pagesAllocation of Resources: 1) What To Produce?mohamed sobahNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document5 pagesLecture 3Natalie100% (1)
- Islamic Economics: ECON 202Document25 pagesIslamic Economics: ECON 202Abbas BalochNo ratings yet
- 20 21 1T Badm CH2 TaDocument13 pages20 21 1T Badm CH2 TaNouran Mohamed Abd AzeemNo ratings yet
- 3 DRH Capitalism Vs Free Market FAQsDocument14 pages3 DRH Capitalism Vs Free Market FAQsfatimazahrahihiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Business - Topic 1Document8 pagesIntroduction To Business - Topic 1cbhiba98No ratings yet
- Market SystemsDocument9 pagesMarket Systemsaxeem1No ratings yet
- Economic System PresentationDocument19 pagesEconomic System PresentationVenkatesh NaraharisettyNo ratings yet
- Understanding Economic Resources and Economic Systems Is Essential To Lessening ProblemsDocument22 pagesUnderstanding Economic Resources and Economic Systems Is Essential To Lessening ProblemsPuneet KaurNo ratings yet
- 4th Form - POB - Types of Economic Systems - Free MarketDocument11 pages4th Form - POB - Types of Economic Systems - Free MarketStephen StewartNo ratings yet
- Market Economy (3) StudentiDocument35 pagesMarket Economy (3) StudentiAndreea CozmaNo ratings yet
- Translete Tugas InggrisDocument5 pagesTranslete Tugas InggrisINGGIT EKA MARDIANANo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document32 pagesChapter 2danialNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2-2Document25 pagesChapter 2-2Tanner MelleNo ratings yet
- Geo 3 ReportingDocument8 pagesGeo 3 ReportingJohncarl MendozaNo ratings yet
- Economic Systems and Decision Making 5Document30 pagesEconomic Systems and Decision Making 5api-263719227No ratings yet
- Lesson 1the Market EconomyDocument17 pagesLesson 1the Market EconomyKai BrightNo ratings yet
- P.O.B - Economic SystemDocument3 pagesP.O.B - Economic SystemDavaanaNo ratings yet
- Free Market EconomyDocument6 pagesFree Market Economyabjafra3No ratings yet
- Eco 201 Mod 1 Notes CHDocument8 pagesEco 201 Mod 1 Notes CHJohn Mark TabusoNo ratings yet
- Goods and ServicesDocument28 pagesGoods and ServicesDevid LuizNo ratings yet
- Asad Law AssignmentDocument7 pagesAsad Law AssignmentSarim ZiaNo ratings yet
- Economic SystemsDocument6 pagesEconomic SystemsAnnika liburdNo ratings yet
- (BEA) 9 After MidtermDocument25 pages(BEA) 9 After MidtermRafika Hamidah HamdiNo ratings yet
- Market FailuresDocument12 pagesMarket Failuresanonydev1No ratings yet
- The 4 Economic SystemsDocument15 pagesThe 4 Economic SystemsThidaphone DouangmanyNo ratings yet
- AE Module5Document16 pagesAE Module5Koshu KunNo ratings yet
- Alishba Naveed BSV Micro Economics AssignmentDocument9 pagesAlishba Naveed BSV Micro Economics AssignmentAlishba NaveedNo ratings yet
- Critical QuestionsDocument23 pagesCritical QuestionsgabytjintjelaarNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Moral Rights and Utilitarianism .???: Ethical Principles in Business:-Justice and FairnessDocument17 pagesDifference Between Moral Rights and Utilitarianism .???: Ethical Principles in Business:-Justice and FairnessIshan BhanotNo ratings yet
- Macro Economics: The Free Market Economy/ Capitalism SystemDocument7 pagesMacro Economics: The Free Market Economy/ Capitalism SystemNimayaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1Document8 pagesLesson 1Regine DimaanoNo ratings yet
- Government and the Economy: Enriching Language and Literacy Through ContentFrom EverandGovernment and the Economy: Enriching Language and Literacy Through ContentNo ratings yet
- Final Value Chain of Edible OilDocument73 pagesFinal Value Chain of Edible OilMelku AbebeNo ratings yet
- Metro Manila PhilippinesDocument27 pagesMetro Manila PhilippinesRaymond AnactaNo ratings yet
- Business Analytics Toolkit PortfolioDocument48 pagesBusiness Analytics Toolkit PortfolioKhaled HasanNo ratings yet
- EOI - Pipeline Integrity Assessment Services-31-12-19Document10 pagesEOI - Pipeline Integrity Assessment Services-31-12-19Saradhi MedapureddyNo ratings yet
- G12 ABM Marketing Lesson 3Document22 pagesG12 ABM Marketing Lesson 3Leo SuingNo ratings yet
- Policy-Amendment-Request-form-PARF-for-PN08043714 (SEE, DIORELLE CHOI) PDFDocument6 pagesPolicy-Amendment-Request-form-PARF-for-PN08043714 (SEE, DIORELLE CHOI) PDFHarold Q. GardonNo ratings yet
- Highest CTC Highest CTC Batch PlacedDocument4 pagesHighest CTC Highest CTC Batch PlacedBond JNo ratings yet
- LNL Iklcqd /: Page 1 of 10Document10 pagesLNL Iklcqd /: Page 1 of 10Manoj ValeshaNo ratings yet
- Chavez v. PEADocument83 pagesChavez v. PEAShielaLyn RiveraNo ratings yet
- Major Project ReportDocument15 pagesMajor Project Report49 Roshni PoojaryNo ratings yet
- MWM18006-TCG3020 Linienbroschuere EN 17 RZ Ks ScreenDocument3 pagesMWM18006-TCG3020 Linienbroschuere EN 17 RZ Ks ScreenSundrakumar RajuNo ratings yet
- A Comparison Enterprise Architecture Imp PDFDocument6 pagesA Comparison Enterprise Architecture Imp PDFHavoc2003No ratings yet
- Recording TransactionsDocument2 pagesRecording TransactionsClyden Jaile RamirezNo ratings yet
- WK 4 Audit Planning and Audit DocumentationDocument60 pagesWK 4 Audit Planning and Audit DocumentationYalliniNo ratings yet
- Final Report of Coca ColaDocument18 pagesFinal Report of Coca ColaNiloy SahaNo ratings yet
- CASE STUDY No. 1Document2 pagesCASE STUDY No. 1tristanbenito80No ratings yet
- Johnny Doc Criminal Complaint 2021Document8 pagesJohnny Doc Criminal Complaint 2021philly victorNo ratings yet
- Caro 2020 Clause by Clause AnalysisDocument78 pagesCaro 2020 Clause by Clause AnalysisJay PatelNo ratings yet
- 4600 Plum Eye Wash 112015 UKDocument7 pages4600 Plum Eye Wash 112015 UKArdXkillerNo ratings yet
- Buncombe County Fiscal Year 2022 Financial AuditDocument206 pagesBuncombe County Fiscal Year 2022 Financial AuditChristian SmithNo ratings yet
- Dairy Project For Zaru Last EditedDocument15 pagesDairy Project For Zaru Last Editedgaromsa degaga100% (1)
- Eller Compliant ResumeDocument1 pageEller Compliant Resumeapi-737638555No ratings yet
- Aditya DecertationDocument44 pagesAditya DecertationAditya PandeyNo ratings yet
- A Framework For Applying Ai in The EnterpriseDocument38 pagesA Framework For Applying Ai in The Enterprisehmt.No ratings yet
- Chapter-4 Aggregate PlanningDocument22 pagesChapter-4 Aggregate PlanningYonatanNo ratings yet
- WAC AssignmentDocument7 pagesWAC Assignmentb00054584100% (1)
- Accommodation Price Guide 2022 23 v2Document4 pagesAccommodation Price Guide 2022 23 v2api-574005418No ratings yet
- Valeura PDFDocument11 pagesValeura PDFRodrigo RodrigoNo ratings yet