Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The Critical Role of Management Skills: - Rapid Change in 21st Century - Computers Within 20 Years
Uploaded by
Md Selim0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views24 pagesManagerial Decision
Original Title
M&D.Introduction
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentManagerial Decision
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views24 pagesThe Critical Role of Management Skills: - Rapid Change in 21st Century - Computers Within 20 Years
Uploaded by
Md SelimManagerial Decision
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 24
The Critical Role of Management
Skills
• Rapid change in 21st century
• Computers within 20 years
“If you are not confused you are not paying attention” --- Tom Peters
“We are in one of those historical periods that occur every 200 or 300 years when people
don’t understand the world anymore, and the past is not sufficient to explain the future”
--- Peter Drucker
• Position of skills despite changes
• We are exposed to more information each
day
• Building trusting relationships – a critical
part of coping with information overload
• In changes, we have to fix on
something that is not changing
• Manage change - by having an
established, unwavering point, to
maintain bearings
• Make sense of change by being able
to identify a fixed, stable, permanent
point that provides us with
perspective
• Skills serve as fixed points
• Skills have changed very little in their
effectiveness and relevance
• What is known is not always
the same as demonstrated
• Principles of effective
relationships have not always
been practices
• What we know and what we
demonstrate do not always
match
George Carlin
The paradox of our time in history is that
• We have taller buildings but shorter
temper
• Wide freeways but narrower viewpoints
• We spend more but have less
• We buy more but enjoy it less
• We have bigger houses and smaller
families
• More convenience but less time
• We have more degrees but less sense
• More knowledge but less judgment
• More experts but more problems
• More medicine but less wellness
• We drink too much, smoke too much,
spend too recklessly,
• Laugh too little, drive too fast, get too
angry too quickly,
• Stay up too late get too tired, read too
seldom, watch TV too much and pray too
seldom
• We have multiplied our possessions
but reduced our values
• We talk too much, love too seldom and
hate too often
• We have learned how to make a living
but not a life
• We have added years to life but not life
to years
• We have been all the way to the moon
and back but have trouble crossing the
street to meet the new neighbour
• We have conquered outer space but not inner
space
• We have done larger but not better things
• We have cleaned up air but polluted the soul
• We have split the atom but not our prejudice
• We write more but learn less
• We plan more but accomplish less
• We have learned to rush but not to wait
• We build more computers to hold more
information
• to produce more copies than ever but have
less communication
• These are the times of fast foods and
slow digestion
• Tall men and short character
• Steep profits and shallow
relationships
• These are the times of world peace
but domestic warfare
• More leisure but less fun; more kinds
of food but less nutrition
• These are the days of two income but
more divorce
• of fancier houses but broken homes
• These are the days of quick trips,
disposable diapers
• Throw-away morality, one night stands,
overweight bodies and pills, that do
everything from cheer to quiet to kill
• It is a time when there is much in the
show window
• and nothing in the stockroom;
• a time when technology can bring this
letter to you
• and a time when you can choose
either to share this insight or just hit
delete
Importance of competent managers
Studies conducted across industry sectors,
international settings and organization types
Skillful management – competence in
management of people is the key determinant
of organizational success
Success of organizations – competent skillful
managers
What explains the financial success of the firms
that are highly effective ?
Five most powerful predictors :
Market share (the higher the market share of the firm the
higher the profitability)
Firm capital intensity (the more a firm is automated and
up-to-date in technology and equipment, the more
profitable it is)
Size of the firm in assets (economies of scale and
efficiency of production can be used in large firms to
increase profitability
Industry average return on sales (firms would reflect the
performance of a highly profitable industry)
Ability of managers to effectively manage their people (an
emphasis on good people management helps produce
profitability in firms)
Management attributes
Case of General Motors Automobile Plant pp6-7
Good management fosters financial success, whereas less
effective management fosters financial distress
Successful organizations have managers with well-developed
people management skills
Management skills are most important than industry,
environment, competition and economic factors combined
Finding people who effectively manage people is not as
common as might be expected.
Common sense and common knowledge are not necessarily
common practice.
Knowing and doing are not the same things.
Implementing effective management skills are more than just
analyzing a case, identifying a problem, reciting correct answer
to a question.
Skills of effective managers
Attributes, behaviors, orientations and strategies for
successful performance
7 key practices for organizational effectiveness ( pfeffer,
1998)
Ensure employment security
Selectively hire people
Foster decentralization and self managing teams
Institute high levels of pay based on performance
Train extensively
Reduce status differences
Share information
Skills of effective managers
Eight seeds of effective management and
leadership (Quinn, 2000)
Envision the productive community
First look within
Embrace the hypocritical self
Transcend fear
Embody a vision of the common good
Disturb the system
Surrender to the emergent process
Entice through moral power
Skills of effective managers
According to Brodbeck et.al.,2000; Rigby, 1998
Inspirational
Self sacrificial
Integrity
Diplomatic
Malevolent
Visionary
Administrative
Self-centered
Status conscious
Autocratic
Modest
Autonomous attributes
According to 4137 managers in North America, Europe
and Asia tools associated with organization success
Strategic planning
Pay for performance
Strategic alliances
Customer satisfaction measurement
Shareholder value analysis
Mission and vision statements
Benchmarking
Cycle time reduction
Agile strategies
Self directed teams
Groupware
These are organizational strategies,
personality orientations, and philosophical
approaches to management. Their
implementation is usually outside the explicit
control of the individual manager.
The effectiveness of the attributes on these
kinds of lists depends on the manager’s skill in
implementing in them, and that means being
competent in fundamental management skills.
Management skills form the vehicle by which
management strategy, management practice,
tools and techniques, personality attributes,
and style work to produce effective outcomes
in organizations.
Management skills are the building blocks
upon which effective management rests.
Management skills are the means by which
managers translate their own style, strategy,
and favorite tools or techniques into practice.
Emotional Intelligence (EQ) : Consists of skills
of self awareness, self-regulation, self control,
motivation, the ability to understand others’
emotional and behavioral cues (empathy), and
interpersonal skills.
Cognitive Intelligence (IQ) : which remains
largely the same throughout life.
EQ can be developed and improved over time
with concerted effort.
What are management skills
Management skills are behavioral
Mgt skills consist of identifiable sets of actions that individuals
perform and lead to certain outcomes. Skills can be observed by
others, unlike attributes that are purely mental or are embedded in
personality. There is a core set of observable attributes in effective
skill performance that are common across a range of individual
differences.
Management skills are controllable
The performance of these behaviors is under the control of the
individual. Skills can be consciously demonstrated, practiced,
improved, or restrained by individuals themselves. Skills may
certainly engage other people and require cognitive work, but they
are behaviors that people can control themselves.
Management Skills
Management skills are developable.
Performance can improve. Individuals can improve their
competency in skill performance through practice and
feedback.
Management skills are interrelated and overlapping
Skills are integrated sets of complex responses. Effective
managers develop a constellation of skills that overlap and
support one another and allow flexibility in managing
diverse situations.
Management skills are sometimes contradictory and
paradoxical
They are oriented neither toward teamwork and
interpersonal relations exclusively nor toward
individualism and technical entrepreneurship exclusively.
Research found that skills fall into four main
groups or clusters
Participative and human relations skills
Competitive and control skills
Innovativeness and individuals entrepreneurship
skills
Maintaining order and rationality skills
Most effective managers are both participative
and hard driving, both nurturing and
competitive.
Model for developing management skills : This has been most successful
in helping individuals develop managerial skills which is based on social
learning theory
Components Contents Objectives
Skill assessment Survey instruments, Assess current level of skill competence
role plays and knowledge; create readiness to change
Skill Learning Written text Teach correct principles and present a
Behavioral guidelines rationale for behavioral guidelines
Skill analysis cases Provide examples of appropriate and
inappropriate skill performance. Analyze
behavioral principles and reasons they
work
Skill practice Exercises Practice behavioral guidelines. Adapt
simulations, Role principles to personal style. Receive
plays feedback and assistance
Skill application Assignments Transfer classroom learning to real-life
(behavioral and situations. Foster ongoing personal
written develpment
You might also like
- Managerial Skills Development: Nsu Emba HRM 631 Spring 2015, Friday 23, January 15Document24 pagesManagerial Skills Development: Nsu Emba HRM 631 Spring 2015, Friday 23, January 15Flora TanjilaNo ratings yet
- Good Business Sense for Doing Good Business: A Guide to Enhance Your Business AcumenFrom EverandGood Business Sense for Doing Good Business: A Guide to Enhance Your Business AcumenNo ratings yet
- Industrial Management FST 2210: S.P. NgwaruDocument46 pagesIndustrial Management FST 2210: S.P. Ngwarumatthew matawoNo ratings yet
- Managing Workplace Diversity: Building Effective and Efficient Work RelationshipsFrom EverandManaging Workplace Diversity: Building Effective and Efficient Work RelationshipsNo ratings yet
- Mastering the Art of Management: A Comprehensive Guide to Becoming a Great ManagerFrom EverandMastering the Art of Management: A Comprehensive Guide to Becoming a Great ManagerNo ratings yet
- Uncommonly Observant Leadership; Overcoming 'Management by Ignorance'From EverandUncommonly Observant Leadership; Overcoming 'Management by Ignorance'No ratings yet
- Role of ManagersDocument25 pagesRole of ManagersAnubhav Singh100% (1)
- Best Practices: Managing People: Secrets to Leading for New ManagersFrom EverandBest Practices: Managing People: Secrets to Leading for New ManagersRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- Management Theory and PracticeDocument20 pagesManagement Theory and PracticeSrinivas ShinuNo ratings yet
- Effective Leadership: Tips to motivate and inspire your team membersFrom EverandEffective Leadership: Tips to motivate and inspire your team membersNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of International Management: Compiled by Dr. M.VenkatesanDocument72 pagesFundamentals of International Management: Compiled by Dr. M.Venkatesanvijay ranjanNo ratings yet
- Management in India: Grow from an Accidental to a Successful Manager in the IT & Knowledge IndustryFrom EverandManagement in India: Grow from an Accidental to a Successful Manager in the IT & Knowledge IndustryNo ratings yet
- Lead with Impact Practical Tips for Elevating Your Leadership SkillsFrom EverandLead with Impact Practical Tips for Elevating Your Leadership SkillsNo ratings yet
- The Art of Influence: Qualities and Traits of Successful LeadersFrom EverandThe Art of Influence: Qualities and Traits of Successful LeadersNo ratings yet
- Smart Decisions: Mastering Problem Solving with Strategic Solutions for Business SuccessFrom EverandSmart Decisions: Mastering Problem Solving with Strategic Solutions for Business SuccessNo ratings yet
- Results that Last (Review and Analysis of Studer's Book)From EverandResults that Last (Review and Analysis of Studer's Book)No ratings yet
- Organization and Management Lesson1Document24 pagesOrganization and Management Lesson1Desserie NovalNo ratings yet
- STRATMANDocument4 pagesSTRATMANChristian CañasNo ratings yet
- Managerial EffectivenessDocument25 pagesManagerial EffectivenesskadamnidhiNo ratings yet
- Performance Management: Excellence as an Attitude. Performance as a Habit.From EverandPerformance Management: Excellence as an Attitude. Performance as a Habit.Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (4)
- Lack of Collaboration, Public Criticism, Crisis, Financial Shortage OppositionDocument41 pagesLack of Collaboration, Public Criticism, Crisis, Financial Shortage OppositionGudissa EnkossaNo ratings yet
- 1.-PrinciplesofManagement 01 IntroductiontoManagementDocument33 pages1.-PrinciplesofManagement 01 IntroductiontoManagementVirgelio Sayson AbesNo ratings yet
- The Effective ExecutiveDocument12 pagesThe Effective ExecutiveRAVI KUMARNo ratings yet
- Leading for Success: Unleash your leadership potential to achieve extraordinary resultsFrom EverandLeading for Success: Unleash your leadership potential to achieve extraordinary resultsNo ratings yet
- Making It in Management: Developing the Thinking You Need to Move up the Organization Ladder … and Stay ThereFrom EverandMaking It in Management: Developing the Thinking You Need to Move up the Organization Ladder … and Stay ThereNo ratings yet
- HBR's 10 Must Reads on Managing People (with featured article "Leadership That Gets Results," by Daniel Goleman)From EverandHBR's 10 Must Reads on Managing People (with featured article "Leadership That Gets Results," by Daniel Goleman)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (15)
- Introduction To Management: Know How To Manage Your Time. Develop Your Skill at Being Politically AwareDocument34 pagesIntroduction To Management: Know How To Manage Your Time. Develop Your Skill at Being Politically AwaremubasherNo ratings yet
- OB-I Intro - Diversity - Personality & Values - Emotions & MoodsDocument92 pagesOB-I Intro - Diversity - Personality & Values - Emotions & MoodsshivamenonNo ratings yet
- Empower! to Win: An Action Guide to the Imperative Leadership Style of the 21St CenturyFrom EverandEmpower! to Win: An Action Guide to the Imperative Leadership Style of the 21St CenturyNo ratings yet
- Executive SOS: 7 Easy Steps to a Proven Strategic Operating SystemFrom EverandExecutive SOS: 7 Easy Steps to a Proven Strategic Operating SystemNo ratings yet
- Leading Through Transitions Participant Workbook One-Day WorkshopFrom EverandLeading Through Transitions Participant Workbook One-Day WorkshopNo ratings yet
- Managing in Turbulent TimeDocument29 pagesManaging in Turbulent TimePaingNo ratings yet
- Basic Managerial SkillsDocument79 pagesBasic Managerial SkillsRoy Amores100% (1)
- Leadership Skills - How To Improve Your Leadership Skills And Become The Leader That You Meant To BeFrom EverandLeadership Skills - How To Improve Your Leadership Skills And Become The Leader That You Meant To BeNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Management & Managing PeopleDocument95 pagesIntroduction To Management & Managing Peoplehillary opilloNo ratings yet
- How To Manage People: The No Waffle Guide To Managing Performance, Change And Stress In The WorkplaceFrom EverandHow To Manage People: The No Waffle Guide To Managing Performance, Change And Stress In The WorkplaceRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- The Traits of Today's CFO: A Handbook for Excelling in an Evolving RoleFrom EverandThe Traits of Today's CFO: A Handbook for Excelling in an Evolving RoleNo ratings yet
- Management Styles and ApproachDocument18 pagesManagement Styles and ApproachChelsea MartinezNo ratings yet
- Job Aid Effective Delegation WorksheetDocument19 pagesJob Aid Effective Delegation WorksheetCosmin Corlatescu100% (1)
- Chap 1, 2 and 3Document60 pagesChap 1, 2 and 3ashishNo ratings yet
- Principles of Management Essentials You Always Wanted To Know (Second Edition)From EverandPrinciples of Management Essentials You Always Wanted To Know (Second Edition)Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Unit 4001: An Introduction To Managerial StyleDocument24 pagesUnit 4001: An Introduction To Managerial StyleAzm FaisalNo ratings yet
- Leadership Excellence: Creating a New Dimension of Organizational SuccessFrom EverandLeadership Excellence: Creating a New Dimension of Organizational SuccessNo ratings yet
- The Critical Role of Management Skills: - Rapid Change in 21st Century - Computers Within 20 YearsDocument24 pagesThe Critical Role of Management Skills: - Rapid Change in 21st Century - Computers Within 20 YearsMd SelimNo ratings yet
- North South University: Economic Conditions of Bangladesh (July 2016-September 2016)Document1 pageNorth South University: Economic Conditions of Bangladesh (July 2016-September 2016)Md SelimNo ratings yet
- Gaining Power and InfluenceDocument17 pagesGaining Power and InfluenceMd SelimNo ratings yet
- Bus 690 Final DFADocument13 pagesBus 690 Final DFAMd SelimNo ratings yet
- Cover Page StrategicDocument1 pageCover Page StrategicMd SelimNo ratings yet
- Coaching, Counseling, and Supportive CommunicationDocument31 pagesCoaching, Counseling, and Supportive CommunicationMd SelimNo ratings yet
- Building Strong Power Base and Using Influence WiselyDocument16 pagesBuilding Strong Power Base and Using Influence WiselyMd SelimNo ratings yet
- Arla: Health Food Drinks Marketing Strategy in BangladeshDocument27 pagesArla: Health Food Drinks Marketing Strategy in BangladeshMd SelimNo ratings yet
- Arla: Health Food Drinks Marketing Strategy in BangladeshDocument27 pagesArla: Health Food Drinks Marketing Strategy in BangladeshMd SelimNo ratings yet
- LakmeDocument34 pagesLakmeSuraj Pratap Sawhney79% (14)
- (Durt, - Christoph - Fuchs, - Thomas - Tewes, - Christian) Embodiment, Enaction, and Culture PDFDocument451 pages(Durt, - Christoph - Fuchs, - Thomas - Tewes, - Christian) Embodiment, Enaction, and Culture PDFnlf2205100% (3)
- History of The UST School of Fine Arts, Chapter 4Document27 pagesHistory of The UST School of Fine Arts, Chapter 4Hannibal F. CaradoNo ratings yet
- Unsolved Problems - Mathematics Edition: August 2020Document28 pagesUnsolved Problems - Mathematics Edition: August 2020Nixon LagrisolaNo ratings yet
- OrthoDocument22 pagesOrthosivaleela gNo ratings yet
- Midterm Decision Analysis ExercisesDocument5 pagesMidterm Decision Analysis ExercisesAYLEN INJAYANo ratings yet
- INTRODUCTIONDocument1 pageINTRODUCTIONNabila Gaming09No ratings yet
- Brochure 8 VT 8Document24 pagesBrochure 8 VT 8David GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Dopamine What It Is, Function & SymptomsDocument7 pagesDopamine What It Is, Function & SymptomsRaj KumarNo ratings yet
- Fascinating Numbers: Some Numbers of 3 Digits or More Exhibit A Very Interesting PropertyDocument2 pagesFascinating Numbers: Some Numbers of 3 Digits or More Exhibit A Very Interesting PropertyAnonymous JGW0KRl6No ratings yet
- AIDA Deconstruction of Surf Excel AdDocument6 pagesAIDA Deconstruction of Surf Excel AdRoop50% (2)
- Resume Testing6+ SaptagireswarDocument5 pagesResume Testing6+ SaptagireswarSuresh RamasamyNo ratings yet
- VestibuleDocument17 pagesVestibuleDeepti MangalNo ratings yet
- 06 Cruz v. Dalisay, 152 SCRA 482Document2 pages06 Cruz v. Dalisay, 152 SCRA 482avatarboychrisNo ratings yet
- FreeMarkets: Procurement & Outsourcing StrategiesDocument44 pagesFreeMarkets: Procurement & Outsourcing StrategiesFarhaad MohsinNo ratings yet
- Plastique: Art and EducationDocument7 pagesPlastique: Art and EducationJackStevensonNo ratings yet
- Financial Crisis Among UTHM StudentsDocument7 pagesFinancial Crisis Among UTHM StudentsPravin PeriasamyNo ratings yet
- Angel Number 1208 Meaning Increased FaithDocument1 pageAngel Number 1208 Meaning Increased FaithKhally KatieNo ratings yet
- Man Is Made by His BeliefDocument2 pagesMan Is Made by His BeliefLisa KireechevaNo ratings yet
- Marriage Practices Among The Gidda Oromo, Northern Wollega, EthiopiaDocument2 pagesMarriage Practices Among The Gidda Oromo, Northern Wollega, Ethiopiajoseph mathewNo ratings yet
- Commercial CrimesDocument3 pagesCommercial CrimesHo Wen HuiNo ratings yet
- Openfire XXMPP Server On Windows Server 2012 R2Document9 pagesOpenfire XXMPP Server On Windows Server 2012 R2crobertoNo ratings yet
- Resume of Masterchef Contestant, Melissa GutierrezDocument3 pagesResume of Masterchef Contestant, Melissa GutierrezMikhail GalatinovNo ratings yet
- Contracts ChecklistDocument3 pagesContracts ChecklistSteve WatmoreNo ratings yet
- Humanistic Developmental Physiological RationalDocument10 pagesHumanistic Developmental Physiological RationalJin TippittNo ratings yet
- Chan Sophia ResumeDocument1 pageChan Sophia Resumeapi-568119902No ratings yet
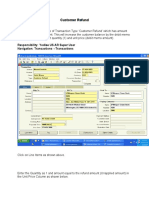
- Customer Refund: Responsibility: Yodlee US AR Super User Navigation: Transactions TransactionsDocument12 pagesCustomer Refund: Responsibility: Yodlee US AR Super User Navigation: Transactions TransactionsAziz KhanNo ratings yet
- Direct Filter Synthesis Rhea PreviewDocument25 pagesDirect Filter Synthesis Rhea Previewoprakash9291No ratings yet
- 7 - LESSON PLAN CULTURAL HERITAGE AND CULTURAL DIVERSITY - Lesson PlanDocument4 pages7 - LESSON PLAN CULTURAL HERITAGE AND CULTURAL DIVERSITY - Lesson PlanRute SobralNo ratings yet
- Music in The United KingdomDocument33 pagesMusic in The United KingdomIonut PetreNo ratings yet