Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Heat Exchange
Uploaded by
shravaniOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Heat Exchange
Uploaded by
shravaniCopyright:
Available Formats
HEAT EXCHANGE
Heat transfer is a discipline of thermal engineering that concerns the generation, use, conversion, and exchange of thermal energy (heat)
between physical systems. Heat transfer is classified into various mechanisms, such as thermal conduction, thermal convection, thermal
radiation, and transfer of energy by phase changes
Heat exchange between an individual and the surrounding environment is realized through conventional heat exchange pathways of
conduction, convection, radiation, and evaporation
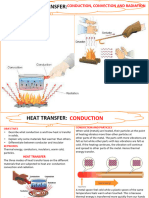
• Conduction is heat traveling through a solid material. On hot days,
heat is conducted into your home through the roof, walls, and
windows. Heat-reflecting roofs, insulation, and energy efficient
windows will help to reduce that heat conduction.
• Radiation is heat traveling in the form of visible and non-visible light.
Sunlight is an obvious source of heat for homes. In addition, low-
wavelength, non-visible infrared radiation can carry heat directly from
warm objects to cooler objects. Infrared radiation is why you can feel the
heat of a hot burner element on a stovetop, even from across the room.
Older windows will allow infrared radiation coming from warm objects
outside to radiate into your home; shades can help to block this radiation.
Newer windows have low-e coatings that block infrared radiation. Infrared
radiation will also carry the heat of your walls and ceiling directly to your
body.
• Convection is another means for the heat from your walls and
ceiling to reach you. Hot air naturally rises, carrying heat away from
your walls and causing it to circulate throughout your home. As the
hot air circulates past your skin (and you breathe it in), it warms
you.
Heat Exchange is Applied for Human Comfort
Your body can cool down through three processes: convection, radiation, and perspiration. Ventilation enhances all these processes. You can
also cool your body via conduction -- some car seats now feature cooling elements, for instance -- but this is not generally practical for use
in your home.
Convection occurs when heat is carried away from your body via moving air. If the surrounding air is cooler than your skin, the air will
absorb your heat and rise. As the warmed air rises around you, cooler air moves in to take its place and absorb more of your warmth. The
faster this convecting air moves, the cooler you feel.
Radiation occurs when heat radiates across the space between you and the objects in your home. If objects are warmer than you are, heat will
travel toward you. Removing heat through ventilation reduces the temperature of the ceiling, walls, and furnishings. The cooler your
surroundings, the more you will radiate heat to the objects, rather than the other way around.
Perspiration can be uncomfortable, and many people would prefer to stay cool without it. However, during hot weather and physical
exercise, perspiration is the body's powerful cooling mechanism. As moisture leaves your skin pores, it carries a lot of heat with it, cooling
your body. If a breeze (ventilation) passes over your skin, that moisture will evaporate more quickly, and you'll be even cooler.
You might also like
- UntitledDocument1 pageUntitledOladimeji BobolaNo ratings yet
- Radiation PDFDocument4 pagesRadiation PDFTahmeed AzizNo ratings yet
- Basics of Building Heating and CoolingDocument4 pagesBasics of Building Heating and CoolingVgie QuanicoNo ratings yet
- Group 5 - Passive DesigningDocument26 pagesGroup 5 - Passive DesigningSiddhant VoraNo ratings yet
- Heat TransferDocument11 pagesHeat TransferNajeela BanuNo ratings yet
- Environmental ScienceDocument115 pagesEnvironmental ScienceShauqi MustafarNo ratings yet
- Research Infrared RadiatorDocument13 pagesResearch Infrared Radiatormonther alsharifNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer in The AtmosphereDocument21 pagesHeat Transfer in The Atmosphereesthy angeliaNo ratings yet
- Section 3-Thermal InsulationDocument51 pagesSection 3-Thermal InsulationxvNo ratings yet
- 1.6 The Science of InsulationDocument4 pages1.6 The Science of InsulationisteboiNo ratings yet
- Topic 9 PhysicsDocument13 pagesTopic 9 PhysicsYHSNo ratings yet
- Ph10 - 05.08 - Thermal Equilibrium & Heat FlowDocument17 pagesPh10 - 05.08 - Thermal Equilibrium & Heat FlowРубабе ХалиловаNo ratings yet
- Passive Solar Design For The Home: Heat-Movement PhysicsDocument8 pagesPassive Solar Design For The Home: Heat-Movement PhysicsbekkuNo ratings yet
- Applications of Thermal Energy Transfer: Made by Hashir Razvi O-Ii FDocument12 pagesApplications of Thermal Energy Transfer: Made by Hashir Razvi O-Ii FHashir RazviNo ratings yet
- Cape Phy Mod 3 - Heat Transfer 2Document3 pagesCape Phy Mod 3 - Heat Transfer 2kerriemarsNo ratings yet
- Conduction Convection RadiationDocument32 pagesConduction Convection RadiationShalini Kulshrestha100% (2)
- Reem Ibrahim 21100391Document12 pagesReem Ibrahim 21100391rokai0436No ratings yet
- Part 2Document14 pagesPart 2api-298420434No ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Thermal Energy TransferDocument18 pagesChapter 11 Thermal Energy TransferNayeem HakimNo ratings yet
- Course Code: en 12 - : Heat TransferDocument7 pagesCourse Code: en 12 - : Heat TransferAkim ApallaNo ratings yet
- HT Assgnmnt 2Document3 pagesHT Assgnmnt 2Tamoor TariqNo ratings yet
- NAME - Divi Rajpal 2215991513Document7 pagesNAME - Divi Rajpal 2215991513arpitrajpal2008No ratings yet
- ConvectionandradiationDocument16 pagesConvectionandradiationapi-276003030No ratings yet
- Heat Transfer and Thermal Performance of Wall & Roof: Submitted by Darshini.MDocument17 pagesHeat Transfer and Thermal Performance of Wall & Roof: Submitted by Darshini.MDarshini manoharanNo ratings yet
- 14-Revision Heat TransferDocument23 pages14-Revision Heat TransferYuichi AkasakaNo ratings yet
- 05B-Thermal InsulationDocument25 pages05B-Thermal InsulationRitikaNo ratings yet
- Transfer of Thermal Energy: ConductionDocument10 pagesTransfer of Thermal Energy: ConductionmelissaNo ratings yet
- PhysicssDocument5 pagesPhysicsschionumaraliaNo ratings yet
- 5054 Handouts Topic-9 Transfer of Thermal EnergyDocument8 pages5054 Handouts Topic-9 Transfer of Thermal EnergyShehzad EhsanNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Questions:: Heat, The Ultimate Form of EnergyDocument12 pagesFundamental Questions:: Heat, The Ultimate Form of EnergyMohd HaniffNo ratings yet
- Consequences of Thermal Energy Transfer - IIDocument1 pageConsequences of Thermal Energy Transfer - IITamilore AdegbonmireNo ratings yet
- Free Energy - Passive Solar CoolingDocument21 pagesFree Energy - Passive Solar CoolingGiuseppe VaccinaNo ratings yet
- Energy LabDocument3 pagesEnergy Labkrbfcbyc4vNo ratings yet
- 41 HeatDocument5 pages41 Heattriangle123No ratings yet
- 00 - Heat Flow Through BuildingDocument20 pages00 - Heat Flow Through Building052 Deepak NaralaNo ratings yet
- 4 Fundamentals of Heat TransferDocument36 pages4 Fundamentals of Heat TransferShaurya ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Building Services - Vi: Assignment 2Document6 pagesBuilding Services - Vi: Assignment 2Pooja SharmaNo ratings yet
- Ch-13 (Limit and Derivatives FINAL 02.01.06)Document9 pagesCh-13 (Limit and Derivatives FINAL 02.01.06)AnnNo ratings yet
- How To Make Your Homes Energy SufficientDocument12 pagesHow To Make Your Homes Energy SufficientapurvaNo ratings yet
- 1 Heat TransferDocument3 pages1 Heat TransferAdam HartmannNo ratings yet
- Heat Lec2 MethodDocument15 pagesHeat Lec2 MethodVincent ManganaanNo ratings yet
- Services Assignment 3Document7 pagesServices Assignment 3arpitrajpal2008No ratings yet
- Conduction Convection and Radiation Lesson 2Document9 pagesConduction Convection and Radiation Lesson 2Ajeet KumarNo ratings yet
- (2.3) C - Transfer of Thermal Energy - RadiationDocument2 pages(2.3) C - Transfer of Thermal Energy - Radiationzahra1No ratings yet
- Hot Dry Climate AnalysisDocument23 pagesHot Dry Climate AnalysisBTSyologyNo ratings yet
- HEATDocument16 pagesHEATHoney Mae CarvajalNo ratings yet
- Heat TransfersDocument16 pagesHeat Transfersrahayuutami30No ratings yet
- Indirect Heat Gain System:: Five Elements of A Thermal Storage Wall Can Be IdentifiedDocument17 pagesIndirect Heat Gain System:: Five Elements of A Thermal Storage Wall Can Be IdentifiedAbishaTeslinNo ratings yet
- Passive HouseDocument9 pagesPassive HouseRakesh VdNo ratings yet
- Thermal Effects - Do Now!: - Make A List of Good and Bad Conductors of HeatDocument50 pagesThermal Effects - Do Now!: - Make A List of Good and Bad Conductors of HeatErna GampalNo ratings yet
- Heat EnergyDocument18 pagesHeat EnergyCrazzy RamNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer 2Document24 pagesHeat Transfer 2AshMere MontesinesNo ratings yet
- ACTIVIDAD DE CIENCIA DE LOS MATERIALES - Ingles y Español - Jose Daniel BallestasDocument15 pagesACTIVIDAD DE CIENCIA DE LOS MATERIALES - Ingles y Español - Jose Daniel BallestasJose Daniel BallestasNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer TransesDocument2 pagesHeat Transfer TransesERICKA MAE CANTOSNo ratings yet
- Transmission of HeatDocument1 pageTransmission of HeatWEI SHANGLI STANLEY NGAINo ratings yet
- NGSS3D MSPS ThermalEnergyTransfer EXPLAIN STEMscopediaDocument7 pagesNGSS3D MSPS ThermalEnergyTransfer EXPLAIN STEMscopediaSivekiNo ratings yet
- P2 Energy Transfer by HeatingDocument1 pageP2 Energy Transfer by HeatingArun DonteNo ratings yet
- Topic: Heat Transfer MechanismsDocument17 pagesTopic: Heat Transfer MechanismsJaime Leal NavarroNo ratings yet
- WD Washroom (Material Board)Document2 pagesWD Washroom (Material Board)shravaniNo ratings yet
- COLOUR PSYCHOLOGY (GRP Project)Document1 pageCOLOUR PSYCHOLOGY (GRP Project)shravaniNo ratings yet
- What Makes and Executive Chair Different From A StandardDocument16 pagesWhat Makes and Executive Chair Different From A StandardshravaniNo ratings yet
- Colour PsychologyDocument1 pageColour PsychologyshravaniNo ratings yet
- NUBRADocument25 pagesNUBRAshravaniNo ratings yet
- Nubra Shipping Container ResortsDocument140 pagesNubra Shipping Container ResortsshravaniNo ratings yet
- Sports Tournament Management SystemDocument6 pagesSports Tournament Management SystemPusparajan PapusNo ratings yet
- CMMI DAR Effectively Apply The Decision Analysis and Resolution (DAR) ProcessDocument26 pagesCMMI DAR Effectively Apply The Decision Analysis and Resolution (DAR) Processjgonzalezsanz8914100% (1)
- Data Center Cooling SolutionsDocument24 pagesData Center Cooling SolutionsGemelita Ortiz100% (1)
- Transitive & Intransitive Verbs: Grammar PracticeDocument5 pagesTransitive & Intransitive Verbs: Grammar PracticeSzeman YipNo ratings yet
- Fallas de ManeaderoDocument17 pagesFallas de ManeaderoGerman Martinez RomoNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 RespirationDocument6 pagesGrade 8 RespirationShanel WisdomNo ratings yet
- Syncronex Single Copy 3.1 Users GuideDocument208 pagesSyncronex Single Copy 3.1 Users GuideTony BoscoNo ratings yet
- SAES-L-610 PDF Download - Nonmetallic Piping in Oily Water Services - PDFYARDocument6 pagesSAES-L-610 PDF Download - Nonmetallic Piping in Oily Water Services - PDFYARZahidRafiqueNo ratings yet
- Last Boat Not Least - An Unofficial Adventure For Fallout 2d20Document14 pagesLast Boat Not Least - An Unofficial Adventure For Fallout 2d20Veritas Veritati100% (3)
- Measurement of Hindered Phenolic Antioxidant Content in HL Turbine Oils by Linear Sweep VoltammetryDocument6 pagesMeasurement of Hindered Phenolic Antioxidant Content in HL Turbine Oils by Linear Sweep VoltammetryMohanadNo ratings yet
- PH G12 S1Document9 pagesPH G12 S1mahmoudNo ratings yet
- Format of Actual BatchDocument16 pagesFormat of Actual Batchaljhon dela cruzNo ratings yet
- Load Tracing PDFDocument19 pagesLoad Tracing PDFAngelique StewartNo ratings yet
- Technical DescriptionDocument6 pagesTechnical DescriptionJigar MehtaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - Adlerian TherapyDocument28 pagesChapter 5 - Adlerian TherapyRhalf100% (1)
- Rwanda National Examinations Council Organisational Chart DeputyDocument1 pageRwanda National Examinations Council Organisational Chart DeputymugobokaNo ratings yet
- COMSOL WebinarDocument38 pagesCOMSOL WebinarkOrpuzNo ratings yet
- Why Facts Don't Change Our MindsDocument13 pagesWhy Facts Don't Change Our MindsNadia Sei LaNo ratings yet
- Differences ISO11737-1 2018 and 2006 VersionsDocument11 pagesDifferences ISO11737-1 2018 and 2006 VersionsVickysh MevawalaNo ratings yet
- MIT15 093J F09 Rec04Document4 pagesMIT15 093J F09 Rec04santiago gonzalezNo ratings yet
- Codel: Monitoring SolutionsDocument4 pagesCodel: Monitoring SolutionsCindy HenaoNo ratings yet
- The Brain's Sense of Movement - Alan BerthozDocument352 pagesThe Brain's Sense of Movement - Alan BerthozKaroline MarxNo ratings yet
- Curs FinalDocument8 pagesCurs FinalandraNo ratings yet
- Transportation Research Part C: Xiaojie Luan, Francesco Corman, Lingyun MengDocument27 pagesTransportation Research Part C: Xiaojie Luan, Francesco Corman, Lingyun MengImags GamiNo ratings yet
- Sop 905Document10 pagesSop 905harryNo ratings yet
- System 9898XT Service ManualDocument398 pagesSystem 9898XT Service ManualIsai Lara Osoria100% (3)
- Miele G 666Document72 pagesMiele G 666tszabi26No ratings yet
- Middle East Product Booklet 5078 NOV18Document56 pagesMiddle East Product Booklet 5078 NOV18Mohamed987No ratings yet
- Final Examination SEMESTER 1, SESSION 2014/2015: SKAA 2722 1Document10 pagesFinal Examination SEMESTER 1, SESSION 2014/2015: SKAA 2722 1Hanis SyafiqNo ratings yet
- Aras Jung Curriculum IndividualDocument72 pagesAras Jung Curriculum IndividualdianavaleriaalvarezNo ratings yet