Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 11 Thermal Energy Transfer
Chapter 11 Thermal Energy Transfer
Uploaded by
Nayeem Hakim0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
0 views18 pagesThis document discusses three methods of heat transfer: conduction, convection, and radiation. Conduction involves the transfer of heat through direct contact of particles. Convection occurs through the movement of fluids like gases and liquids. Radiation transfers heat via electromagnetic waves and does not require a medium. The document provides examples of each type of heat transfer and factors that influence radiation. It also discusses the greenhouse effect and global warming.
Original Description:
Original Title
CHAPTER 11 THERMAL ENERGY TRANSFER
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses three methods of heat transfer: conduction, convection, and radiation. Conduction involves the transfer of heat through direct contact of particles. Convection occurs through the movement of fluids like gases and liquids. Radiation transfers heat via electromagnetic waves and does not require a medium. The document provides examples of each type of heat transfer and factors that influence radiation. It also discusses the greenhouse effect and global warming.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
0 views18 pagesChapter 11 Thermal Energy Transfer
Chapter 11 Thermal Energy Transfer
Uploaded by
Nayeem HakimThis document discusses three methods of heat transfer: conduction, convection, and radiation. Conduction involves the transfer of heat through direct contact of particles. Convection occurs through the movement of fluids like gases and liquids. Radiation transfers heat via electromagnetic waves and does not require a medium. The document provides examples of each type of heat transfer and factors that influence radiation. It also discusses the greenhouse effect and global warming.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 18
CHAPTER 11
‘THERMAL
ENERGY
TRANSFER’
PREPARED BY: S. M. NAYEEM
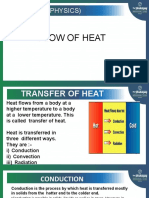
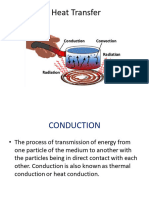
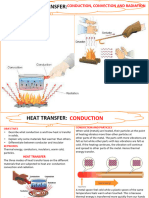
Conduction
• Conduction is the flow of heat energy from a region of
high temperature to a region of low temperature without
overall movement of the material itself.
• The greater the density of a substance better is the
substance as thermal conductor.
• Particles are most tightly packed in solids and least tightly
packed in gases.
• Solids are better conductors than liquids which are again
better conductors than gases.
• Metals are good conductors than non-metals.
• Metals conduct heat through the vibration of the atoms
and the motion of delocalized electrons but non-metals
conduct heat only through the vibration of atoms.
Convection
• Convection is the flow of heat energy from a region of
high temperature to a region of low temperature by
movement of a fluid. Convection only occurs in fluids
(liquids and gases).
• Liquids and gases are fluids. They are able to flow.
• Convection occurs when particles of fluid with a lot of
heat energy expand, becomes less dense and rise up and
take the place of particles with less heat energy that are
denser and therefore sinks down.
• Convection current in air causes sea breeze and land
breeze.
• Convection current inside the core of the Earth causes
tectonic plates and thereby the continents to move.
Radiation
• Radiation is the transfer of heat energy from a region of
high temperature to a region of low temperature by
infrared radiation which a type of electromagnetic wave.
• All hot objects emit thermal energy as radiant heat.
• Unlike conduction and convection, radiation takes place
without the need of any particles.
• Because no particles are involved, radiation can work
through the vacuum of space. This is why we can still feel
the heat of the Sun even though it is 150 million km away
from the Earth.
• Radiation depends on four factors: (i) colour, (ii) texture,
(iii) surface temperature and (iv) surface area.
Radiation (continued)
• Dull coloured surfaces are good absorbers of heat and
good radiators of heat. They are poor reflectors of heat.
• Radiation depends on four factors: (i) colour, (ii) texture,
(iii) surface temperature and (iv) surface area.
• The surfaces which are good absorbers are also good
emitters of infrared radiation. They are also poor
reflectors of infrared radiation.
• Dull surfaces are better absorbers of thermal energy than
bright surfaces.
• Rough surfaces are better absorbers than shiny surfaces.
• Higher the surface temperature better the emission.
• Larger the surface area better the emission.
SEA BREEZE & LAND BREEZE
• During day, land heats up • During day, land cools up
faster than sea. faster than sea.
• Air above the land gets • Air above the land gets
warmer than air above the colder than air above the
sea. sea.
• Hot air above land expands • Hot air above sea expands
becomes lighter and rises. becomes lighter and rises.
• Cold dense air above sea • Cold dense air above land
flows towards land forming flows towards sea forming
sea breeze. land breeze.
INVESTIGATING HEAT RADIATION
INVESTIGATING THERMAL RADIATION
• Apparatus used: Leslie cube, boiling water radiation sensor,
rate meter.
• Method:
(i) Boiling water is poured into Leslie cube and mouth closed by
rubber stopper.
(ii) One infrared detector is placed in front of each faces.
(iii) The distance between cube and detector is kept constant.
(iv) The radiation emitted is received by the detector and
measured by the meter.
(v) The reading from the meter is taken at equal time intervals.
(vi) The readings are used to plot a bar chart of the amount of
radiation emitted against type of surface.
Summary Of The Observation
Type of Surface Type of Radiator
Dull black Very good radiator
Shiny black Good radiator
Dull white Poor radiator
Shiny silvery Very poor radiator
DOMESTIC THERMAL HEAT LOSS
Part of the
house Measures taken Method of reduction of heat
Roof Insulation fitted in the Tapped air in the loft reduces heat lost by
loft conduction and convection
Windows Fit double glazing glass Tapped air between glasses reduces heat
windows lost by conduction and convection
Tapped air between glasses reduces heat
Doors Fitting curtains lost by conduction and convection
Walls Fitting insulation in Tapped air in the insulation reduces heat
cavity walls lost by conduction and convection
Trapped air in the carpet reduces heat
Floors Fitting carpet
lost due to convection
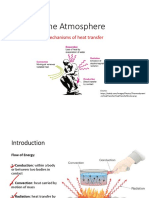
Green House Effect & Global Warming
• Sun sends heat through infrared radiation of high
energy having shorter wavelength.
• The radiation reaches Earth through the
atmosphere.
• Earth warms up and sends then radiates heat out.
• The radiation emitted by Earth has lower energy
having longer energy.
• The radiation emitted cannot pass through the
atmosphere due to presence of carbon dioxide.
• The heat gets trapped and causes global warming.
You might also like
- Chapter 24 'Earth and The Solar System'Document6 pagesChapter 24 'Earth and The Solar System'Nayeem Hakim100% (1)
- Skin Temp of Pipe Exposed To SunDocument8 pagesSkin Temp of Pipe Exposed To SunDebasis PalNo ratings yet
- Transmission of HeatDocument1 pageTransmission of HeatWEI SHANGLI STANLEY NGAINo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer ANTONIO VIDA VDocument40 pagesHeat Transfer ANTONIO VIDA Vshahanajmunni178No ratings yet
- 2-Heating of The AtmosphereDocument31 pages2-Heating of The AtmosphereBSE 2D - AYENZA JOSHUA P.No ratings yet
- GCSE 1a1 HeatTransferDocument64 pagesGCSE 1a1 HeatTransfernitika chawlaNo ratings yet
- Igcse 42 ThermalenergyDocument43 pagesIgcse 42 ThermalenergyHany ElGezawy75% (4)
- Flow of Heat: Chapter 6 (Physics)Document56 pagesFlow of Heat: Chapter 6 (Physics)Pratham KanwraniNo ratings yet
- Heat-Module 3 PDFDocument9 pagesHeat-Module 3 PDFCc givenNo ratings yet
- L3-Ch15 - Thermal Energy (Lesson 1)Document35 pagesL3-Ch15 - Thermal Energy (Lesson 1)Jamal RamadanNo ratings yet
- Transfer of Thermal Energy: Physics Notes GCE Study BuddyDocument20 pagesTransfer of Thermal Energy: Physics Notes GCE Study Buddyanwar9602020No ratings yet
- Thermal Energy TransferDocument40 pagesThermal Energy TransferTania Ferdous RipaNo ratings yet
- 02 - Atmospheric Heat 1Document14 pages02 - Atmospheric Heat 1api-332249032No ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - ThermodynamicsDocument27 pagesLecture 1 - ThermodynamicsCasey Louisse GarciaNo ratings yet
- Sci101 - 23 05 08Document22 pagesSci101 - 23 05 08koalibrahimNo ratings yet
- Transfer of Thermal Energy - Conduction - Convection - Radiation - Applications of Thermal Energy TransferDocument47 pagesTransfer of Thermal Energy - Conduction - Convection - Radiation - Applications of Thermal Energy TransfervaishnaviNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer 2Document24 pagesHeat Transfer 2AshMere MontesinesNo ratings yet
- Thermal Energy TransferDocument44 pagesThermal Energy Transferp geetha raniNo ratings yet
- The Atmosphere - Mechanisms of Heat TransferDocument29 pagesThe Atmosphere - Mechanisms of Heat Transferkaushik baruahNo ratings yet
- Heat TransferDocument27 pagesHeat TransferOmar EzzatNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8 2-10-2004Document19 pagesLecture 8 2-10-2004s9a9nNo ratings yet
- Transmissionof HeatDocument61 pagesTransmissionof HeatSudheer RevanthNo ratings yet
- Transfer of Thermal Energy: ConductionDocument10 pagesTransfer of Thermal Energy: ConductionmelissaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1-1 - Heat ConductionDocument51 pagesLecture 1-1 - Heat ConductionBilal AhmedNo ratings yet
- 4NA - Heat TransferDocument24 pages4NA - Heat TransferChico AlvesNo ratings yet
- 3q Lesson 5 Mechanisms of Heat TransferDocument39 pages3q Lesson 5 Mechanisms of Heat Transfergracelyanjoeyray19No ratings yet
- Transfer of Thermal Energy: Test Yourself 10.1 (Page 168)Document5 pagesTransfer of Thermal Energy: Test Yourself 10.1 (Page 168)Jack Kowman100% (8)
- Topic 9 PhysicsDocument13 pagesTopic 9 PhysicsYHSNo ratings yet
- Thermal Effects - Do Now!: - Make A List of Good and Bad Conductors of HeatDocument50 pagesThermal Effects - Do Now!: - Make A List of Good and Bad Conductors of HeatErna GampalNo ratings yet
- Chapter3 MeteorologyDocument84 pagesChapter3 MeteorologyGiovanni PelobilloNo ratings yet
- 02 - Atmospheric HeatDocument14 pages02 - Atmospheric Heatapi-242405009No ratings yet
- Method of Heat TransferDocument2 pagesMethod of Heat TransferNikki LorraineNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer and Expansion NotesDocument8 pagesHeat Transfer and Expansion NotesmelissaNo ratings yet
- Heat Lec2 MethodDocument15 pagesHeat Lec2 MethodVincent ManganaanNo ratings yet
- Transfer of Thermal Energy - Conduction - Convection - Radiation - Applications of Thermal Energy TransferDocument49 pagesTransfer of Thermal Energy - Conduction - Convection - Radiation - Applications of Thermal Energy TransferImmanuel Suman ShijuNo ratings yet
- Interface Mass TraDocument26 pagesInterface Mass TraWahid AliNo ratings yet
- TP 2Document16 pagesTP 2thunderj43No ratings yet
- Science Form 1Document40 pagesScience Form 1Nka EixNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 HeatDocument6 pagesChapter 5 HeatRajesh JNo ratings yet
- Topic: Heat Transfer MechanismsDocument17 pagesTopic: Heat Transfer MechanismsJaime Leal NavarroNo ratings yet
- Solar Energy and The AtmosphereDocument22 pagesSolar Energy and The AtmosphereJasper CulipNo ratings yet
- Thermal Energy Transfer: ConductionDocument2 pagesThermal Energy Transfer: ConductionJaniah Aaliyah M. DrakesNo ratings yet
- Part 2Document14 pagesPart 2api-298420434No ratings yet
- SS1 Physics Transference of HeatDocument5 pagesSS1 Physics Transference of HeatAbimbola Brodie-MendsNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Heat TransferDocument65 pagesIntroduction To Heat TransferDivya DevhariNo ratings yet
- Bridge CourseDocument49 pagesBridge CourseNAVINRAJ RSNo ratings yet
- Environmental ScienceDocument115 pagesEnvironmental ScienceShauqi MustafarNo ratings yet
- Heat TransferDocument11 pagesHeat TransferNajeela BanuNo ratings yet
- Atmosphere 15 110612161432 Phpapp01Document53 pagesAtmosphere 15 110612161432 Phpapp01A. Nurul Virninda YusufNo ratings yet
- 5054 Handouts Topic-9 Transfer of Thermal EnergyDocument8 pages5054 Handouts Topic-9 Transfer of Thermal EnergyShehzad EhsanNo ratings yet
- Chapter-15 Thermal EnergyDocument8 pagesChapter-15 Thermal Energyananafra861No ratings yet
- Thermal Energy TransferDocument19 pagesThermal Energy TransferProdootNo ratings yet
- PhysicssDocument5 pagesPhysicsschionumaraliaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Transfer of Thermal Energy-1Document6 pagesChapter 7 Transfer of Thermal Energy-1Boss's I will be a superheroNo ratings yet
- Methods of Heat TransferDocument29 pagesMethods of Heat TransferRodriguez ArthursNo ratings yet
- ConvectionandradiationDocument16 pagesConvectionandradiationapi-276003030No ratings yet
- Heat EnergyDocument18 pagesHeat EnergyCrazzy RamNo ratings yet
- Temperature Distribution On Earth and Heat BudgetDocument36 pagesTemperature Distribution On Earth and Heat Budgetbking bbNo ratings yet
- C08 Transfer of Thermal Energy (Teacher)Document49 pagesC08 Transfer of Thermal Energy (Teacher)a m i rNo ratings yet
- Physics Worksheet 14 - Methods of Heat TransferDocument6 pagesPhysics Worksheet 14 - Methods of Heat TransferOsmany MadrigalNo ratings yet
- Book of SIP Geography ExportDocument1 pageBook of SIP Geography ExportSATYAM RATHOURNo ratings yet
- Chapter 23 HandoutDocument2 pagesChapter 23 HandoutNayeem HakimNo ratings yet
- Topic 5 - 'Stoichiometry'Document28 pagesTopic 5 - 'Stoichiometry'Nayeem HakimNo ratings yet
- Lens PresentationDocument40 pagesLens PresentationNayeem HakimNo ratings yet
- Cie Igcse o Level Maths Topic 4Document24 pagesCie Igcse o Level Maths Topic 4Nayeem HakimNo ratings yet
- Venn Diagrams Notation WorksheetDocument4 pagesVenn Diagrams Notation WorksheetNayeem HakimNo ratings yet
- Class Ix Physics Quiz Competition.Document11 pagesClass Ix Physics Quiz Competition.Nayeem HakimNo ratings yet
- Chapter 25 - Star & The UniverseDocument4 pagesChapter 25 - Star & The UniverseNayeem HakimNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 18 Electrical QuantitiesDocument98 pagesChapter - 18 Electrical QuantitiesNayeem HakimNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 17 Static ElectricityDocument54 pagesChapter - 17 Static ElectricityNayeem HakimNo ratings yet
- Chapter 25 - 'Stars and The Universe'Document24 pagesChapter 25 - 'Stars and The Universe'Nayeem HakimNo ratings yet
- EXPERIMENT - 3 Thermal Conductivity of Composite WallDocument7 pagesEXPERIMENT - 3 Thermal Conductivity of Composite WallMuskan JainNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer: Prof. Dr. Mohammad Pervez MughalDocument27 pagesHeat Transfer: Prof. Dr. Mohammad Pervez MughalSyed MunawarNo ratings yet
- NS EquationDocument80 pagesNS EquationYash JainNo ratings yet
- RAB AC DRAFT - PulihkanDocument92 pagesRAB AC DRAFT - PulihkanFendi HNo ratings yet
- Functional Description: Outside Air Temperature Compensated Supply Water Flow Temperature Control W1Document8 pagesFunctional Description: Outside Air Temperature Compensated Supply Water Flow Temperature Control W1AliDelavarNo ratings yet
- Einstein Relations: Prof - Siva PrasadDocument11 pagesEinstein Relations: Prof - Siva PrasadRenuNo ratings yet
- TLDDocument1 pageTLDAA TNo ratings yet
- Heat Exchanger Design - Tubular Heat Exchangers - HRS PDFDocument4 pagesHeat Exchanger Design - Tubular Heat Exchangers - HRS PDFbecpavanNo ratings yet
- Review of Thermal Performance Criteria in The Bca2009 FOR Abcb June 2009Document45 pagesReview of Thermal Performance Criteria in The Bca2009 FOR Abcb June 2009John PierpointNo ratings yet
- Final LAS Science 10 Q2 W1Document11 pagesFinal LAS Science 10 Q2 W1Melogen LabradorNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 3 EP 209 - Thermal Physics: B B G G G GDocument2 pagesTutorial 3 EP 209 - Thermal Physics: B B G G G GAmeyNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer Characteristics of Tubes Immersed in FluidDocument10 pagesHeat Transfer Characteristics of Tubes Immersed in FluidSairam GodithiNo ratings yet
- Cooling ScaniaDocument3 pagesCooling Scanialilik sukristianto100% (1)
- Cemi - 321 - Lecture 4 - 2023Document15 pagesCemi - 321 - Lecture 4 - 2023Mare' TaljaardNo ratings yet
- Sytemair Catalog - UkDocument64 pagesSytemair Catalog - UkAli HabibNo ratings yet
- Panel ATE 2004 PDFDocument18 pagesPanel ATE 2004 PDFMUKUL KHARVANo ratings yet
- Physics Project XIIDocument10 pagesPhysics Project XIISam SolomonNo ratings yet
- IJTS Naturalconvectionheattransferinsideanopenverticalpipe-InfluenceofLDPrDocument12 pagesIJTS Naturalconvectionheattransferinsideanopenverticalpipe-InfluenceofLDPrmartin sabusNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration and Air-Conditioning SystemDocument30 pagesRefrigeration and Air-Conditioning Systemkeval patel100% (3)
- Shell and Tube Heat ExchDocument5 pagesShell and Tube Heat ExchamitsagaNo ratings yet
- Radiation Risk AssessmentDocument48 pagesRadiation Risk AssessmentKonstantinos G. ZeimpekisNo ratings yet
- PSC 2 - ConductionDocument1 pagePSC 2 - ConductionAnonymous 32No ratings yet
- BOWMAN - Exhaust Gas Heat ExchangerDocument8 pagesBOWMAN - Exhaust Gas Heat Exchangerryan pratiktoNo ratings yet
- Exp. UQ (Style A)Document8 pagesExp. UQ (Style A)missael.alvramNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Internal DosimetryDocument125 pagesUnit 5 Internal DosimetryHashir SaeedNo ratings yet
- Design of Coooling TubesDocument4 pagesDesign of Coooling Tubeslvb123No ratings yet
- Breve Historia Da RadiologiaDocument8 pagesBreve Historia Da RadiologiadridepmatNo ratings yet
- 1 IntroductionDocument15 pages1 IntroductionAlif AimanNo ratings yet
- ASHRAE OR-10-025 Seawater Heat Pump Assisted Multipurpose Solar SystemsDocument15 pagesASHRAE OR-10-025 Seawater Heat Pump Assisted Multipurpose Solar SystemsPacco HmNo ratings yet