Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Learning Difficulties Possible with Triple X Syndrome
Uploaded by
Cams Blog0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
36 views10 pagesOriginal Title
TRIPLE XXX SYNDROME
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
36 views10 pagesLearning Difficulties Possible with Triple X Syndrome
Uploaded by
Cams BlogCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 10
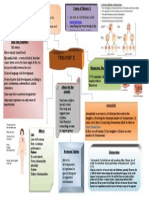
TRIPLE X SYNDROME
Triple X Syndrome
Triple X Syndrome, also called trisomy X or 47,XXX, is
characterized by the presence of an additional X chromosomes in each
of a female cells.
Females with this condition may be taller than average, this
chromosomal change typically causes no unusual physical features.
Most females with triple X syndrome have normal sexual
development and are able to conceive children.
associated with an increased risk of learning disabilities and delayed
development of speech and language skills. Delayed development of
motor skills( such as sitting and walking), weak muscle tone
( hypotonia), and behavioral and emotional difficulties are posssible,
but these characteristics vary widely among affected girls and women.
Seizures or kidney abnormalities occur in about 10 percent of affected
females.
FREQUENCY
This condition occurs in about 1 in 1,000 newborn girls. Five to 10
girls with triple X syndrome are born in the United States each day.
CAUSES
Trisomy X is a chromosomal abnormality characterized by the
presence of an extra X chromosome. Chromosomes are found in the
nucleus of all body cells. They carry the genetic characteristics of each
individual. Pairs of human chromosomes are numbered from 1
through 22, with an unequal 23rd pair that normally consists of an X
and Y chromosomes for males and two X chromosomes for females.
Females with trisomy X have 47 chromosomes, three of which X
chromosomes ( 47, XXX karyotype)
Presence of the extra X chromosomes results from errors during
the normal division of reproductive cells in one of the parents
( nondisjunction during meiosis). These errors occur randomly for
no apparent reason ( sporadically).
Studies have shown that the risk of such errors increases with
advanced paternal age.
INHERITANCE PATTERN
The most cases of Triple x is not inherited. The chromosomal change
usually occurs as a random event during the formation of reproductive
cells ( eggs and sperm). An error in the cell division called
nondisjunction can result in reproductive cells with an abnormal
number of chromosomes.
For example, an egg or sperm cell may gain an extra copy of the X
chromosomes as a result of nondisjunction. If one of these atypical
reproductive cells contributes to the genetic makeup of a child, the
child will have an extra X chromosome in each of the body's cells.
46,XXX/ 47,XXX mosaicism is also not inherited. It occurs as a
random event during cell division in early embryonic development. As
a result, some of an affected person's cells have two X chromosomes
( 46,XXX), and other cells have three X chromosomes ( 47,XXX).
You might also like
- Life Sciences Genetics Activities SolutionsDocument152 pagesLife Sciences Genetics Activities Solutionszuraidaibrahim685100% (5)
- The Plot Against Asthma and Allergy PatientsDocument422 pagesThe Plot Against Asthma and Allergy PatientsAngelo100% (1)
- Chromosomal AbberationsDocument33 pagesChromosomal AbberationsMubeena MoossaNo ratings yet
- How Sex Is Determined: MeiosisDocument2 pagesHow Sex Is Determined: MeiosisLiezl Cutchon CaguiatNo ratings yet
- UNIT I Genetic DisordersDocument4 pagesUNIT I Genetic DisordersAmmar BhattiNo ratings yet
- Chromosomal Disorders SimpleDocument8 pagesChromosomal Disorders SimpleSadia KanwalNo ratings yet
- KJ - Ppt..chromosome DefectsDocument84 pagesKJ - Ppt..chromosome DefectsGerald CatiponNo ratings yet
- Chromo Syndromes XIDocument12 pagesChromo Syndromes XIRosyadiAdnan100% (1)
- How Is Turner Syndrome DiagnosedDocument9 pagesHow Is Turner Syndrome DiagnosedAnonymous lKO78aNo ratings yet
- Turner Syndrome or Ulrich - Turner Syndrome (Also Known As "Gonadal Dysgenesis"), 45, XDocument4 pagesTurner Syndrome or Ulrich - Turner Syndrome (Also Known As "Gonadal Dysgenesis"), 45, XsweetpialiciousNo ratings yet
- Conditions/triple X Syndrome/symptoms Causes/syc 20350977Document2 pagesConditions/triple X Syndrome/symptoms Causes/syc 20350977Minh Nguyen DucNo ratings yet
- Lab Genetics 1Document10 pagesLab Genetics 1Nurul Iman Che AwangNo ratings yet
- Chromosomal Aberrations Just in CaseDocument8 pagesChromosomal Aberrations Just in CaseJahn Alaina DadoNo ratings yet
- Ppt. Sex LinkageDocument37 pagesPpt. Sex LinkageDeanise JusayNo ratings yet
- Ppt. Sex LinkageDocument38 pagesPpt. Sex LinkageAj Myco EstorNo ratings yet
- GEN NIPT - Scainconclusive Tcm63-1515179Document2 pagesGEN NIPT - Scainconclusive Tcm63-1515179ptsrvNo ratings yet
- Document Ni IndayDocument7 pagesDocument Ni IndayAj Myco EstorNo ratings yet
- X Chromosome: Genetics Home ReferenceDocument10 pagesX Chromosome: Genetics Home ReferenceAditya SelvarajanNo ratings yet
- Wikipedia - Triple X Syndrome (CHECKED)Document4 pagesWikipedia - Triple X Syndrome (CHECKED)pixoguiasNo ratings yet
- SasangDocument11 pagesSasangVince Cinco ParconNo ratings yet
- A Guide to Understanding Trisomy X (47,XXXDocument14 pagesA Guide to Understanding Trisomy X (47,XXXAnandNo ratings yet
- Intersex or The Third GendrerDocument5 pagesIntersex or The Third GendrerEraj ShafiqNo ratings yet
- Midterm Reviewer, Dev PsychDocument10 pagesMidterm Reviewer, Dev PsychkatNo ratings yet
- LyonizationDocument1 pageLyonizationCindyVortexNo ratings yet
- 8-Abnormal-Chromosome-Number 2Document34 pages8-Abnormal-Chromosome-Number 2PCHS-REYES, Reyza Jane BNo ratings yet
- Chromosomal Abnormalities ExplainedDocument7 pagesChromosomal Abnormalities ExplainedSaqib AmeenNo ratings yet
- Biologic and Psychosocial Dynamics in Disease CausationDocument35 pagesBiologic and Psychosocial Dynamics in Disease Causationlivelinami100% (4)
- Chromosomal Abnormalities ExplainedDocument3 pagesChromosomal Abnormalities ExplainedMelodogyne Alay-ayNo ratings yet
- Bio Chromosomal Disorders 2019Document8 pagesBio Chromosomal Disorders 2019Ekram YimerNo ratings yet
- Chromosomal Aberration Causes Genetic DisordersDocument4 pagesChromosomal Aberration Causes Genetic DisordersSyed Shah HussainNo ratings yet
- Biology Project: Chromosomal DisorderDocument44 pagesBiology Project: Chromosomal DisorderArun Kumar ANo ratings yet
- Study of Molecular Cytogenetic Analysis To Determine The Genetic Defect of A PatientDocument6 pagesStudy of Molecular Cytogenetic Analysis To Determine The Genetic Defect of A PatientInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research Technology100% (1)
- Klinefelter Syndrome: by Priscila Janeth Arenas CastroDocument9 pagesKlinefelter Syndrome: by Priscila Janeth Arenas CastroPriscila Janeth Arenas CastroNo ratings yet
- CHROMOSOMESDocument17 pagesCHROMOSOMESrydk2ptz92No ratings yet
- Etiology PPPDocument24 pagesEtiology PPPCresty Estalilla100% (1)
- Chromosome Pathology: S. DahounDocument9 pagesChromosome Pathology: S. DahounSkybreakerNo ratings yet
- Chromosomal Mutations: Monosomia, Trisomy, Down SyndromeDocument31 pagesChromosomal Mutations: Monosomia, Trisomy, Down SyndromeZainab Jamal SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Trisomy XDocument1 pageTrisomy XSyaza Ahmad JaisNo ratings yet
- Genetics NotesDocument50 pagesGenetics Notespoorvikg29No ratings yet
- Chap 13 - Genetics and InheritanceDocument7 pagesChap 13 - Genetics and Inheritancediamehta1512No ratings yet
- 2 Chromosomal AbnormalitiesDocument26 pages2 Chromosomal Abnormalitiesmuhammad zakriaNo ratings yet
- Autosomal Deletion SyndromesDocument50 pagesAutosomal Deletion SyndromesZainab Jamal SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Chromosomal Syndromes and Genetic Disease: Introductory ArticleDocument12 pagesChromosomal Syndromes and Genetic Disease: Introductory ArticleAh MagdyNo ratings yet
- Presentación 137Document18 pagesPresentación 137Nathaly TobarNo ratings yet
- Sex Chromosome Aberration: By: Moncera, Miguel Gabriel R. Dela Rosa, Hannah ShaneDocument14 pagesSex Chromosome Aberration: By: Moncera, Miguel Gabriel R. Dela Rosa, Hannah ShaneKaycee Gretz LorescaNo ratings yet
- Numerical Chromosomal AbnormalitiesDocument2 pagesNumerical Chromosomal AbnormalitiesPradip SahaNo ratings yet
- GeneticsDocument2 pagesGeneticschesnablythe_chesNo ratings yet
- Numerical Aberrations: Meiotic NondisjunctionDocument36 pagesNumerical Aberrations: Meiotic NondisjunctionHemanth_Prasad_2860No ratings yet
- Genetic disorders and family historyDocument5 pagesGenetic disorders and family historyFrancisco Lozano GómezNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument22 pagesBiologysinjiniwasanNo ratings yet
- Non DisjunctionDocument59 pagesNon DisjunctionsagaralkimsaimonNo ratings yet
- How The X Chromosome Recombines and Is Passed From Generation To GenerationDocument6 pagesHow The X Chromosome Recombines and Is Passed From Generation To Generationbjo7000_438333726No ratings yet
- Notes - Genetic DisordersDocument6 pagesNotes - Genetic Disordersanirudhramesh289No ratings yet
- PDF DocumentDocument47 pagesPDF DocumentLadymae Galola100% (1)
- 2010.a Review of Trisomy X (47,XXX)Document9 pages2010.a Review of Trisomy X (47,XXX)rpina.genNo ratings yet
- Biology Project: Name Ajit Kumar CLASS 12 S2Document7 pagesBiology Project: Name Ajit Kumar CLASS 12 S2ajitNo ratings yet
- Assignment 5BDocument3 pagesAssignment 5BKrishna Bharatbhai PatelNo ratings yet
- Genetic Disorders-1Document42 pagesGenetic Disorders-1Bala UrmarNo ratings yet
- Genetic DisordersDocument17 pagesGenetic DisordersNgz Krystle ChukwudifuNo ratings yet
- Genetic DisordersDocument36 pagesGenetic Disordersqurat-ul-ain.sonNo ratings yet
- Disorders and Diseases That Result From The Malfunction of The Cell During The Cell CycleDocument73 pagesDisorders and Diseases That Result From The Malfunction of The Cell During The Cell Cyclekuramachakra13No ratings yet
- Sex Ed Uncensored - Sexual Identity: Mind Blowing Sex Sh8t!!! for Young AdultsFrom EverandSex Ed Uncensored - Sexual Identity: Mind Blowing Sex Sh8t!!! for Young AdultsNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Activity 3 Say Something About ItDocument4 pagesLesson 2 Activity 3 Say Something About ItCams BlogNo ratings yet
- 1Document3 pages1Cams BlogNo ratings yet
- What Are Anxiety Disorders/depressions?Document2 pagesWhat Are Anxiety Disorders/depressions?Cams BlogNo ratings yet
- Trouble Controlling Impulses: Balanced TranslocationDocument3 pagesTrouble Controlling Impulses: Balanced TranslocationCams BlogNo ratings yet
- Formula:: Mode Lmo + (Document3 pagesFormula:: Mode Lmo + (Cams BlogNo ratings yet
- Sunny'S Kamote Lumps (SKL) : Senior High SchoolDocument7 pagesSunny'S Kamote Lumps (SKL) : Senior High Schoolsfjs/olfdNo ratings yet
- SpeechDocument4 pagesSpeechsfjs/olfdNo ratings yet
- Mode of Grouped Data and MidrangeDocument16 pagesMode of Grouped Data and MidrangeCams BlogNo ratings yet
- Mapeh Report 10Document11 pagesMapeh Report 10Cams BlogNo ratings yet
- Face Lab Manual PDFDocument12 pagesFace Lab Manual PDFFabiolaNo ratings yet
- Formative assessment on inheritance in goatsDocument4 pagesFormative assessment on inheritance in goatsTarshihiNo ratings yet
- Transgenic AnimalsDocument13 pagesTransgenic AnimalsRudrangispharmacyNo ratings yet
- Cyto 2Document80 pagesCyto 2newusernvNo ratings yet
- Bmat Test SpecificationDocument42 pagesBmat Test SpecificationAli EslamiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Basic Structure, Composition, Size and Shape of ChromosomesDocument14 pagesChapter 2: Basic Structure, Composition, Size and Shape of ChromosomesankurbiologyNo ratings yet
- Week 6 Experiment Answer Sheet ROOTDocument8 pagesWeek 6 Experiment Answer Sheet ROOTOksana Kristina Root0% (1)
- Chapter 7: Nucleic Acids: 7.1: DNA Structure and ReplicationDocument5 pagesChapter 7: Nucleic Acids: 7.1: DNA Structure and ReplicationMariamNo ratings yet
- Lab 5Document13 pagesLab 5Chikaodinaka Okoro0% (4)
- CDNA Lab Report - Docx2Document4 pagesCDNA Lab Report - Docx2cxs5278100% (1)
- Protein As MicromoleculesDocument7 pagesProtein As MicromoleculesPrincess JacintoNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 2: Science Form 1Document40 pagesCHAPTER 2: Science Form 1Aisyah Hassan67% (6)
- 1 Mendelian Genetics Preliminary ActivitiesDocument7 pages1 Mendelian Genetics Preliminary ActivitiesJenny PartozaNo ratings yet
- Meiosis Pipe Cleaner LabDocument3 pagesMeiosis Pipe Cleaner Labmaeko nayuNo ratings yet
- Lecture 11 Digital Signals SystemsDocument11 pagesLecture 11 Digital Signals Systemsraguraj8No ratings yet
- UNIT 5 Students Topic 1 and 2 NotesDocument25 pagesUNIT 5 Students Topic 1 and 2 Noteskayecec996No ratings yet
- 5 Gene InteractionDocument9 pages5 Gene InteractionPrem ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Human Evolution: The Process of HumanizationDocument177 pagesHuman Evolution: The Process of HumanizationChrisTselentisNo ratings yet
- Mutationbreedingppt 161203184149Document41 pagesMutationbreedingppt 161203184149MuneebNo ratings yet
- Evolution (Biology Class 12 Isc)Document4 pagesEvolution (Biology Class 12 Isc)arushilal84No ratings yet
- FaBio M4 Rapport - 2Document7 pagesFaBio M4 Rapport - 2ester.shkwana2002No ratings yet
- CORRECT Pathway of The Sperm?Document7 pagesCORRECT Pathway of The Sperm?Harold Nalla HusayanNo ratings yet
- BIO153 Lecture and Assignment Schedule for Next WeekDocument19 pagesBIO153 Lecture and Assignment Schedule for Next WeekUsama AdnanNo ratings yet
- Macarena Silva-Guzman Seminar AnnouncementDocument1 pageMacarena Silva-Guzman Seminar AnnouncementAnonymous tGJ2lopsNo ratings yet
- DNA Programming Kit Manual PDFDocument65 pagesDNA Programming Kit Manual PDFavrajamohamedNo ratings yet
- Biotech Apps Conserve BiodiversityDocument4 pagesBiotech Apps Conserve BiodiversitysaranyaNo ratings yet
- NIHMS63446 Supplement 1Document68 pagesNIHMS63446 Supplement 1fdfgfgfgdfgdfgNo ratings yet
- Chromosomal AberrationsDocument29 pagesChromosomal Aberrationsjohnkourus19No ratings yet