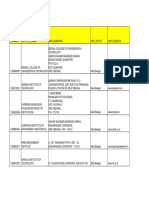
Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Child Abuse or Child Maltreatment Is
Uploaded by
sandeep singh cheema0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views13 pagesOriginal Title
presentation harpreet
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views13 pagesChild Abuse or Child Maltreatment Is
Uploaded by
sandeep singh cheemaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 13
Child Abuse
Child abuse or child maltreatment is
physical, sexual, psychological maltreatment or
neglect of a child or children, especially by a
parent or other caregiver.
Types of child abuse
Physical abuse
This includes hitting, beating, kicking, shaking,
biting, strangling, scalding, burning, poisoning and
suffocating.
Much physical violence against children in the home
is inflicted with the object of punishing.
Sexual abuse
Forms of CSA include asking or pressuring a child to
engage in sexual activities, indecent exposure of the
genitals to a child, displaying pornography to a child.
Actual sexual contact with a child, physical contact with
the child's genitals, viewing of the child's genitalia
without physical contact.
Psychological abuse
Describing it as "no accidental verbal or symbolic
acts by a child's parent or caregiver that result, or
have reasonable potential to result, in significant
psychological harm to the child.
Neglect
Child neglect is the failure of a parent or other person with
responsibility for the child, to provide needed food,
clothing, shelter, medical care, or supervision to the degree
that the child's health, safety or well-being may be
threatened with harm
Causes
Assessment
Assessment
High Scope COR (Child Observation Record)
Educators follow COR’s three step process:
1) observe and record,
2) score, using the Online COR
3) report findings to share.
Treatment
Medical care
f necessary, help the child seek appropriate medical care..
Follow-up care with a doctor or other health care provider
may be required.
Psychotherapy
Help a child who has been abused learn to trust again
Teach a child about normal behavior and relationships
Teach a child conflict management and boost self-esteem
Treatment
Trauma-focused cognitive behavioral therapy. This type
of therapy helps a child to better manage distressing feelings
and to deal with trauma-related memories..
Child-parent psychotherapy. Discover the roots of abuse
Learn effective ways to cope with life's inevitable frustrations
Learn healthy parenting strategies
Support
Encourage the child to tell you what happened. .
Remind the child that he or she isn't responsible for
the abuse. .
Offer comfort. .
Support
Report the abuse. Contact a local child protective
agency or the police department. Authorities will
investigate the report and, if necessary, take steps to
ensure the child's safety.
Help the child remain safe. Consider additional
support. If the abuse has occurred at school.
You might also like
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- CMM 7 2023 17 02 2023 Interim OrderDocument1 pageCMM 7 2023 17 02 2023 Interim Ordersandeep singh cheemaNo ratings yet
- Cra-S 508 2023 21 02 2023 Interim Order PDFDocument1 pageCra-S 508 2023 21 02 2023 Interim Order PDFsandeep singh cheemaNo ratings yet
- I68033 PDFDocument4 pagesI68033 PDFsandeep singh cheemaNo ratings yet
- LifeCare Dera PDFDocument9 pagesLifeCare Dera PDFsandeep singh cheemaNo ratings yet
- Display pdf-2Document1 pageDisplay pdf-2sandeep singh cheemaNo ratings yet
- Examples 1 PDFDocument4 pagesExamples 1 PDFsandeep singh cheemaNo ratings yet
- Examples 3 PDFDocument5 pagesExamples 3 PDFsandeep singh cheemaNo ratings yet
- 1200 Commonly Repeated Spellings or Words in IELTSDocument5 pages1200 Commonly Repeated Spellings or Words in IELTSsandeep singh cheemaNo ratings yet
- LifeCare DeraDocument13 pagesLifeCare Derasandeep singh cheemaNo ratings yet
- Parminder Singh-1 PDFDocument2 pagesParminder Singh-1 PDFsandeep singh cheemaNo ratings yet
- Comparative Analysis of Therapeutic Benefits of Ocimum: Gratissimum and Vernonia AmygdalinaDocument4 pagesComparative Analysis of Therapeutic Benefits of Ocimum: Gratissimum and Vernonia Amygdalinasandeep singh cheemaNo ratings yet
- CRM 9997 2023 24 04 2023 Interim Order PDFDocument1 pageCRM 9997 2023 24 04 2023 Interim Order PDFsandeep singh cheemaNo ratings yet
- Nanny 15Document92 pagesNanny 15sandeep singh cheemaNo ratings yet
- Old Age Booklet RechcedDocument26 pagesOld Age Booklet Rechcedsandeep singh cheemaNo ratings yet
- Amitabh Ba C Chan 1984Document30 pagesAmitabh Ba C Chan 1984sandeep singh cheemaNo ratings yet
- Nitnem by Dr. Kulwant Singh, With Punjabi & Eng Transla & PTDocument322 pagesNitnem by Dr. Kulwant Singh, With Punjabi & Eng Transla & PTParneet Walia100% (1)
- JappsahibDocument18 pagesJappsahibAman DeepNo ratings yet
- August-2021-Pdf-Free-Download/: (Updated)Document12 pagesAugust-2021-Pdf-Free-Download/: (Updated)sandeep singh cheemaNo ratings yet
- Saka 84Document209 pagesSaka 84Nirmal SinghNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Fire Protection in BuildingsDocument2 pagesFire Protection in BuildingsJames Carl AriesNo ratings yet
- 50114a Isolemfi 50114a MonoDocument2 pages50114a Isolemfi 50114a MonoUsama AwadNo ratings yet
- Activity On Noli Me TangereDocument5 pagesActivity On Noli Me TangereKKKNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 (Automatic Transmission)Document26 pagesChapter 13 (Automatic Transmission)ZIBA KHADIBINo ratings yet
- 8051 NotesDocument61 pages8051 Notessubramanyam62No ratings yet
- Speech On Viewing SkillsDocument1 pageSpeech On Viewing SkillsMera Largosa ManlaweNo ratings yet
- WBDocument59 pagesWBsahil.singhNo ratings yet
- Webinar Gizi - Patho StuntingDocument16 pagesWebinar Gizi - Patho StuntingMiftahul HikmahNo ratings yet
- EPAS 11 - Q1 - W1 - Mod1Document45 pagesEPAS 11 - Q1 - W1 - Mod1Alberto A. FugenNo ratings yet
- Health Post - Exploring The Intersection of Work and Well-Being - A Guide To Occupational Health PsychologyDocument3 pagesHealth Post - Exploring The Intersection of Work and Well-Being - A Guide To Occupational Health PsychologyihealthmailboxNo ratings yet
- Music 10 (2nd Quarter)Document8 pagesMusic 10 (2nd Quarter)Dafchen Villarin MahasolNo ratings yet
- Unsuccessful MT-SM DeliveryDocument2 pagesUnsuccessful MT-SM DeliveryPitam MaitiNo ratings yet
- Week-3-Q1-Gen Chem-Sep-11-15-DllDocument12 pagesWeek-3-Q1-Gen Chem-Sep-11-15-DllJennette BelliotNo ratings yet
- Continue Practice Exam Test Questions Part 1 of The SeriesDocument7 pagesContinue Practice Exam Test Questions Part 1 of The SeriesKenn Earl Bringino VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Rom 2 - 0-11 (En)Document132 pagesRom 2 - 0-11 (En)Mara HerreraNo ratings yet
- My Mother at 66Document6 pagesMy Mother at 66AnjanaNo ratings yet
- FuzzingBluetooth Paul ShenDocument8 pagesFuzzingBluetooth Paul Shen许昆No ratings yet
- Antena TelnetDocument4 pagesAntena TelnetMarco PiambaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 - ReviewerDocument6 pagesLesson 3 - ReviewerAdrian MarananNo ratings yet
- DLP - Light Science 7Document6 pagesDLP - Light Science 7Samara M. SalacayanNo ratings yet
- Cisco BGP ASPATH FilterDocument115 pagesCisco BGP ASPATH FilterHalison SantosNo ratings yet
- Resume: Mr. Shubham Mohan Deokar E-MailDocument2 pagesResume: Mr. Shubham Mohan Deokar E-MailAdv Ranjit Shedge PatilNo ratings yet
- Gas Dynamics and Jet Propulsion 2marksDocument15 pagesGas Dynamics and Jet Propulsion 2marksAbdul rahumanNo ratings yet
- Delusion in SocietyDocument2 pagesDelusion in SocietyGasimovskyNo ratings yet
- Injections Quiz 2Document6 pagesInjections Quiz 2Allysa MacalinoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of the pulp cavity กย 2562-1Document84 pagesAnatomy of the pulp cavity กย 2562-1IlincaVasilescuNo ratings yet
- SOL LogicDocument21 pagesSOL LogicJa RiveraNo ratings yet
- Prevention of Waterborne DiseasesDocument2 pagesPrevention of Waterborne DiseasesRixin JamtshoNo ratings yet
- Chapter - I Introduction and Design of The StudyDocument72 pagesChapter - I Introduction and Design of The StudyramNo ratings yet
- Nanolithography - Processing Methods PDFDocument10 pagesNanolithography - Processing Methods PDFNilesh BhardwajNo ratings yet