Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Anatomy & Physiology Review
Uploaded by
shirley0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views63 pagesThis document provides a review of various topics in anatomy and physiology for a final exam in December 2021. It covers chemistry of life including inorganic vs organic chemicals. It also reviews epithelial tissue, glands, mitosis vs meiosis, action potentials, the nephron, immunity, DNA, RNA, cranial nerves, reflex arcs, association areas of the brain, the respiratory system, mechanics of breathing, the digestive system, muscles, types of joints, and acid-base balance. The document concludes by wishing the reader good luck on their final exams.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides a review of various topics in anatomy and physiology for a final exam in December 2021. It covers chemistry of life including inorganic vs organic chemicals. It also reviews epithelial tissue, glands, mitosis vs meiosis, action potentials, the nephron, immunity, DNA, RNA, cranial nerves, reflex arcs, association areas of the brain, the respiratory system, mechanics of breathing, the digestive system, muscles, types of joints, and acid-base balance. The document concludes by wishing the reader good luck on their final exams.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views63 pagesAnatomy & Physiology Review
Uploaded by
shirleyThis document provides a review of various topics in anatomy and physiology for a final exam in December 2021. It covers chemistry of life including inorganic vs organic chemicals. It also reviews epithelial tissue, glands, mitosis vs meiosis, action potentials, the nephron, immunity, DNA, RNA, cranial nerves, reflex arcs, association areas of the brain, the respiratory system, mechanics of breathing, the digestive system, muscles, types of joints, and acid-base balance. The document concludes by wishing the reader good luck on their final exams.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 63
Anatomy & Physiology
Review Dec 2021
Subtitle
Chemistry of life review
Inorganic vs organic
› Organic chemicals contain both (H)and (C)
› The rest are inorganic
› Examples of inorganic oxygen, water, salt and carbon dioxide
› Examples of organic substances include carbohydrates, lipds
proteins and Nucleic Acids
Epithelial Tissue
Glands
Mitosis vs Meiosis
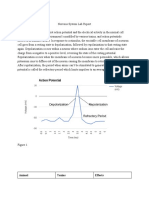
Action Potential
› Action potentials are the rapid changes in charge across the
membrane that occur when a neuron is firing
› Action potentials occur in three main stages: depolarization,
repolarization and a refractory period
Resting membrane potential
Depolarization
› Depolarization
› Depolarization refers to a sudden change in membrane potential
– usually from a (relatively) negative to positive internal charge
› In response to a signal initiated at a dendrite, sodium
channels open within the membrane of the axon
› As Na+ ions are more concentrated outside of the neuron, the
opening of sodium channels causes a passive influx of sodium
› The influx of sodium causes the membrane potential to become
more positive (depolarization)
Repolarization
› Repolarization
› Repolarization refers to the restoration of a membrane potential
following depolarization (i.e. restoring a negative internal charge)
› Following an influx of sodium, potassium channels open within
the membrane of the axon
› As K+ ions are more concentrated inside the neuron, opening
potassium channels causes a passive efflux of potassium
› The efflux of potassium causes the membrane potential to return
to a more negative internal differential (repolarization
› Refractory Period
› The refractory period refers to the period of time following a
nerve impulse before the neuron is able to fire again
› In a normal resting state, sodium ions are predominantly outside
the neuron and potassium ions mainly inside (resting potential)
› Following depolarization (sodium influx) and repolarization
(potassium efflux), this ionic distribution is largely reversed
› Before a neuron can fire again, the resting potential must be
restored via the antiport action of the sodium-potassium pump
Sodium /Potassium PUMP
The nephron
The Glomerulus
The nephron
Immunity
Cell mediated Immunity
DNA “Deoxyribose nucleic Acid”
RNA “Ribose Nucleic Acid”
Cranial Nerves
Reflex arc
Association areas
› Are parts of the cerebral cortex that receive inputs from multiple
areas
› They integrate incoming SENORY information and also form
connections between sensory and motor areas.
› Allows us to analyze recognize and act on sensory input with
respect to past experiences.
› When damaged we loose the ability to recognize objects, sounds,
voices, or visions from our memories
Respiratory System
Mechanics of breathing
Digestive system
muscles
Types of Joints
Acid /base balance
›
› Good luck on your final exams!!
› You got this!!! I BELIEVE in you!!
You might also like
- Action Potential - Communication Within NeuronsDocument6 pagesAction Potential - Communication Within NeuronsPeehuNo ratings yet
- 981-0602 Onan MDKUB MDKWB Spec E-J Install Manual (2-2010)Document65 pages981-0602 Onan MDKUB MDKWB Spec E-J Install Manual (2-2010)pepa 007No ratings yet
- ECG-Dr - Najeeb-By Kurdish Medico PDFDocument265 pagesECG-Dr - Najeeb-By Kurdish Medico PDFMarwa Ahmad Abdelmohsen75% (4)
- Neural PhysiologyDocument45 pagesNeural PhysiologyHakim Asif Haider100% (1)
- Ec8073-Medical Electronics Study MaterialDocument116 pagesEc8073-Medical Electronics Study Materialpurushothsatha100% (1)
- The Phases of Matter - Chemistry Book Grade 1 | Children's Chemistry BooksFrom EverandThe Phases of Matter - Chemistry Book Grade 1 | Children's Chemistry BooksNo ratings yet
- Proximate Analysis of CoalDocument30 pagesProximate Analysis of Coalvince coNo ratings yet
- Action Potential: DR Raghuveer Choudhary Associate ProfessorDocument63 pagesAction Potential: DR Raghuveer Choudhary Associate ProfessorPhysiology by Dr Raghuveer100% (2)
- Action Potential NotesDocument2 pagesAction Potential NotesJohn OsborneNo ratings yet
- Summary Biological PsychologyDocument133 pagesSummary Biological PsychologyAnastasia100% (1)
- 1.nerve Fibers PhysioDocument29 pages1.nerve Fibers PhysioHamza Ahmad100% (1)
- Nervous SystemDocument23 pagesNervous SystemMartyn PereiraNo ratings yet
- NEURON ACTION POTENTIAL - PPT - ReadyDocument83 pagesNEURON ACTION POTENTIAL - PPT - Readyelle leeNo ratings yet
- Lesson Exemplar Dry RunDocument5 pagesLesson Exemplar Dry Runcristito inovalNo ratings yet
- Mnemonics For AntibioticsDocument1 pageMnemonics For AntibioticsshirleyNo ratings yet
- Technical Specification - ACDocument7 pagesTechnical Specification - ACRabin ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Biolistrik: DR - Susy OliviaDocument97 pagesBiolistrik: DR - Susy OliviaHartomas BumiharjoNo ratings yet
- Biological Psychology Tutorial Task - 2 AnswerDocument1 pageBiological Psychology Tutorial Task - 2 AnswerCarlKanneyngeNo ratings yet
- 5.3 Neuronal Communication POWERPOINTDocument55 pages5.3 Neuronal Communication POWERPOINTsohailnoreen5062No ratings yet
- Types of Neuron Transmission and Communication SystemDocument5 pagesTypes of Neuron Transmission and Communication SystemRbbani AwanNo ratings yet
- Human Physiology Assignment 01Document9 pagesHuman Physiology Assignment 01Evaristo MK VincentNo ratings yet
- Action Potential-Nervous SystemDocument12 pagesAction Potential-Nervous SystemKELVINNo ratings yet
- Orgin of Biopotential and Its PropogationDocument11 pagesOrgin of Biopotential and Its PropogationAleeshaNo ratings yet
- Action PotentialDocument74 pagesAction PotentialAnbreena RasoolNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Membrane PhysiologyDocument11 pagesChapter 2 - Membrane Physiologytahira UroojNo ratings yet
- Action PotentialDocument21 pagesAction PotentialjolilarmatarNo ratings yet
- There Are Many Different Kinds of Ions in NeuronsDocument1 pageThere Are Many Different Kinds of Ions in NeuronsKentNo ratings yet
- Autonomic Nervous SystemDocument19 pagesAutonomic Nervous SystemAnuvabNo ratings yet
- SHS.108.Lect-10 Tubular ReabsorptionDocument61 pagesSHS.108.Lect-10 Tubular ReabsorptionAzlan YasirNo ratings yet
- Neuronal Conduction1Document61 pagesNeuronal Conduction1ISHITA GOEL 19224115No ratings yet
- Action PotentialDocument4 pagesAction PotentialfarahNo ratings yet
- Y13 How The Nervous System WorksDocument17 pagesY13 How The Nervous System WorksFaye SweeneyNo ratings yet
- Ent 311 - Medical Electronics and Bio-Instrumentation: WEEK: 4 & 5Document35 pagesEnt 311 - Medical Electronics and Bio-Instrumentation: WEEK: 4 & 5Nitin PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- Photos YnDocument55 pagesPhotos YnSANSKRITI 3928No ratings yet
- Hyperpolarization (Biology) : Wiki Loves Monuments: Photograph A Monument, Help Wikipedia and Win!Document6 pagesHyperpolarization (Biology) : Wiki Loves Monuments: Photograph A Monument, Help Wikipedia and Win!Jennie KimNo ratings yet
- Guyton Notes Chapter 05Document4 pagesGuyton Notes Chapter 05aima_uy50% (2)
- Physiology Course: Dr. Velu M. RachelDocument56 pagesPhysiology Course: Dr. Velu M. RachelKunda JosephNo ratings yet
- NEURONDocument4 pagesNEURONsummerbombabeNo ratings yet
- Membrane PotentialDocument66 pagesMembrane PotentialGksNo ratings yet
- IB Biology: Neurobiology & Behaviour Lesson 3: Propagation of Action PotentialsDocument19 pagesIB Biology: Neurobiology & Behaviour Lesson 3: Propagation of Action Potentialsperlmutter.poNo ratings yet
- PHR109 Assignment-02 1Document2 pagesPHR109 Assignment-02 1Rifatul Hasan RickyNo ratings yet
- Nerve ImpluseDocument22 pagesNerve ImpluseZulaikha ZulkifliNo ratings yet
- Action PotentialDocument51 pagesAction PotentialDrishti SainiNo ratings yet
- Title of Seminar: Oxidation - Reduction in Biological ProcessesDocument11 pagesTitle of Seminar: Oxidation - Reduction in Biological ProcessesDTM FHKNo ratings yet
- Action PotentialDocument9 pagesAction Potentialmedicine lifeNo ratings yet
- Action PotentialDocument12 pagesAction PotentialArooj FatimaNo ratings yet
- PHS 211 Membrane PotentialsDocument22 pagesPHS 211 Membrane Potentialsmetasynthronos748No ratings yet
- Membrane Potentials and Action PotentialsDocument24 pagesMembrane Potentials and Action PotentialsDenniel Dela Cuadra GasmenNo ratings yet
- 4 - Membrane PhysiologyDocument31 pages4 - Membrane PhysiologysadaffardoosNo ratings yet
- Neurotransmitters and ReceptorsDocument4 pagesNeurotransmitters and ReceptorsXyzNo ratings yet
- Perpindahan Ion IonDocument12 pagesPerpindahan Ion IonTriono AssamsulNo ratings yet
- Physiologi Neuron (Kuliah I)Document17 pagesPhysiologi Neuron (Kuliah I)Alfian Hari GunawanNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Nerve Fibers: Dr. Zara BatoolDocument30 pagesPhysiology of Nerve Fibers: Dr. Zara BatoolZuhaib AhmedNo ratings yet
- A Level Biology: Nervous CoordinationDocument39 pagesA Level Biology: Nervous CoordinationAhmedNo ratings yet
- NervoussystemlabreportDocument4 pagesNervoussystemlabreportapi-296594565No ratings yet
- The Flow of Energy Part 3Document18 pagesThe Flow of Energy Part 3nancie8No ratings yet
- Chapter 16 Berne and LevyDocument3 pagesChapter 16 Berne and LevyCristina A Rodriguez100% (2)
- Nerve Impulse 28770Document18 pagesNerve Impulse 28770Vicente S. CuberoNo ratings yet
- Biomedical Instrumentation I: Lecture-5: The Origin of BiopotentialsDocument35 pagesBiomedical Instrumentation I: Lecture-5: The Origin of BiopotentialsNitin PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- Nerve Impulse-Week 4-5Document69 pagesNerve Impulse-Week 4-5COPY PAPAGAJKANo ratings yet
- Lecure-5 The Origin of Biopotentials - 2Document34 pagesLecure-5 The Origin of Biopotentials - 2Noor Ahmed100% (1)
- The Action of Nerves: Appendix 4Document4 pagesThe Action of Nerves: Appendix 4natjeros12No ratings yet
- Action PotentialDocument30 pagesAction PotentialMuhammad AhmedNo ratings yet
- AP Class MergedDocument217 pagesAP Class MergedANWESHA DUTTNo ratings yet
- Psybio Lesson 3Document25 pagesPsybio Lesson 3Lago, Azel Chin L.No ratings yet
- Structures of The Ear Trudy's HandoutDocument3 pagesStructures of The Ear Trudy's HandoutshirleyNo ratings yet
- DrugmedsDocument52 pagesDrugmedsshirleyNo ratings yet
- Anpy 1000 Review Unit 3Document82 pagesAnpy 1000 Review Unit 3shirleyNo ratings yet
- Why Facebook Is BeneficialDocument3 pagesWhy Facebook Is BeneficialshirleyNo ratings yet
- Gland Stimulation of Hormones Produced Action Gland: Fsh/Lh-Gonads ActhDocument2 pagesGland Stimulation of Hormones Produced Action Gland: Fsh/Lh-Gonads ActhshirleyNo ratings yet
- Essential Attitudes, Personal Qualities, and Professional Behaviors Required in NursingDocument27 pagesEssential Attitudes, Personal Qualities, and Professional Behaviors Required in NursingshirleyNo ratings yet
- Valve Package - Herz Technical CatalogueDocument12 pagesValve Package - Herz Technical CatalogueChris SolonNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Subunit 1 Test-Periodic Table/Trends Form A Integrated Science-1 You Will Need A Periodic Table To Complete This Exam. Multiple ChoiceDocument5 pagesChemistry Subunit 1 Test-Periodic Table/Trends Form A Integrated Science-1 You Will Need A Periodic Table To Complete This Exam. Multiple ChoiceRuby Angel MannNo ratings yet
- Manuscript-Ikmo LeavesDocument79 pagesManuscript-Ikmo LeavesQuebec GC RPhNo ratings yet
- Reaction Mechanism IDocument15 pagesReaction Mechanism IFilmodeNo ratings yet
- Polimers PDFDocument71 pagesPolimers PDFomer faruqeNo ratings yet
- Class XI Chemistry BlueprintDocument1 pageClass XI Chemistry Blueprintroythomasc63% (8)
- Alkali Metal Cations Na, K, Li 7405: NIOSH Manual of Analytical Methods (NMAM), Fifth EditionDocument5 pagesAlkali Metal Cations Na, K, Li 7405: NIOSH Manual of Analytical Methods (NMAM), Fifth EditionLINDA IVON PARRADO SÁNCHEZNo ratings yet
- Teledyne - Meridian Universal Gas Detector - Data SheetDocument12 pagesTeledyne - Meridian Universal Gas Detector - Data SheetMarthin PurbaNo ratings yet
- Enzymes Material PDFDocument7 pagesEnzymes Material PDFSalma AhmedNo ratings yet
- Expperiment 1a Ras1132a Group 2Document7 pagesExpperiment 1a Ras1132a Group 2Salazar ZawawiNo ratings yet
- Antiscalant White PaperDocument5 pagesAntiscalant White PaperMohamed SabryNo ratings yet
- Official Report Practicum of Chemical Separation Principles Fracsination DestilationDocument22 pagesOfficial Report Practicum of Chemical Separation Principles Fracsination DestilationFitriyah AbidinNo ratings yet
- Composites Part A: SciencedirectDocument7 pagesComposites Part A: SciencedirectJulia LizNo ratings yet
- Poly (Vinyl Chloride) (PVC) Plastic Drain, Waste, and Vent (DWV) Pipe and Fittings Having Post-Industrial Recycle ContentDocument7 pagesPoly (Vinyl Chloride) (PVC) Plastic Drain, Waste, and Vent (DWV) Pipe and Fittings Having Post-Industrial Recycle Contentastewayb_964354182No ratings yet
- BT 302: Biochemical Engineering Tutorial-1Document1 pageBT 302: Biochemical Engineering Tutorial-1Brenda BanderadoNo ratings yet
- GB Twin Shafts Paddle MixerDocument2 pagesGB Twin Shafts Paddle MixerBanzragch JamsranNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of The Effects of Hydrogen Peroxide On Common Aviation Structural MaterialsDocument24 pagesEvaluation of The Effects of Hydrogen Peroxide On Common Aviation Structural MaterialsDarius MaximusNo ratings yet
- 2nd Law of ThermodynamicsDocument13 pages2nd Law of Thermodynamicsfatima janine feicianoNo ratings yet
- Exercise 12 (Permanganimetric Determination of Calcium) PrelabDocument2 pagesExercise 12 (Permanganimetric Determination of Calcium) PrelabPrincess Requiso100% (5)
- 6 Major Classes of EnzymesDocument6 pages6 Major Classes of EnzymesnoorNo ratings yet
- Coloration TechnologyDocument17 pagesColoration Technologyfathi mustafaNo ratings yet
- Safety Data Sheet: AlamineDocument13 pagesSafety Data Sheet: AlamineIbnu BakriNo ratings yet
- Xii English Reading Text Ten Life in The UniverseDocument3 pagesXii English Reading Text Ten Life in The UniverseNiketa LakhwaniNo ratings yet
- Chemosphere: Li Yang, Jie Gao, Ying Liu, Guoqiang Zhuang, Xiawei Peng, Wei-Min Wu, Xuliang ZhuangDocument10 pagesChemosphere: Li Yang, Jie Gao, Ying Liu, Guoqiang Zhuang, Xiawei Peng, Wei-Min Wu, Xuliang ZhuangAndres DavidNo ratings yet
- Journal of Ethnopharmacology: The Ayurvedic Medicine Clitoria Ternatea-From Traditional Use To Scientific AssessmentDocument12 pagesJournal of Ethnopharmacology: The Ayurvedic Medicine Clitoria Ternatea-From Traditional Use To Scientific Assessmentdyah ayu noer fadilaNo ratings yet
- Influence of Different Inducers On Ligninolytic Enzyme ActivitiesDocument7 pagesInfluence of Different Inducers On Ligninolytic Enzyme ActivitiesAlina CoralinaNo ratings yet