Professional Documents
Culture Documents
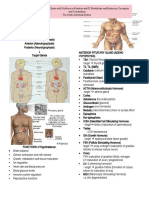
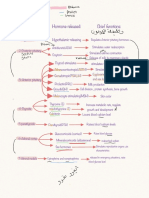
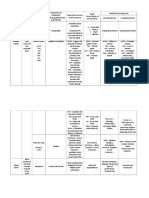
Gland Stimulation of Hormones Produced Action Gland: Fsh/Lh-Gonads Acth
Uploaded by
shirley0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views2 pagesOriginal Title
endocrine 2 2021
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views2 pagesGland Stimulation of Hormones Produced Action Gland: Fsh/Lh-Gonads Acth
Uploaded by
shirleyCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
.
Gland Stimulation of Hormones Action
Gland Produced
Pineal Gland Time of day/closed melatonin Circadian
eyes Rhythm
FSH/LH-gonads
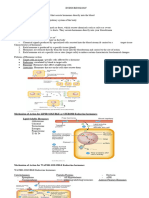
Anterior Pituitar't Hypothalamus - FSH ,LH, AcTH, Prolactin ,GH AcTH-
releasing/inhibiting cortisol(adrenal
hormones glands)
GH-cell growth
These produced by Oxytocin-
Posterior Pituitar't Nerve impulse from hypothalamus BUT stored in uterine
the hypothalamus pp contraction
Oxytocin & ADH ADH-.1,,urine
production
Th"troid Gland Hypothalamus-TRH- T3 T4 (follicular cells) Metabolism
-Anterior Pit. TSH
Calcitonin -
Calcitonin-blood { } Calcitonin (extrafollicular decreases
levels cells) blood ca+ levels
Parath"troid Blood { } levels PTH Increases ca+
Gland blood levels
Insulin- Beta cells '1,blood sugar Both endocrine and
Pancreas Blood { } of glucose exocrine
levels Glucagon -Alpha cells 1'blood sugar
Adrenal cortex (outer Blood { } of na+ ions Aldosterone Conserves Na+
larg_est reg_ionl or increase in K+ ions (mineralocorticoid) /excretes K+
thus retains flds Steroid hormones
Cortisol (glucocorticoid)
-affects glue
ose metabolism
Adrenal medulla
Middlel Nerve impulses Epinephrine/norepinephrine SNS effects Fight /flight
Ovary Hypothalamus estrogen
Testes Hypoth alamus testosterone
Thymus Thymosins Affect
production and
specialization of
WBC---
immunity
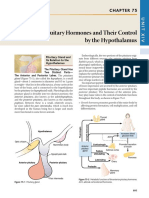
The connection btwn
These can be also inhibiting See above*** hypothalamus & AP is
H othalamus GHRH,GnRH,CRH,TRH the hypophyseal
portal vein
Connection btwn
Hypothalamus & PP is
the axons /nervous
sytem
You might also like
- Chart of HormonesDocument2 pagesChart of HormonesspringdingNo ratings yet
- Care of The Patient With Complex Endocrine Disorders Endocrine SystemDocument11 pagesCare of The Patient With Complex Endocrine Disorders Endocrine SystemgoodgoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument14 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyIssaiah Nicolle CeciliaNo ratings yet
- PPT-Endocrine-SystemDocument56 pagesPPT-Endocrine-SystemNoreen BengoNo ratings yet
- Endocrine PathologyDocument13 pagesEndocrine Pathologysarguss14100% (1)
- Katwalker11 Bio 251 Exam 1Document6 pagesKatwalker11 Bio 251 Exam 1khunarak.2008No ratings yet
- Endocrinology TableDocument3 pagesEndocrinology TableWilliam PartonNo ratings yet
- 2009 John Wiley Sons Inc The Endocrine SystemDocument23 pages2009 John Wiley Sons Inc The Endocrine SystemnobodyNo ratings yet
- Hypothalamus and The Pituitary LectureDocument51 pagesHypothalamus and The Pituitary LecturealkalicharanNo ratings yet
- Reproduction & Endocrinology 1: Hypothalamus and PituitaryDocument41 pagesReproduction & Endocrinology 1: Hypothalamus and PituitaryabdulNo ratings yet
- Review of Endocrine SystemDocument32 pagesReview of Endocrine SystemJames FNo ratings yet
- GH Chap 2Document12 pagesGH Chap 2Shellz2428No ratings yet
- Exercise 13 EditDocument10 pagesExercise 13 EditSamantha De JesusNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System Regulates Animal PhysiologyDocument9 pagesEndocrine System Regulates Animal PhysiologyFlor SagnipNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry of Hypertension: Etiology and TreatmentDocument44 pagesBiochemistry of Hypertension: Etiology and TreatmentAlberto MayorgaNo ratings yet
- Hipofise and PancreasDocument104 pagesHipofise and PancreasCitra Utami ViolletyNo ratings yet
- CH 18 Endo F 2017Document152 pagesCH 18 Endo F 2017JuliaNo ratings yet
- MUST To KNOW in BacteriologyDocument3 pagesMUST To KNOW in BacteriologySam CatanghalNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System Chemical MessengersDocument14 pagesEndocrine System Chemical MessengersElaine Victoria ElizanNo ratings yet
- Endocrine in Animals (CBSE)Document3 pagesEndocrine in Animals (CBSE)Ashwani GahlotNo ratings yet
- 19 Lecture PresentationDocument65 pages19 Lecture PresentationLeilaNo ratings yet
- Male ReproductiveDocument10 pagesMale ReproductivevivekNo ratings yet
- ENDOCRINOLOGYDocument8 pagesENDOCRINOLOGYshaairatogleNo ratings yet
- 90905094-ec03-4cc8-b69e-6ce793206e1bDocument1 page90905094-ec03-4cc8-b69e-6ce793206e1bNaman SinhaNo ratings yet
- Mar 10 - Fisiologi Hormon HypophysisDocument45 pagesMar 10 - Fisiologi Hormon HypophysisLailatuz ZakiyahNo ratings yet
- Pituitary Gland and Its HormonesDocument45 pagesPituitary Gland and Its HormonesLailatuz ZakiyahNo ratings yet
- Pediatrics Trans EndoDocument6 pagesPediatrics Trans EndoyayayanizaNo ratings yet
- Lab CH 27Document4 pagesLab CH 27Gricelda VasquezNo ratings yet
- Hormones Updated ShortDocument72 pagesHormones Updated ShortAbdur RehmanNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System: Citation NeededDocument8 pagesEndocrine System: Citation NeededAsif Hassan BiswasNo ratings yet
- The Pituitary - Adrenal Axis and Pa Tho Physiology of HyperadrenocorticismDocument7 pagesThe Pituitary - Adrenal Axis and Pa Tho Physiology of Hyperadrenocorticismtaner_soysurenNo ratings yet
- Phys 8Document39 pagesPhys 8sakwork30No ratings yet
- Gland of Endocrine System_AVCN2Document3 pagesGland of Endocrine System_AVCN2Nguyễn Thành DanhNo ratings yet
- Science: Endocrine & Nervous SystemDocument5 pagesScience: Endocrine & Nervous SystemLUISE DANIELLA DELOS REYES DOLOTALLASNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry of HormonesIDocument24 pagesBiochemistry of HormonesIStephie GhassanNo ratings yet
- Topic 3 THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEMDocument41 pagesTopic 3 THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEMIreneNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 WorksheetDocument7 pagesChapter 5 Worksheetapi-372001543No ratings yet
- ENDOCRINOLOGY CLINICAL CHEMISTRY OVERVIEWDocument39 pagesENDOCRINOLOGY CLINICAL CHEMISTRY OVERVIEWJanelle RemorozaNo ratings yet
- General Biology Lesson 13Document13 pagesGeneral Biology Lesson 13GUCOR, LOVELY SHANE C.No ratings yet
- Drugs Affecting The Endocrine SystemDocument43 pagesDrugs Affecting The Endocrine SystemJustine Vens G. AgustinNo ratings yet
- Week 1 - Jeremy Evans Darmawan 01071180101Document12 pagesWeek 1 - Jeremy Evans Darmawan 01071180101Jeremy EvansNo ratings yet
- Endocrine PhysiologyDocument32 pagesEndocrine PhysiologyAziem ShazwanNo ratings yet
- Science - LensDocument8 pagesScience - LensAte DannyNo ratings yet
- Msl Ec MidtermsDocument27 pagesMsl Ec Midtermsmendozajanice0601No ratings yet
- ENDORCRINE SYSTEM - Review Anaphy NotesDocument10 pagesENDORCRINE SYSTEM - Review Anaphy NotesJae TyNo ratings yet
- L44 - Pituitary DisordersDocument20 pagesL44 - Pituitary DisordersKiprono Keitany TimothyNo ratings yet
- Endocrinology and Metabolic Diseases OverviewDocument49 pagesEndocrinology and Metabolic Diseases OverviewFathimathNo ratings yet
- Overview of hormones-BRSDocument1 pageOverview of hormones-BRSk8rbwkpgn7No ratings yet
- Endocrine System: Navigation SearchDocument9 pagesEndocrine System: Navigation SearchAnnagella De JesusNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Day 1 TemplateDocument17 pagesEndocrine Day 1 TemplateMikeNo ratings yet
- Amended Endocrine System SummerDocument41 pagesAmended Endocrine System SummerKatherineVoNo ratings yet
- L44 - Pituitary DisordersDocument20 pagesL44 - Pituitary Disorderschai rinNo ratings yet
- The Pituitary Gland and its HormonesDocument1 pageThe Pituitary Gland and its HormonesAnonymous wRiKUO07DHNo ratings yet
- 4a.endocrine Gland Secretions and FunctionsDocument3 pages4a.endocrine Gland Secretions and FunctionssikaboaduaNo ratings yet
- LIGHT - Endo Pituitary GlandDocument6 pagesLIGHT - Endo Pituitary GlandMiguel Cuevas DolotNo ratings yet
- Hormone Gland Functions ChartDocument2 pagesHormone Gland Functions ChartmNo ratings yet
- Endo ReviewerDocument5 pagesEndo ReviewerZIAN LABADIANo ratings yet
- ENDOCRINE DISORDERS Ms HandoutsDocument14 pagesENDOCRINE DISORDERS Ms HandoutsCatherine FaithNo ratings yet
- On The Posterior Surface of Thyroid GlandDocument2 pagesOn The Posterior Surface of Thyroid GlandRica Marie G. UyNo ratings yet
- Final Exam REVIEW LABELLINGDocument23 pagesFinal Exam REVIEW LABELLINGshirleyNo ratings yet
- Structures of The Ear Trudy's HandoutDocument3 pagesStructures of The Ear Trudy's HandoutshirleyNo ratings yet
- DrugmedsDocument52 pagesDrugmedsshirleyNo ratings yet
- ANPY Chapter 1-5 Review Unit 1Document46 pagesANPY Chapter 1-5 Review Unit 1shirleyNo ratings yet
- Anpy Quiz 6Document6 pagesAnpy Quiz 6shirleyNo ratings yet
- Anpy Quiz 1&2Document23 pagesAnpy Quiz 1&2shirleyNo ratings yet
- Embraced by The Needle Critical EssayDocument5 pagesEmbraced by The Needle Critical EssayshirleyNo ratings yet
- ANPY 1000 Review of CNS and Sensory SystemsDocument82 pagesANPY 1000 Review of CNS and Sensory SystemsshirleyNo ratings yet
- ANPY 1000 Review of CNS and Sensory SystemsDocument82 pagesANPY 1000 Review of CNS and Sensory SystemsshirleyNo ratings yet
- Business Law Activity 1Document1 pageBusiness Law Activity 1shirleyNo ratings yet
- Anterior Thorax Third Clavicle) To: RUL: From Apex (2-3cm Above The InnerDocument5 pagesAnterior Thorax Third Clavicle) To: RUL: From Apex (2-3cm Above The InnershirleyNo ratings yet
- 4 Classes of Anti Dysrhythmic DrugsDocument1 page4 Classes of Anti Dysrhythmic DrugsshirleyNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology ReviewDocument63 pagesAnatomy & Physiology ReviewshirleyNo ratings yet
- Charting Examples For Physical AssessmentDocument16 pagesCharting Examples For Physical Assessmentim3in1No ratings yet
- Procter and GambleDocument2 pagesProcter and GambleshirleyNo ratings yet
- Mnemonics For AntibioticsDocument1 pageMnemonics For AntibioticsshirleyNo ratings yet
- The Universal, Theoretical, and Psychological Facets of The Aging PhenomenonDocument7 pagesThe Universal, Theoretical, and Psychological Facets of The Aging PhenomenonshirleyNo ratings yet
- Why Facebook Is BeneficialDocument3 pagesWhy Facebook Is BeneficialshirleyNo ratings yet
- Management Assignment - EdwinDocument3 pagesManagement Assignment - EdwinshirleyNo ratings yet
- Examples of Diversity Problems in The WorkplaceDocument2 pagesExamples of Diversity Problems in The WorkplaceshirleyNo ratings yet
- HRM Class Activity Edwin BelmesDocument1 pageHRM Class Activity Edwin BelmesshirleyNo ratings yet
- Essential Attitudes, Personal Qualities, and Professional Behaviors Required in NursingDocument27 pagesEssential Attitudes, Personal Qualities, and Professional Behaviors Required in NursingshirleyNo ratings yet
- Sales Confirmation: Alpha Trading S.P.A. Compagnie Tunisienne de NavigationDocument1 pageSales Confirmation: Alpha Trading S.P.A. Compagnie Tunisienne de NavigationimedNo ratings yet
- Sri Sathya Sai Bhagavatam Part IDocument300 pagesSri Sathya Sai Bhagavatam Part ITumuluru Krishna Murty67% (6)
- Anglo Agriparts Trade CatalogueDocument609 pagesAnglo Agriparts Trade CatalogueJoanne Champion100% (1)
- Biology and Aquaculture of Tilapia-Routledge (2022)Document324 pagesBiology and Aquaculture of Tilapia-Routledge (2022)Pablo Antonio Pintos TeránNo ratings yet
- How To Comp For A Vocalist - Singer - The Jazz Piano SiteDocument5 pagesHow To Comp For A Vocalist - Singer - The Jazz Piano SiteMbolafab RbjNo ratings yet
- Valvula ContraincendioDocument6 pagesValvula ContraincendiowidNo ratings yet
- Barrett Preliminary Injunction in 'Heartbeat Bill' CaseDocument12 pagesBarrett Preliminary Injunction in 'Heartbeat Bill' CaseCincinnatiEnquirerNo ratings yet
- Mall Tenant Design ManualDocument52 pagesMall Tenant Design ManualWaleed AliNo ratings yet
- (English (Auto-Generated) ) Reviving The Labor Movement - Margaret Levi - TEDxSeattle (DownSub - Com)Document14 pages(English (Auto-Generated) ) Reviving The Labor Movement - Margaret Levi - TEDxSeattle (DownSub - Com)Surat PEHKTNo ratings yet
- Jack Turner - Not On Any MapDocument13 pagesJack Turner - Not On Any MapormrNo ratings yet
- PDF Penstock Manual DLDocument160 pagesPDF Penstock Manual DLWilmer Fernando DuarteNo ratings yet
- Inventory ControlDocument4 pagesInventory ControlabassalishahNo ratings yet
- 18 MN216 Fluid Mechanics IDocument2 pages18 MN216 Fluid Mechanics Ijorge luisNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Insurance AccountingDocument86 pagesAn Introduction To Insurance AccountingTricia PrincipeNo ratings yet
- WWII 2nd Army HistoryDocument192 pagesWWII 2nd Army HistoryCAP History Library100% (1)
- Current Openings: The Sirpur Paper Mills LTDDocument3 pagesCurrent Openings: The Sirpur Paper Mills LTDMano VardhanNo ratings yet
- Lab Skill Workbook - Applied Physics - Seph0009 07-12-2023Document87 pagesLab Skill Workbook - Applied Physics - Seph0009 07-12-2023rahulsaitalasilaNo ratings yet
- IEC 61850 Configuration of A Phoenix Contact IED: User ManualDocument68 pagesIEC 61850 Configuration of A Phoenix Contact IED: User ManualHarold PuinNo ratings yet
- Hidden Divergence Reveals Profitable Trading PatternsDocument12 pagesHidden Divergence Reveals Profitable Trading PatternsSubrata PaulNo ratings yet
- Lcasean PaperDocument6 pagesLcasean Paperkean ebeoNo ratings yet
- Course Registration Slip MBA 2023Document3 pagesCourse Registration Slip MBA 2023Piyush RaghuwanshiNo ratings yet
- Gateway A2 Test 1BDocument3 pagesGateway A2 Test 1BNewteacher29100% (6)
- Window Server 2008 Lab ManualDocument51 pagesWindow Server 2008 Lab ManualpadaukzunNo ratings yet
- Commodities Storage V CADocument4 pagesCommodities Storage V CAElah ViktoriaNo ratings yet
- Royalstone ReadmeDocument2 pagesRoyalstone ReadmeAdnan BrianNo ratings yet
- The Residents of The British East India Company at Indian Royal Courts, C. 1798-1818Document224 pagesThe Residents of The British East India Company at Indian Royal Courts, C. 1798-1818Ajay_Ramesh_Dh_6124No ratings yet
- Step 5 - PragmaticsDocument7 pagesStep 5 - PragmaticsRomario García UrbinaNo ratings yet
- Persons Choki MotobuDocument4 pagesPersons Choki MotobuHessabi max100% (1)
- Year 11 GCSE Revision Guidance and Exam Booklet Solihull PDFDocument27 pagesYear 11 GCSE Revision Guidance and Exam Booklet Solihull PDFNoor Ulain Nabeela83% (6)
- Business Plan Template For AfterSchool ProgramsDocument6 pagesBusiness Plan Template For AfterSchool Programsshelana BarzeyNo ratings yet