0% found this document useful (0 votes)
204 views17 pagesUnderstanding Management Information Systems
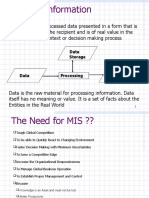
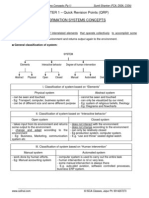
This document discusses management information systems (MIS) and decision making. It defines MIS as the study of information technology in business settings and systems used for operational and tactical decision making. A basic problem solving model is presented involving intelligence gathering, design, choice, implementation, and monitoring. Decision making involves defining the problem, gathering data, identifying alternatives and selecting a solution. Structured problems lend themselves to programmed decisions that can be automated while unstructured problems require unprogrammed decisions addressed by decision support systems. MIS are used to provide managers with information to support regular operations, control, and planning.
Uploaded by
Renu SharmaCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
204 views17 pagesUnderstanding Management Information Systems
This document discusses management information systems (MIS) and decision making. It defines MIS as the study of information technology in business settings and systems used for operational and tactical decision making. A basic problem solving model is presented involving intelligence gathering, design, choice, implementation, and monitoring. Decision making involves defining the problem, gathering data, identifying alternatives and selecting a solution. Structured problems lend themselves to programmed decisions that can be automated while unstructured problems require unprogrammed decisions addressed by decision support systems. MIS are used to provide managers with information to support regular operations, control, and planning.
Uploaded by
Renu SharmaCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd