Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Acid Rain New
Uploaded by
Azmain Iktedar0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views12 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views12 pagesAcid Rain New
Uploaded by
Azmain IktedarCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 12
Acid Rain
• Acid rain is mainly a mixture of sulphuric and nitric
acids depending upon the relative quantities of
oxides of sulphur and nitrogen emissions.
• Acid rain is rain that is more acidic than it should
be. Acid rain is a complicated problem affecting soil
and water chemistry, as well as the life cycles of
plants and animals on land and in the water.
• In addition, weather conditions contribute to air
pollution and cause acid rain to spread vast
distances.
Air Pollution Causes Acid Rain
• Air pollution from the burning of fossil fuels is the
major cause of acid rain.
• Power plants and factories burn coal, oil, and natural
gas to produce the electricity we need to do all kinds
of things, like light our homes.
• Cars, trucks, and airplanes also run on gasoline, a
fossil fuel.
Cont..
• Burning of fossil fuels sends smoke and fumes into the
ATMOSPHERE, or the air above the Earth. In the air, these
pollutants combine with moisture to form acid rain.
• The main chemicals in air pollution that create acid rain are
sulfur dioxide (SO2) and nitrogen oxides (NOX).
• Acid rain usually forms high in the clouds where SO2 and NOX
react with water and oxygen. This forms SULFURIC ACID and
NITRIC ACID in the atmosphere.
• Sunlight increases the speed of these reactions, and therefore
increases the amount of acid in the atmosphere. Rainwater,
snow, fog, and other forms of PRECIPITATION then mix with
the sulfuric and nitric acids in the air and fall to Earth as acid
rain.
Formation of Acid Rain
Acidity Observation
Wet Deposition
• Wet deposition refers to
acidic rain, fog, and snow.
• If the acid chemicals in the
air are blown into areas
where the weather is wet,
the acids can fall to the
ground in the form of rain,
snow, fog, or mist.
• As this acidic water flows
over and through the
ground, it affects a variety
of plants and animals.
Dry Deposition
• Acid rain does not account for all of the acidity that falls back
to Earth from pollutants. About half of the acidity in the
atmosphere is deposited onto buildings, cars, homes, and
trees as particles and gases. This process is called DRY
DEPOSITION.
• In some instances, these gases and particles can damage or
alter the things on which they settle. Dry deposition (gases
and particles) is sometimes washed from trees and other
surfaces by rainstorms.
• When that happens, the RUNOFF water contains acid from
acid rain and dry deposition, making the combination more
acidic than the falling rain alone. The combination of acid rain
(wet deposition) plus dry deposition is called acid deposition .
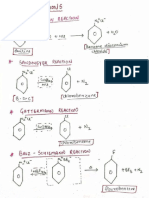
Reaction Occur during acid rain
• O3 → O2 + O
• O + H2O → OH- (hydroxyl radical)
• OH- + SO2 → HSO3
• HSO3 + OH-→H2 SO4
• OH- + NO2→ HNO3
Effect of Acid Rain
• Ecosystem
• Human Health
• Tress
• Forrest
• Stone Buildings and Monuments
• Accelerated leaching of heavy metals from rocks
and soil.
You might also like
- Acid Rain: Assignment 1 Muhamad Amirul Aqil Bin Mat Rozali 5521311529 Azyyati Binti JohariDocument12 pagesAcid Rain: Assignment 1 Muhamad Amirul Aqil Bin Mat Rozali 5521311529 Azyyati Binti JohariSyazani HussainiNo ratings yet
- Acid RainDocument6 pagesAcid RainDeliaNo ratings yet
- Acid RainDocument12 pagesAcid Rainprabhu jiNo ratings yet
- Acid Rain (Group 2)Document23 pagesAcid Rain (Group 2)Viviane O. BaylonNo ratings yet
- Acid RainDocument21 pagesAcid Raintehseenmohsin6No ratings yet
- Acid Rain: by Samuel Quintero, Jeffry GilDocument4 pagesAcid Rain: by Samuel Quintero, Jeffry GilJaime Leal NavarroNo ratings yet
- Acid RainDocument9 pagesAcid RainrohitjhasyawariNo ratings yet
- Acid Rain File AMOLDocument15 pagesAcid Rain File AMOLpari0000No ratings yet
- Generally: What Is Acid Rain: Key Pointss!!!Document4 pagesGenerally: What Is Acid Rain: Key Pointss!!!aihpendoyNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reactions Involving Acid RainDocument8 pagesChemical Reactions Involving Acid RainCarodan Mark JosephNo ratings yet
- Acid RainDocument12 pagesAcid Rainprabhu jiNo ratings yet
- ACID RAINS How They Form and Effect The WorldDocument19 pagesACID RAINS How They Form and Effect The WorldNOPEENo ratings yet
- Acid Rain and Its EffectsDocument6 pagesAcid Rain and Its Effectstamoor aliNo ratings yet
- Acid RainDocument12 pagesAcid RainZackNo ratings yet
- Sources of Acid RainDocument1 pageSources of Acid RainMohd Najmi HakimNo ratings yet
- Acid Rain - EDSDocument2 pagesAcid Rain - EDSNafeesa NazNo ratings yet
- Acid Rain by Zerkash SheikhDocument12 pagesAcid Rain by Zerkash Sheikhشیخ زرکاش امرتسریہNo ratings yet
- Acid Rain and Ozone DepletionDocument40 pagesAcid Rain and Ozone DepletionmalarNo ratings yet
- Acid Rain: Guru Nanak Dev UniversityDocument20 pagesAcid Rain: Guru Nanak Dev UniversityManwinder Singh GillNo ratings yet
- Acid Rain Research PaperDocument15 pagesAcid Rain Research Paperaysilislam528No ratings yet
- Acid Rain - Acid DepositionDocument4 pagesAcid Rain - Acid DepositionjincodyNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Acid RainDocument8 pagesIntroduction To Acid RainDevendarsingh rawatNo ratings yet
- Arunima Shandilya Scienc e 10 BDocument22 pagesArunima Shandilya Scienc e 10 BHOWE CHENG TENGNo ratings yet
- Acid Rain: Acid Rain Is A Rain or Any Other Form of Precipitation That Is Unusually AcidicDocument5 pagesAcid Rain: Acid Rain Is A Rain or Any Other Form of Precipitation That Is Unusually AcidicLucille BallaresNo ratings yet
- Acid RainDocument11 pagesAcid RainTEJAS JAINNo ratings yet
- What Causes Acid Rain?Document3 pagesWhat Causes Acid Rain?mountain girlNo ratings yet
- Acid Rain: Acid Rain Is Basically Rain That Has A Higher Than Normal Acid Level (Low PH)Document36 pagesAcid Rain: Acid Rain Is Basically Rain That Has A Higher Than Normal Acid Level (Low PH)Arjit GoswamiNo ratings yet
- Acid Precipitation: Salisid and EscuetaDocument10 pagesAcid Precipitation: Salisid and EscuetaChristine EscuetaNo ratings yet
- AcidrainDocument15 pagesAcidrainPolar PenguinNo ratings yet
- Acid RainDocument4 pagesAcid RainMian Ahmed ShahNo ratings yet
- Aci D RainDocument16 pagesAci D RainShuvoNo ratings yet
- Acid Rain: The Problem Continues: Presented by Navjot Singh Roll No. 95222454108 Bba 6 SemesterDocument38 pagesAcid Rain: The Problem Continues: Presented by Navjot Singh Roll No. 95222454108 Bba 6 SemesterlovleshrubyNo ratings yet
- Acid RainDocument25 pagesAcid RainMuruganNo ratings yet
- Presented By: Fayza Kamal Khattab: Presented To: Dr. Sayed ShalabyDocument11 pagesPresented By: Fayza Kamal Khattab: Presented To: Dr. Sayed ShalabyMohamed Maher TorkyNo ratings yet
- 6.3.4. Acid Deposition - GEC 007-ARCH41S2 - Science, Technology and SocietyDocument3 pages6.3.4. Acid Deposition - GEC 007-ARCH41S2 - Science, Technology and SocietyKIRSTENNo ratings yet
- What Is Acid RainDocument6 pagesWhat Is Acid RainPrerna VoraNo ratings yet
- What Is Acid RainDocument6 pagesWhat Is Acid RainPrerna VoraNo ratings yet
- What Is Acid RainDocument5 pagesWhat Is Acid RainHafiz hassanNo ratings yet
- Acid RainDocument15 pagesAcid RainSayem Ahmmed RiponNo ratings yet
- Acid RainDocument25 pagesAcid RainApril Bartolome FloresNo ratings yet
- What Is Acid Rain and What Causes ItDocument1 pageWhat Is Acid Rain and What Causes ItkhloudsaeidNo ratings yet
- Acid RainDocument22 pagesAcid RainShankarNo ratings yet
- Topic 6 - Acid RainDocument54 pagesTopic 6 - Acid RainJaidil Jaiden YakopNo ratings yet
- Acid RainDocument29 pagesAcid RainAakash BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- What Is Acid RainDocument5 pagesWhat Is Acid RainEhteshamNo ratings yet
- Environmental ChemistryDocument16 pagesEnvironmental Chemistryrajesh.pandey9870606No ratings yet
- Acid Rain: Acid Rain Is Rain Consisting of That Are Unusually Because ofDocument11 pagesAcid Rain: Acid Rain Is Rain Consisting of That Are Unusually Because ofAna BellaNo ratings yet
- What Is Acid RainDocument7 pagesWhat Is Acid RainSai sasindhar MalapatiNo ratings yet
- Enter Post Title HereDocument6 pagesEnter Post Title HereRohit ShalgarNo ratings yet
- Effects of Air Polllution On The AtmosphereDocument19 pagesEffects of Air Polllution On The Atmospherechristian ringorNo ratings yet
- Acid RainDocument7 pagesAcid RainAnoshKhanNo ratings yet
- Acid RainDocument6 pagesAcid RainАнастасия МелешкоNo ratings yet
- Acid Rain-The Major Cause of Pollution: Its Causes, Effects: Subodh KumarDocument6 pagesAcid Rain-The Major Cause of Pollution: Its Causes, Effects: Subodh KumarShruthi GNo ratings yet
- Acid Rain: Wet Deposition:-Dry DepositionDocument5 pagesAcid Rain: Wet Deposition:-Dry DepositionRycel De Los ReyesNo ratings yet
- Acid RainDocument19 pagesAcid RainRObin KhanNo ratings yet
- Acid Rain Description and Analysis: TreeboxDocument6 pagesAcid Rain Description and Analysis: TreeboxNanthini RajanderanNo ratings yet
- Acid RainDocument17 pagesAcid RainSaif YounusNo ratings yet
- Acid Rain: Acid Rain Is Rain or Any Other Form of Precipitation That Is Unusually Acidic, I.EDocument7 pagesAcid Rain: Acid Rain Is Rain or Any Other Form of Precipitation That Is Unusually Acidic, I.ESarvesh JaiswalNo ratings yet
- PrOdUcT QuIz 4.1Document7 pagesPrOdUcT QuIz 4.1Azmain IktedarNo ratings yet
- Adhir Sir Product 3.2 All SheetDocument28 pagesAdhir Sir Product 3.2 All SheetAzmain IktedarNo ratings yet
- Leather Apparel Design PDFDocument13 pagesLeather Apparel Design PDFAzmain IktedarNo ratings yet
- BCS Prostuti App Link: June 25, 2022Document71 pagesBCS Prostuti App Link: June 25, 2022Azmain IktedarNo ratings yet
- Anik Last PartDocument16 pagesAnik Last PartAzmain IktedarNo ratings yet
- Khulna University of Engineering & TechnologyDocument8 pagesKhulna University of Engineering & TechnologyAzmain IktedarNo ratings yet
- Embossing Printing Attaching FullDocument49 pagesEmbossing Printing Attaching FullAzmain IktedarNo ratings yet
- Khulna University of Engineering & TechnologyDocument5 pagesKhulna University of Engineering & TechnologyAzmain IktedarNo ratings yet
- Khulna University of Engineering & TechnologyDocument4 pagesKhulna University of Engineering & TechnologyAzmain IktedarNo ratings yet
- Assignment of 2k17Document1 pageAssignment of 2k17Azmain IktedarNo ratings yet
- Product Adhir Sir Key Case 3.Document17 pagesProduct Adhir Sir Key Case 3.Azmain IktedarNo ratings yet
- Bacteriology: Where N Is The Number of Bacterial Generations. - (12Document4 pagesBacteriology: Where N Is The Number of Bacterial Generations. - (12Azmain IktedarNo ratings yet
- Ova View: Aooignmant CagDocument8 pagesOva View: Aooignmant CagAzmain IktedarNo ratings yet
- Course No: LE 3219: Presentation OnDocument15 pagesCourse No: LE 3219: Presentation OnAzmain IktedarNo ratings yet
- Roll 1719027 Sajedur Rahman LE3209Document6 pagesRoll 1719027 Sajedur Rahman LE3209Azmain IktedarNo ratings yet
- Me Lab Report GRP DistributionDocument2 pagesMe Lab Report GRP DistributionAzmain IktedarNo ratings yet
- A1 Experiment No 03Document6 pagesA1 Experiment No 03Azmain IktedarNo ratings yet
- Me Lab Report GRP DistributionDocument2 pagesMe Lab Report GRP DistributionAzmain IktedarNo ratings yet
- A1-Experiment No-01Document6 pagesA1-Experiment No-01Azmain IktedarNo ratings yet
- Me 3220 LeDocument12 pagesMe 3220 LeAzmain IktedarNo ratings yet
- Me Lab Report GRP DistributionDocument2 pagesMe Lab Report GRP DistributionAzmain IktedarNo ratings yet
- 43 Me Lab ReportDocument5 pages43 Me Lab ReportAzmain IktedarNo ratings yet
- Cationic FinishingDocument3 pagesCationic FinishingAzmain IktedarNo ratings yet
- Me 3220 LeDocument12 pagesMe 3220 LeAzmain IktedarNo ratings yet
- Me Lab Report GRP DistributionDocument2 pagesMe Lab Report GRP DistributionAzmain IktedarNo ratings yet
- 43 Me Lab ReportDocument5 pages43 Me Lab ReportAzmain IktedarNo ratings yet
- Drying Defects and Remedy 14Document3 pagesDrying Defects and Remedy 14Azmain IktedarNo ratings yet
- Pollutants and Environmental Impacts ofDocument20 pagesPollutants and Environmental Impacts ofAzmain IktedarNo ratings yet
- Cow Shoe Upper Leather Full Grain Millingnappa Black: Material 1 2 3 4 5Document2 pagesCow Shoe Upper Leather Full Grain Millingnappa Black: Material 1 2 3 4 5Azmain IktedarNo ratings yet
- Ceran XM 220 - 080100 - MSDSDocument13 pagesCeran XM 220 - 080100 - MSDSLisa WhiteNo ratings yet
- The Role of Plants As Indicator For Air Pollution (Mahadi)Document3 pagesThe Role of Plants As Indicator For Air Pollution (Mahadi)Muhammad Mahadi100% (1)
- Supporting SUT, Air Quality, and Climate Change - Roland Haas (GTZ) - Joint Transport Urban & EnvDocument30 pagesSupporting SUT, Air Quality, and Climate Change - Roland Haas (GTZ) - Joint Transport Urban & EnvarlenechavezNo ratings yet
- Pto Engineering Report SampleDocument3 pagesPto Engineering Report SampleRJ PadillaNo ratings yet
- 22447-mcq-EVS MCQ With AnswersDocument20 pages22447-mcq-EVS MCQ With Answerskomal ghodkeNo ratings yet
- 1 Validation Report Gyapa ICS Ghana - Final 27-04-2010Document43 pages1 Validation Report Gyapa ICS Ghana - Final 27-04-2010Kkaran SinghNo ratings yet
- Carbon Footprint TS311Document20 pagesCarbon Footprint TS311Wiineta TaameriNo ratings yet
- Critical Thinking Essay FinalDocument14 pagesCritical Thinking Essay FinalAnonymous ClhEs0sNo ratings yet
- Module 1. Lesson3.Urban IndustryDocument8 pagesModule 1. Lesson3.Urban IndustryJohnmeri Dale Genodiala Baldo100% (1)
- Global Warming NotesDocument4 pagesGlobal Warming NotesPatrice DavisNo ratings yet
- 10 Thermal TechnologyDocument97 pages10 Thermal TechnologyNguyenHuanNo ratings yet
- 16jan2017 Black Carbon Measurement Methods and Emission Factors Ships Final ICCTDocument184 pages16jan2017 Black Carbon Measurement Methods and Emission Factors Ships Final ICCTtrunghieu254No ratings yet
- Group 1-6 HvacDocument22 pagesGroup 1-6 Hvacryan bhinogNo ratings yet
- Vsa 032 - Vsa 068 - Vsa 100 - AuDocument9 pagesVsa 032 - Vsa 068 - Vsa 100 - AuMariana CardosoNo ratings yet
- Basic Design Calculations For Flue Gas Stack Design For A Diesel Genset in IndiaDocument5 pagesBasic Design Calculations For Flue Gas Stack Design For A Diesel Genset in IndiaDurjoy ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Chem Hydrogen SulfideDocument2 pagesChem Hydrogen SulfidefardhaNo ratings yet
- CIVIL Green Building ReportDocument23 pagesCIVIL Green Building ReportJoe ChristyNo ratings yet
- Msds CPD Intraplast N UsDocument10 pagesMsds CPD Intraplast N UsJose David CastroNo ratings yet
- Rigid PVC Conduit Installation GuideDocument7 pagesRigid PVC Conduit Installation GuideReydel QuimnoNo ratings yet
- 04 HSE Weekly Statistics Report Nov 29th - Dec 5 THDocument1 page04 HSE Weekly Statistics Report Nov 29th - Dec 5 THAjas AjuNo ratings yet
- Easy Dab Msds EnglishDocument5 pagesEasy Dab Msds EnglishLendhyNo ratings yet
- Global Warming SummaryDocument2 pagesGlobal Warming SummaryWinston QuilatonNo ratings yet
- Named Organic ReactionsDocument8 pagesNamed Organic ReactionscrawlskullNo ratings yet
- Safety Data Sheet: 1. IdentificationDocument9 pagesSafety Data Sheet: 1. IdentificationU.s. Ezhil ArivudainambiNo ratings yet
- As 4211.3-1996 Gas Recovery or Combined Recovery and Recycling Equipment Fluorocarbon Refrigerants From CommeDocument8 pagesAs 4211.3-1996 Gas Recovery or Combined Recovery and Recycling Equipment Fluorocarbon Refrigerants From CommeSAI Global - APACNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6.Document16 pagesChapter 6.Taimori FadhiliNo ratings yet
- Design Principles For Wood Burning Cook StovesDocument40 pagesDesign Principles For Wood Burning Cook StovesKAFKAJK100% (3)
- PEGGEN02Document70 pagesPEGGEN02aliijaz007100% (1)
- The Seven Sins of GreenwashingDocument26 pagesThe Seven Sins of GreenwashingDaily Freeman100% (2)
- Sustainable Development Lesson PlanDocument11 pagesSustainable Development Lesson PlanRomano LuisNo ratings yet