Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Well Stimulation-Mine Vocational
Uploaded by
Vinal KumarOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Well Stimulation-Mine Vocational
Uploaded by
Vinal KumarCopyright:
Available Formats
Well Stimulation
Operation & Safety Considerations
By:
Rohan Kumar, EE (P)
MINE VOCATIONAL TRAINING
CBM ASSET, BOKARO
18/05/2022
Content
Reservoir Properties
Stimulation
Fracturing Fluid
Coiled Tubing
Safety Considerations
CBM ASSET, BOKARO
Reservoir Properties
Porosity: Fraction of void space
Permeability : Ability of a porous material
to allow the material to flow through it
CBM ASSET, BOKARO
Formation Damage
•Any process causing a reduction in the natural inherent productivity or injectivity of an oil and gas production or
injection/ disposal well
Drilling & Cementing Completion & workover
operations
Formation
Damage
Production or injection Stimulation
•Skin: Quantitative measure of formation damage
•Negative Skin is favourable
CBM ASSET, BOKARO
Stimulation
Stimulation : Any activity intended to reduce the formation
damage or skin
• Chemicals (Acid) are injected at pressure less than formation
breakdown pressure to dissolve near wellbore damage.
Matrix Acidization • Mud Acid ( 12 % HCl + 3 % HF) or Organic HF ( 10% Acetic acid + 2
% HF ).
• Acid is injected at pressure higher than fracture pressure .
Acid Fracturing • Due to acid flow, the fracture face is dissolved in a non uniform
(Carbonates) manner, creating conductive or etched channels that remain
open when the fracture closes.
Hydraulic
• Base fluid (Water, Oil or Foam) is injected with proppant to
Fracturing fracture the formation and keep it open after pumping stops.
(Sandstones)
CBM ASSET, BOKARO
Blender
Hydraulic fracturing
Pumps
Pad fluid • Creation of highly conductive
path in the reservoir
Sand slurry Well • Fracture connects far reservoir
with wellbore
Displacing fluid • Allows untapped hydrocarbon
to flow into the well
50-1000ft Propped Frac
Shale
Reservoir
Shale
CBM ASSET, BOKARO
Hydraulic Fracture Growth
1 - Fracture initiation as pumping of fluid is
Time
started
during 2 - Fracture propagation with fluid
fracture
treatment 3 – Proppant (usually sand) enters
hydraulic fracture as it is suspended in
the fracturing fluid
4 - Proppant advances further into the
fracture as pumping continues
5 – Proppant advances further in the
fracture and may reach the tip of the
hydraulic fracture as fluid continues to
leak into the permeable formation
6 – Pumping of the fluid/proppant mixture
is stopped and fluid continues to leak
away into the permeable formation
7 – Formation closes on proppant and a
conductive path remains in the reservoir
CBM ASSET, BOKARO
Fracturing Fluid
Objective
• Provides hydraulic energy to
– Initiate a fracture
– Propagate or extend the fracture
• Transports propping agent to the fracture
• Needs to be flowed out of well after treatment
Desired Properties
• Sufficient viscosity
• Low friction and fluid loss
• Clean breaking
CBM ASSET, BOKARO
Types of fracturing fluid
• Most commonly used
Water Based • Ease of handling, inexpensive, less risk
• Used where water base fluid creates problems
Oil Based • Diesel, Condensate
• Clean fluid with better flowback properties
Foam Based • CO2 , N2 types
CBM ASSET, BOKARO
Fluid Additives
Crosslinker
Gelling Agent Clay Stabilizers
(Borax)
(Guar) (Kcl)
Surfactant/Non Buffering Agent
Emulsifier Water Based Fluid (Acetic Acid ,Soda
Ash)
Breakers Bactericide
(APS,TEA) (Formaldehyde)
CBM ASSET, BOKARO
Proppant
•Keeps the created fracture open (propping)
•Provides a highly conductive path from reservoir to wellbore
•Types of Proppants
Low Strength proppant
Medium strength proppant
High Strength proppant
CBM ASSET, BOKARO
v
Coiled Tubing
CBM ASSET, BOKARO
Coiled Tubing Components
CBM ASSET, BOKARO
Coiled Tubing Reel
CBM ASSET, BOKARO
Power Pack
•A power pack unit
provides hydraulic power
to control and operate a
coiled tubing unit and
pressure control
equipment. Generally, the
power pack units have an
independent electric or
diesel power source
which is designed to
operate in Zone 1 and
Zone 2 areas.
CBM ASSET, BOKARO
Injector Head
The injector assembly is designed to
perform three basic functions:
•Provide the thrust required to snub
the tubing into the well against
surface pressure and/or to overcome
wellbore friction forces.
•Control the rate of lowering the
tubing into the well under various well
conditions.
•Support the full weight of the tubing
and accelerate it to operating speed
when extracting it from the well.
CBM ASSET, BOKARO
Pressure Control Equipment
Primary Control
A primary barrier is an initial barrier for pressure containment
which is normally closed.
Stripper/Packer
•Stripper/packer is a primary barrier in a coiled
tubing unit
•Stripper is designed to provide a pressure seal
around a coiled tubing unit when it is being
run into or pulled out of a live well.
CBM ASSET, BOKARO
Pressure Control Equipment
Primary Control
A primary barrier is an initial barrier for pressure containment
which is normally closed.
Stripper/Packer
•Stripper/packer is a primary barrier in a coiled
tubing unit
•Stripper is designed to provide a pressure seal
around a coiled tubing unit when it is being
run into or pulled out of a live well.
CBM ASSET, BOKARO
Pressure Control Equipment
Secondary Barrier
A secondary barrier is a mechanical normally open system and it is used
when the primary barrier fails or becomes impaired.
Tertiary Barrier
A tertiary barrier is a mechanical normally open system and it will be
used when a primary and a secondary barrier fails and the well integrity is
badly impaired.
CBM ASSET, BOKARO
Blowout Preventer
1-Blind ram - seals the wellbore
when the CT is out of the BOP
2- Shear ram - cuts the CT
3- Slip ram - supports the weight of
CT hanging below it (some are
bidirectional and prevent the CT
from moving upward)
4- Pipe ram - seals around the
hanging CT
CBM ASSET, BOKARO
Sand Jet perforation
&
Hydro-fracturing through
CTU
CBM ASSET, BOKARO
Sand Jetting Process
CBM ASSET, BOKARO
Sand Jetting Process
CBM ASSET, BOKARO
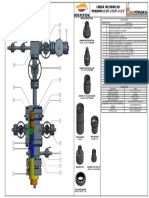
Location Layout
CBM ASSET, BOKARO
Safety Considerations
CBM ASSET, BOKARO
Personal Protective Equipments
CBM ASSET, BOKARO
Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS)
Purpose:
“…ensure that employers and employees
know about work hazards and how to
protect themselves so that the incidence of
illnesses and injuries due to hazardous
chemicals is reduced.”
CBM ASSET, BOKARO
Definitions/Terminologies
•Flammable: ANY substance easily ignited and quick burning, including liquids with a flash point below 95
degrees Fahrenheit.
•Flash point--the lowest temperature at which a liquid produces enough vapor to ignite.
•Density--(% of Water & Air); Specific Gravity
•Toxic: ANY substance (alone or via chemical reaction) able to cause harm/produce injury to the body
through absorption, ingestion, inhalation, or injection.
•Caustic: ANY substance able to burn, damage or destroy organic tissue by chemical reaction; Corrosive.
•Acute: rapid effects, as a result of short-term exposures, of short duration
CBM ASSET, BOKARO
Definitions/Terminologies
•Chronic: effects as a result of long-term exposure, of long duration
•Corrosive: Visible destruction or irreversible damage to body tissue, including acids and caustics (bases)
•PEL–-Permissible Exposure Limit is the standard recognized by industry as the maximum amount or
concentration of a chemical that a worker may be exposed to.
•TLV—Threshold Limit Value is a recommended limit for chemical substance exposures, similar to the PEL
but most often more restrictive than the PEL.
•TWA–-an 8-hour Time-Weighted Average is the concentration the average worker can be exposed during
an 8-hour workday, day after day, without harmful effects.
•STEL— “Short Term Exposure Limit” is a 15 minute period.
•Ceiling—the maximum (C) concentration never to be exceeded.
CBM ASSET, BOKARO
Definitions/Terminologies
•Lethal Dose50 (LD50) is the amount of a material, given all at once,
which causes the death of 50% (one half) of a group of test animals.
The LD50 is one way to measure the short-term poisoning potential
(acute toxicity) of a material.
•Lethal Concentration50 (LC50) is the amount of a substance in air that,
when given by inhalation over a specified period of time, is expected
to cause the death in 50% of a defined animal population.
CBM ASSET, BOKARO
Hazardous Symbol Details
National Fire Protection
Association (NFPA)
creates and maintains private, copyrighted
standards and codes for describing health
hazard, flammability, stability and
specific hazard of any materials by the
specific color code and rating.
CBM ASSET, BOKARO
What do MSDSs contain?
Section 1: Chemical Product and Company Identification
• The chemical name, trade name and manufacturers name
• Chemical Formula
Section 2: Composition and Information on Ingredients
• Includes: substance,
• % content,
• CAS Number, Classification
Section 3: Hazards Identification
• Dangers for humans and the environment such as:
potential acute & chronic health effects
CBM ASSET, BOKARO
What do MSDSs contain?
Section 4: First Aid Measures
• gives instructions on what to do in case of eye contact
• skin contact, inhalation or ingestion
Section 5: Fire and Explosion Data
• Suitable extinguishing media
• Special hazards in fire
• Special Remarks on Explosion Hazards
Section 6: Accidental Release Measures
• Environmental precautions,
• Methods for cleaning
Section 7: Handling and Storage
• Storing temperature & environment
CBM ASSET, BOKARO
What do MSDSs contain?
Section 8: Exposure Controls/Personal Protection
• Provide exhaust ventilation eyewash stations
• Detailed concentrations of vapors of TLV
• Personal Protection: goggles, Synthetic apron,
• Vapor respirator, Gloves (impervious).
Section 9: Physical and Chemical Properties
• Appearance, Odor, pH
• Boiling point, Melting point,Flashpoint,
• Explosive properties, Viscosity
• Vapor pressure, Relative density, Solubility
Section 10: Stability and Reactivity Data
• Conditions to avoid, Hazardous decomposition products
• Incompatibility with various substances
• Corrosivity
CBM ASSET, BOKARO
What do MSDSs contain?
Section 11: Toxicological Information
• Acute toxicity, Local effects.
• Excessive exposure may affect to Skin contact,
Eye contact, Inhalation/ingestion.
Section 12: Ecological Information
• Lists any dangers to the environment
• Biodegrades
Section 13: Disposal Considerations
• Rinse out containers
• Don’t allow to enter drains
• Dispose of according to local regulations
• Do not mix with other waste
CBM ASSET, BOKARO
What do MSDSs contain?
Section 14: Transport Information
• special consideration for transport will be detailed
Section 15: Other Regulatory Information
• Lists any agency that may regulate this product
Section 16: Other Information
• Recommendations/restrictions,
Sources of key data used to compile
Safety Data Sheet
CBM ASSET, BOKARO
MSDS of Acetic Acid
Section Details
1 Identification: Acetic acid, CH3COOH
2 Composition/Information Ingredients: 100% by Wt, CAS no: 64-19-7
3 Hazard(s) Identification: Irritant to eye and skin, very hazardous on inhalation/ingestion
4 First-Aid Measures: Wash with plenty cold water
5 Fire-Fighting Measures: Flammable and use DCP type extinguisher.
6 Accidental Release Measures: Dilute with water or absorb with inert material
7 Handling and Storage: Keep in cool and away from heat.
8 Exposure Controls/Personal Protective Equipment: Use in ventilated atmosphere, use goggles, synthetic
apron, vapor respirator, impervious gloves.
9 Physical and Chemical Properties: liquid, pungent odor, soluble in water.
10 Stability and Reactivity: Stable, corrosive and violently react with base, oxidizer.
11 Toxicological Information: No mutagenic affect,
12 Ecological Information (non-mandatory): No Short term degradation product, may belong term
13 Disposal Considerations (non-mandatory): Will be disposed as per the environmental regulation.
14 Transportation Information (non-mandatory): Not available
15 Regulatory Information (non-mandatory): Health hazard of 3, combustible liquid.
16 Other Information: References: ScienceLab.com.
CBM ASSET, BOKARO
JOB SAFETY ANALYSIS
• All the personnel involved in the job are wearing safety kits?
• First Aid Box is available?
• The units are parked at a safe distance from the well (minimum distance > 15 m)?
• All the X’mas tree valves are functioning?
• All the nuts and bolts fitted and properly tightened on the X’mas tree
• Return line is provided to the waste pit from the well?
• Return line is properly anchored?
• Emergency vehicle is available at the site?
• Escape routes are decided and are clear from obstruction?
• Sufficient water is at the site for emergencies?
• Safety and operational meeting has been conducted for awareness of all safety and
operational aspect?
• All the hammer joints are properly tightened?
• Check valve and hammer valve (plug valve) are installed on the line?
• Line pressure tested before starting the job?
• Fire extinguishers are available?
• Pressure Safety Valve tested?
• Is MSDS and JSA should be present on site?
CBM ASSET, BOKARO
Tool Box Talks
• Welcome to this safety meeting at well____________. Thank you all for being in the safety dress. Anyone
not in the dress is requested to leave the meeting.
• This well has depth of ____________m and the expected pressures would be ____________psi
• The operations will start with line testing upto about 5000psi. Then we will have circulation of____bbl.
We will do minifrac job and then after _____ min, we will start the main frac. We will pump _______bbl
pad followed by sand stages starting at 0.5 ppg and gradually increasing upto ___ppg and lastly we will
pump the flush volume of ____bbl.
• Nobody will be near the pumping line and well during line testing and also the main job, when pumping is
going on.
• The job assignments will be like this:
• Mr. _______________________________________will be operating the blender.
• Mr. _______________________________________ will be on the frac tank.
• Mr. _______________________________________ will be on the frac van.
• Mr. _______________________________________ will be operating the sand dumpers.
• Mr. _______________________________________ will be at ground for tanks valve operations.
• Mr. _______________________________________ will be operating the Acid pumper.
• Mr. _______________________________________ will be in the frac van/blender and will be
responsible for instrumentation and control system smooth functioning.
CBM ASSET, BOKARO
THANK YOU
CBM ASSET, BOKARO
You might also like
- Hydrocarbon Fluid Inclusions in Petroliferous BasinsFrom EverandHydrocarbon Fluid Inclusions in Petroliferous BasinsNo ratings yet
- Depositional History of Franchthi Cave: Stratigraphy, Sedimentology, and Chronology, Fascicle 12From EverandDepositional History of Franchthi Cave: Stratigraphy, Sedimentology, and Chronology, Fascicle 12No ratings yet
- Open Hole or Cased Hole: Wellbore and Producing Formation InterfaceDocument35 pagesOpen Hole or Cased Hole: Wellbore and Producing Formation Interfaceايمن القنونيNo ratings yet
- Cement LoggingDocument58 pagesCement Loggingahoua100% (1)
- Sand Control - Why and HowDocument45 pagesSand Control - Why and HowMahendra KumarNo ratings yet
- Well Stimulation IntroductionDocument15 pagesWell Stimulation IntroductionDinesh KanesanNo ratings yet
- Perforating Methods for Optimal ProductionDocument26 pagesPerforating Methods for Optimal ProductionSeymur AkbarovNo ratings yet
- Well Completion & Stimulation GuideDocument93 pagesWell Completion & Stimulation GuideGiang Nguyen NinhNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Fracturing Process ExplainedDocument4 pagesHydraulic Fracturing Process ExplainedMohammadFaisalQureshiNo ratings yet
- Spe Yp - Coiled Tubing OperationDocument29 pagesSpe Yp - Coiled Tubing Operationfashola adeyemiNo ratings yet
- Ask Echometer - Acoustic Techniques For Gaslift Wells - June 17 2020Document69 pagesAsk Echometer - Acoustic Techniques For Gaslift Wells - June 17 2020Ivan BuenaVibraNo ratings yet
- CT Fatigue ModificDocument24 pagesCT Fatigue Modificfrank vNo ratings yet
- Perforation Techniques for Maximizing Well ProductivityDocument21 pagesPerforation Techniques for Maximizing Well ProductivityDinesh KanesanNo ratings yet
- Yww7Pogiq - Understanding API 6a Gate ValvesDocument1 pageYww7Pogiq - Understanding API 6a Gate ValvesRuilin TanNo ratings yet
- Oilfield Compression 101Document49 pagesOilfield Compression 101Aizaz MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Saltel Expandable Steel Patch PsDocument1 pageSaltel Expandable Steel Patch PsrezaNo ratings yet
- Master of Petroleum Well Engineering - Casing DesignDocument92 pagesMaster of Petroleum Well Engineering - Casing DesignGFarizNo ratings yet
- Short Course Deliquification BasicsDocument95 pagesShort Course Deliquification BasicsKerron RekhaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Processes and Sustainability: PetroleumDocument32 pagesChemical Processes and Sustainability: PetroleumMohd Shahrul Nizam SallehNo ratings yet
- PerforationsDocument0 pagesPerforationsSikander MushtaqNo ratings yet
- Relay Digital Slickline SystemDocument7 pagesRelay Digital Slickline SystemRaed fouadNo ratings yet
- PDFDocument45 pagesPDFDaniel Dennis Escobar SubiranaNo ratings yet
- AcidizingDocument16 pagesAcidizingxion_mew20% (2)
- WST - Hydraulic Fracturing Part 1 - S12020 PDFDocument23 pagesWST - Hydraulic Fracturing Part 1 - S12020 PDFShadishwaren ParameswaranNo ratings yet
- Enm301 - Unit 1Document16 pagesEnm301 - Unit 1Lâm Tuyết NhiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Coiled Tubing: Module 00 - Day OneDocument7 pagesIntroduction To Coiled Tubing: Module 00 - Day OneFauzan Rahman HaqNo ratings yet
- Tubing PatcDocument2 pagesTubing PatcAminollah PayvandNo ratings yet
- As Built Abandonment SchematicDocument1 pageAs Built Abandonment SchematicMarkus LandingtonNo ratings yet
- Causes of Kicks - Tripping: - Failure To Keep The Hole FullDocument41 pagesCauses of Kicks - Tripping: - Failure To Keep The Hole FullShourovjossNo ratings yet
- X-Tree & WellheadDocument35 pagesX-Tree & WellheadSaqib ShahabNo ratings yet
- Artificial Lift Selection for Optimum Reservoir EfficiencyDocument15 pagesArtificial Lift Selection for Optimum Reservoir Efficiencyمحمد المحموديNo ratings yet
- 4 - Multilateral Well DrillingDocument27 pages4 - Multilateral Well DrillingAli AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic FracturingDocument2 pagesHydraulic FracturingJeff LewisNo ratings yet
- Coiltools Dimple Connector PsDocument2 pagesCoiltools Dimple Connector PsCARLOSELSOARESNo ratings yet
- 23 - Carbonate - LabDocument14 pages23 - Carbonate - LabnaiouamNo ratings yet
- Fracture Acidizing: Mechanisms, Design Considerations, and Conductivity EnhancementDocument21 pagesFracture Acidizing: Mechanisms, Design Considerations, and Conductivity EnhancementShahin KhanNo ratings yet
- What Is LNGDocument4 pagesWhat Is LNGsekarsanthanamNo ratings yet
- Kadanwari Well Integrity ProgramDocument28 pagesKadanwari Well Integrity ProgramsalmanNo ratings yet
- Unconventional Hydrocarbon Energy Resources and Hydraulic FracturingDocument8 pagesUnconventional Hydrocarbon Energy Resources and Hydraulic FracturingYash GyanchandaniNo ratings yet
- Carbon Capture & StorageDocument2 pagesCarbon Capture & Storagevelmurugan00000No ratings yet
- Electrical Submersible Pumping (ESP) System Fundamentals: Dr. M. GhareebDocument25 pagesElectrical Submersible Pumping (ESP) System Fundamentals: Dr. M. Ghareebramzi aidliNo ratings yet
- Current Status of CFD Modeling of Liquid Loading Phenomena in Gas Wells: A Literature ReviewDocument15 pagesCurrent Status of CFD Modeling of Liquid Loading Phenomena in Gas Wells: A Literature ReviewAdazeNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Casing: Understanding Casing Strings and Their ImportanceDocument26 pagesIntroduction to Casing: Understanding Casing Strings and Their ImportanceAjay SinghNo ratings yet
- Mud Training SchoolDocument78 pagesMud Training School叶芊No ratings yet
- 03 CT WellControlEquip NEXTDocument19 pages03 CT WellControlEquip NEXTFauzan Rahman HaqNo ratings yet
- Introducing Drilling Fluids Components and ClassificationsDocument25 pagesIntroducing Drilling Fluids Components and ClassificationsyasirismNo ratings yet
- Cabezal Multibowl Bes PROGRAMA 13 3/8" X 9 5/8" X 4 1/2": Instalations ToolsDocument1 pageCabezal Multibowl Bes PROGRAMA 13 3/8" X 9 5/8" X 4 1/2": Instalations ToolsJonathan AguirreNo ratings yet
- Oilfield NGL Liquid HandlingDocument21 pagesOilfield NGL Liquid HandlingDouglas ColemanNo ratings yet
- 01 Why Do We Need Artificial LiftDocument57 pages01 Why Do We Need Artificial Lifttaufiq01No ratings yet
- Graficas de PerforacionDocument6 pagesGraficas de PerforacionCatalina FloresNo ratings yet
- Introduction of Well ProblemsDocument50 pagesIntroduction of Well ProblemsRay YudaNo ratings yet
- Wireline ToolstringDocument1 pageWireline ToolstringJohnNo ratings yet
- 03 - Skin Factor and Wellbore StorageDocument39 pages03 - Skin Factor and Wellbore Storageاحمد محمد عليNo ratings yet
- EOR Methods GuideDocument109 pagesEOR Methods GuideKarwan DilmanyNo ratings yet
- PCP AE1 - DAY 1.1 Introduction To PCP System and ComponentsDocument66 pagesPCP AE1 - DAY 1.1 Introduction To PCP System and ComponentsCristhian LópezNo ratings yet
- 3-4-1-2935 0791 31 - L - tcm795-1697585Document2 pages3-4-1-2935 0791 31 - L - tcm795-1697585Y.EbadiNo ratings yet
- Digital Trigger: Safe, On-Demand, Efficient and Recordable Perforating On SlicklineDocument32 pagesDigital Trigger: Safe, On-Demand, Efficient and Recordable Perforating On SlicklineBizhar.No ratings yet
- WirelineDocument34 pagesWirelineBoedi SyafiqNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic FracturingDocument31 pagesHydraulic FracturingDeepesh KhandelwalNo ratings yet
- Phulpur (Uttar Pradesh) : IFFCO Production UnitsDocument6 pagesPhulpur (Uttar Pradesh) : IFFCO Production UnitsVinal KumarNo ratings yet
- Spot Your Train: Download NTES Mobile Apps For Android, iOS and Windows MobilesDocument2 pagesSpot Your Train: Download NTES Mobile Apps For Android, iOS and Windows MobilesVinal KumarNo ratings yet
- Online QR Code Scanner & QR Code Reader - QR StuffDocument6 pagesOnline QR Code Scanner & QR Code Reader - QR StuffVinal KumarNo ratings yet
- Fertilizer Production Unit Phulpur, Allahabad - IFFCODocument6 pagesFertilizer Production Unit Phulpur, Allahabad - IFFCOVinal KumarNo ratings yet
- Upload 5 Documents To Download: Summer Internship Report (IFFCO)Document2 pagesUpload 5 Documents To Download: Summer Internship Report (IFFCO)Vinal KumarNo ratings yet
- Astronomy-Online VersionDocument150 pagesAstronomy-Online VersionAditya Pratap SinghNo ratings yet
- Recommended List of Suggested Books: AicteDocument49 pagesRecommended List of Suggested Books: AicteVinal KumarNo ratings yet
- Mini Project Vinal 2Document1 pageMini Project Vinal 2Vinal KumarNo ratings yet
- Summer Training Project Report: Your Document Was Successfully Uploaded!Document2 pagesSummer Training Project Report: Your Document Was Successfully Uploaded!Vinal KumarNo ratings yet
- S7300A Brochure ASIA Vol2Document2 pagesS7300A Brochure ASIA Vol2Vinal KumarNo ratings yet
- Printed Pages-4: Optical Fiber Basics & Holography PrinciplesDocument4 pagesPrinted Pages-4: Optical Fiber Basics & Holography PrinciplesVinal KumarNo ratings yet
- NOC Format Charpak LabDocument1 pageNOC Format Charpak LabVinal KumarNo ratings yet
- Jee Advanced PaperDocument17 pagesJee Advanced PaperAbhishek ThawaitNo ratings yet
- Printed Pages-4: Optical Fiber Basics & Holography PrinciplesDocument4 pagesPrinted Pages-4: Optical Fiber Basics & Holography PrinciplesVinal KumarNo ratings yet
- MOOCS Courses For B.tech. AICTE Model CurriculumDocument1 pageMOOCS Courses For B.tech. AICTE Model CurriculumNishant MishraNo ratings yet
- Developing Soft SkillsDocument17 pagesDeveloping Soft SkillsShíkhár ShármãNo ratings yet
- Zinc Catalyzed Easter Bond CleavageDocument16 pagesZinc Catalyzed Easter Bond CleavagerubikaNo ratings yet
- HVOF CoatingDocument3 pagesHVOF CoatingsumohiNo ratings yet
- Germiston / Palm Ridge Load Shedding Schedule and Affected AreasDocument1 pageGermiston / Palm Ridge Load Shedding Schedule and Affected AreasLungisani Dauglas MtshaliNo ratings yet
- Gce O-Level Preliminary Examination 2018: Ahmad Ibrahim Secondary SchoolDocument107 pagesGce O-Level Preliminary Examination 2018: Ahmad Ibrahim Secondary SchoolNamarr SinghNo ratings yet
- Mohammad Abdul Aziz Bin Jamil EC16034 - Muhammad Haris Din Bin Rose Azman EC16036 - Muhammad Syafiq Bin Zakaria EC16064Document16 pagesMohammad Abdul Aziz Bin Jamil EC16034 - Muhammad Haris Din Bin Rose Azman EC16036 - Muhammad Syafiq Bin Zakaria EC16064Abdul AzizNo ratings yet
- College Physics, 9th Ed.-188-200Document13 pagesCollege Physics, 9th Ed.-188-200Dave ImmanuelNo ratings yet
- The Wall Street Journal - 31.01.23Document26 pagesThe Wall Street Journal - 31.01.23MarioNo ratings yet
- Intelligent Load SheddingDocument22 pagesIntelligent Load SheddingNikhil Jagirdar50% (2)
- Biological Nutrient RemovalDocument42 pagesBiological Nutrient RemovalGökhan TurhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Principles of Electromechanical Energy ConversionDocument22 pagesChapter 2 - Principles of Electromechanical Energy Conversionchibssa alemayehuNo ratings yet
- Ingles Teca Punt EsDocument17 pagesIngles Teca Punt EspatNo ratings yet
- Yanmar MOTOR L48N-DDocument15 pagesYanmar MOTOR L48N-DAndre FilipeNo ratings yet
- Hamworthy Topping Up GeneratorDocument2 pagesHamworthy Topping Up GeneratorHARISHNo ratings yet
- Benefits of Variable Speed Drives in Sugar Production: White PaperDocument12 pagesBenefits of Variable Speed Drives in Sugar Production: White PaperMashudi FikriNo ratings yet
- Physics 207 Lecture 22: Ideal Fluid Flow, Bernoulli's PrincipleDocument13 pagesPhysics 207 Lecture 22: Ideal Fluid Flow, Bernoulli's PrincipleAdithyaNo ratings yet
- Place, Space, and Theories of Economic ValueDocument19 pagesPlace, Space, and Theories of Economic ValueMatt TenneyNo ratings yet
- Flange Insulating Gasket Kits: Advance Products & SystemsDocument8 pagesFlange Insulating Gasket Kits: Advance Products & SystemsJF ZLNo ratings yet
- No Load Characteristic of DC Motors: ObjectivesDocument4 pagesNo Load Characteristic of DC Motors: ObjectivesYasser MohammedNo ratings yet
- Reaction 1Document64 pagesReaction 1Tysir Sarhan80% (5)
- STrait Line Stud Finder ManualDocument1 pageSTrait Line Stud Finder ManualRob BrewsterNo ratings yet
- Ms Meganorm A2742 8e 3 PDFDocument19 pagesMs Meganorm A2742 8e 3 PDFiamsam869No ratings yet
- Worthington Blocair BL - BH - BK - enDocument8 pagesWorthington Blocair BL - BH - BK - enandigil2No ratings yet
- Documentación Ziel 400w - Wall Washer 150w PDFDocument250 pagesDocumentación Ziel 400w - Wall Washer 150w PDFJonathanTenorio89No ratings yet
- CSWIP 2017) - Compressed-483-492Document10 pagesCSWIP 2017) - Compressed-483-492Tahar DabbarNo ratings yet
- Master Plumbing Reviewer 2Document24 pagesMaster Plumbing Reviewer 2mcpayodNo ratings yet
- Kimpton Hotel Case - Group 4Document21 pagesKimpton Hotel Case - Group 4Saurabh PaliwalNo ratings yet
- Malaysia's first bioplastics pilot plant converts palm oil into biodegradable plasticDocument2 pagesMalaysia's first bioplastics pilot plant converts palm oil into biodegradable plasticMohamad DinNo ratings yet
- Unit 420, One Oasis Condominium,: Ortigas, Pasig City 1608 Tel. No. (02) 941-1408, 0995-7561767Document6 pagesUnit 420, One Oasis Condominium,: Ortigas, Pasig City 1608 Tel. No. (02) 941-1408, 0995-7561767Jasper AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Notes for First Year Improvement ExamDocument35 pagesChemistry Notes for First Year Improvement ExamAnantha KrishnaNo ratings yet
- CMT Welding: Spatter-Free MIG/MAG for Thin SheetsDocument8 pagesCMT Welding: Spatter-Free MIG/MAG for Thin SheetsFlorin GadeaNo ratings yet