Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Carbon Capture & Storage
Uploaded by
velmurugan00000Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Carbon Capture & Storage
Uploaded by
velmurugan00000Copyright:
Available Formats
Carbon Capture & Storage
Geological Storage Options for CO2
Carbon capture and storage (CCS) technologies allow emissions of carbon dioxide to be 'captured' and 'stored' preventing them from entering the atmosphere. CCS presents one of the most promising options for large-scale reductions in CO2 emissions from energy use. CO2 capture is possible from fossil fuel power stations or from other large CO2 sources, such as the chemical, steel or cement industries or from natural gas production. CO2 can be stored in geological formations such as saline aquifers or expired oil and gas reservoirs. The technologies for geological CCS are all proven and there are a number of large-scale CCS projects in operation today. Current projects include:
Sleipner in Norway Weyburn in Canada In Salah in Algeria
An interactive map of CO2 Storage projects worldwide can be viewed on the Scottish Centre for Carbon Storage website CCS has not yet been applied to large scale electricity generation, although a number of proposed projects will achieve this. Public policy intervention for CCS demonstration is required in the form of additional financing mechanisms for CCS to existing market mechanisms. The benefits from CCS demonstration projects accrue to the whole of society in the form of lower stabilisation costs and not the early movers due to significant 'spill-over' effects. One possible incentive currently under debate is whether CCS projects should be included under the
Kyoto Protocol's Clean Development Mechanism (CDM). The World Coal Institute believes the information is available now to permit CCS to be included under the CDM. A decision on this will be made at the next climate change summit in Poland at the end of this year.
You might also like
- What Is LNGDocument4 pagesWhat Is LNGsekarsanthanamNo ratings yet
- Oil and Gas Pricing 2007 en PDFDocument241 pagesOil and Gas Pricing 2007 en PDFDinesh KanesanNo ratings yet
- Oilfield NGL Liquid HandlingDocument21 pagesOilfield NGL Liquid HandlingDouglas ColemanNo ratings yet
- Polyflow ExPERT Ecuador PresentationDocument29 pagesPolyflow ExPERT Ecuador PresentationRené Luis Perez MagneNo ratings yet
- Project Integration ManagementDocument66 pagesProject Integration ManagementSadiaNo ratings yet
- Enm301 - Unit 1Document16 pagesEnm301 - Unit 1Lâm Tuyết NhiNo ratings yet
- Optimize Chemical ProcessesDocument31 pagesOptimize Chemical ProcessesThiênHiếuNo ratings yet
- Ask Echometer - Acoustic Techniques For Gaslift Wells - June 17 2020Document69 pagesAsk Echometer - Acoustic Techniques For Gaslift Wells - June 17 2020Ivan BuenaVibraNo ratings yet
- Yww7Pogiq - Understanding API 6a Gate ValvesDocument1 pageYww7Pogiq - Understanding API 6a Gate ValvesRuilin TanNo ratings yet
- Oilfield Compression 101Document49 pagesOilfield Compression 101Aizaz MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Correlaciones de GasDocument29 pagesCorrelaciones de GasKathlyn GarcíaNo ratings yet
- PMP 2Document30 pagesPMP 2Abdl Rahman GaberNo ratings yet
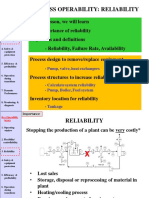
- Process Operability - ReliabilityDocument39 pagesProcess Operability - ReliabilityshakerNo ratings yet
- Perforating Methods for Optimal ProductionDocument26 pagesPerforating Methods for Optimal ProductionSeymur AkbarovNo ratings yet
- 110-Nb1 Anton Marco Fantolini SaipemDocument21 pages110-Nb1 Anton Marco Fantolini SaipemrajachemNo ratings yet
- Spe 196248 MS PDFDocument31 pagesSpe 196248 MS PDFdwidwi novryNo ratings yet
- True Vapour PressureDocument4 pagesTrue Vapour PressureTheyvan T-vanNo ratings yet
- Chemical Processes and Sustainability: PetroleumDocument32 pagesChemical Processes and Sustainability: PetroleumMohd Shahrul Nizam SallehNo ratings yet
- Wireline ToolstringDocument1 pageWireline ToolstringJohnNo ratings yet
- Refigeration KBu Sept 20Document85 pagesRefigeration KBu Sept 20ManeeshNo ratings yet
- UPGA3033: Process Optimization and SimulationDocument55 pagesUPGA3033: Process Optimization and SimulationTko Kai OnnNo ratings yet
- Liquefied Natural Gas PDFDocument16 pagesLiquefied Natural Gas PDFwasita wadariNo ratings yet
- 2012 Mar Natural Gas Facts FiguresDocument98 pages2012 Mar Natural Gas Facts FiguresChristopher Hampton100% (1)
- Pipelines: Liquid or Gas Lines Above Ground or Below Ground Trunk Line or Gathering LineDocument27 pagesPipelines: Liquid or Gas Lines Above Ground or Below Ground Trunk Line or Gathering LineKalaniNo ratings yet
- Sand Control - Why and HowDocument45 pagesSand Control - Why and HowMahendra KumarNo ratings yet
- The Essential of Gas Lift Technologies - Part One 00Document126 pagesThe Essential of Gas Lift Technologies - Part One 00Giuseppe MoriccaNo ratings yet
- Cabezal Multibowl Bes PROGRAMA 13 3/8" X 9 5/8" X 4 1/2": Instalations ToolsDocument1 pageCabezal Multibowl Bes PROGRAMA 13 3/8" X 9 5/8" X 4 1/2": Instalations ToolsJonathan AguirreNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Fracturing Process ExplainedDocument4 pagesHydraulic Fracturing Process ExplainedMohammadFaisalQureshiNo ratings yet
- Well Stimulation-Mine VocationalDocument40 pagesWell Stimulation-Mine VocationalVinal KumarNo ratings yet
- 2 BV PresentationDocument10 pages2 BV PresentationKaran DoshiNo ratings yet
- Relay Digital Slickline SystemDocument7 pagesRelay Digital Slickline SystemRaed fouadNo ratings yet
- Open Hole or Cased Hole: Wellbore and Producing Formation InterfaceDocument35 pagesOpen Hole or Cased Hole: Wellbore and Producing Formation Interfaceايمن القنونيNo ratings yet
- Wet Crude ProcessingDocument39 pagesWet Crude ProcessingMohanad HussienNo ratings yet
- Compressors: Presented By: Andrith Fabian Güiza Zambrano 2134124 Presented To: Ing. Nicolas Santos SantosDocument50 pagesCompressors: Presented By: Andrith Fabian Güiza Zambrano 2134124 Presented To: Ing. Nicolas Santos SantosbrandonNo ratings yet
- 5 LNGDocument32 pages5 LNGOliverTumbayNo ratings yet
- Artificial Lift SelectionDocument15 pagesArtificial Lift SelectionFarid AliyevNo ratings yet
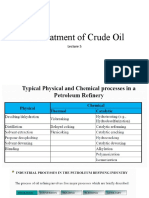
- Pre-Treatment of Crude OilDocument25 pagesPre-Treatment of Crude OilAbhisek AgarwalNo ratings yet
- To NitrogenDocument54 pagesTo Nitrogenbedoo54No ratings yet
- Griffin LanzaTech - 20 July 2011 MASDocument17 pagesGriffin LanzaTech - 20 July 2011 MASNitin ThakurNo ratings yet
- Current Status of CFD Modeling of Liquid Loading Phenomena in Gas Wells: A Literature ReviewDocument15 pagesCurrent Status of CFD Modeling of Liquid Loading Phenomena in Gas Wells: A Literature ReviewAdazeNo ratings yet
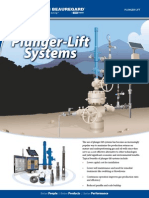
- Plunger Lift BrochureDocument4 pagesPlunger Lift BrochureCluis KeNo ratings yet
- Ammonia Equvments DrawingDocument43 pagesAmmonia Equvments DrawingSaad KhanNo ratings yet
- Day2 2 PINKS PDFDocument30 pagesDay2 2 PINKS PDFPeng TerNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer Fundamentals - 19th JuneDocument75 pagesHeat Transfer Fundamentals - 19th JuneVivek RathodNo ratings yet
- CDU - SlideDocument23 pagesCDU - SlideVăn Bão TôNo ratings yet
- SoluForce Corporate Brochure 2014 06Document15 pagesSoluForce Corporate Brochure 2014 06René Luis Perez MagneNo ratings yet
- DEEPWATER GAS CHALLENGESDocument31 pagesDEEPWATER GAS CHALLENGES1mmahoneyNo ratings yet
- Crude Oil ProcessingDocument58 pagesCrude Oil ProcessingOmariNo ratings yet
- Week 2 Reservoir DeliverabilityDocument43 pagesWeek 2 Reservoir Deliverabilitydaffa teguhNo ratings yet
- 2007 12 17 Egypt Presentation enDocument29 pages2007 12 17 Egypt Presentation entarekeeeNo ratings yet
- Introduction of Well Problems-2Document32 pagesIntroduction of Well Problems-2ROY HANAFI HARAHAPNo ratings yet
- Energy Efficient System for Continuous Production of Fuels and Energy from SyngasDocument14 pagesEnergy Efficient System for Continuous Production of Fuels and Energy from SyngasKeysler PonceNo ratings yet
- NBC-1 Conceptual Well DesignDocument14 pagesNBC-1 Conceptual Well DesignMulyono BanuNo ratings yet
- 17.0 Lec 8membran BioseprationDocument19 pages17.0 Lec 8membran BioseprationChan Chun ChenNo ratings yet
- Presentation on Small Scale LNG: PLL's Targets and ActivitiesDocument36 pagesPresentation on Small Scale LNG: PLL's Targets and ActivitiesUJJWALNo ratings yet
- TEPI - VICO Capillary String WorkshopDocument21 pagesTEPI - VICO Capillary String WorkshopArief FatharoniNo ratings yet
- Ccs Workshop ReportDocument20 pagesCcs Workshop ReportwastequestNo ratings yet
- ccs-_upstreams_commercial_conundrum_Document14 pagesccs-_upstreams_commercial_conundrum_JarodNo ratings yet
- Carbon Capture and Storage: Status of CCS DevelopmentDocument3 pagesCarbon Capture and Storage: Status of CCS DevelopmentAngela MitroiNo ratings yet
- Carbon Capture and Storage SeminarDocument27 pagesCarbon Capture and Storage SeminarSafalsha BabuNo ratings yet
- Exergy or AvailabilityDocument25 pagesExergy or Availabilityvelmurugan00000No ratings yet
- Work and Energy Fundamentals ExplainedDocument6 pagesWork and Energy Fundamentals ExplainedVel MuruganNo ratings yet
- Copper CorrosionDocument9 pagesCopper Corrosionvelmurugan00000No ratings yet
- Steam PurityDocument14 pagesSteam PurityVel MuruganNo ratings yet
- Boiler Water SystemDocument82 pagesBoiler Water Systemvelmurugan00000No ratings yet
- Air Fuel RatioDocument5 pagesAir Fuel Ratiovelmurugan00000No ratings yet
- Coal and The EnvironmentDocument2 pagesCoal and The Environmentvelmurugan00000No ratings yet
- Air Dispersion Modeling Conversions and FormulasDocument16 pagesAir Dispersion Modeling Conversions and Formulasvelmurugan00000No ratings yet
- Carbon Capture & StorageDocument2 pagesCarbon Capture & Storagevelmurugan00000No ratings yet
- Bottom Ash: Coal Furnace Byproduct Used in ConstructionDocument1 pageBottom Ash: Coal Furnace Byproduct Used in Constructionvelmurugan00000No ratings yet
- Air Fuel RatioDocument5 pagesAir Fuel Ratiovelmurugan00000No ratings yet
- Air Fuel RatioDocument5 pagesAir Fuel Ratiovelmurugan00000No ratings yet
- Bottom Ash: Coal Furnace Byproduct Used in ConstructionDocument1 pageBottom Ash: Coal Furnace Byproduct Used in Constructionvelmurugan00000No ratings yet
- Bottom Ash: Coal Furnace Byproduct Used in ConstructionDocument1 pageBottom Ash: Coal Furnace Byproduct Used in Constructionvelmurugan00000No ratings yet
- Ash Chemistry (% Ash) : Fuel Name Sio2 Al2O3 Fe2O3 Tio2 Cao Mgo Na2O K2O So3 P2O5 CLDocument1 pageAsh Chemistry (% Ash) : Fuel Name Sio2 Al2O3 Fe2O3 Tio2 Cao Mgo Na2O K2O So3 P2O5 CLvelmurugan00000No ratings yet
- Ash Chemistry (% Ash) : Fuel Name Sio2 Al2O3 Fe2O3 Tio2 Cao Mgo Na2O K2O So3 P2O5 CLDocument1 pageAsh Chemistry (% Ash) : Fuel Name Sio2 Al2O3 Fe2O3 Tio2 Cao Mgo Na2O K2O So3 P2O5 CLvelmurugan00000No ratings yet
- Coal AssayDocument5 pagesCoal Assayvelmurugan00000No ratings yet