Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Merchant Banking: A Concise History and Overview
Uploaded by
nishant haweliaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Merchant Banking: A Concise History and Overview
Uploaded by
nishant haweliaCopyright:
Available Formats
Merchant Banking
Scope
• Definition
• Origin of Merchant Banking Services in India
• Merchant banks and Commercial Banks Services Of Merchant Banks.
• Qualities required of Merchant Bankers.
Definition/ Meaning
• Merchant Banking involves all those professional skill based services
provided by merchant bankers such as issue management, loan services
underwriting services, fundraising project capital, international trade
services for large corporations for adequate consideration in the form of a
fee.
History-growth-changes in Merchant Banking In India
• Started in the year 1967 by Grindlay’s bank followed by CITI Bank in 1970
• SBI was the first Bank to set up a Merchant Banking division in 1972
followed by ICICI Bank in 1973 followed by other banks such as Canara
bank, bank of Baroda, Bank of India etc.
• Merchant bankers were initially corporate counsellors for restructuring
capital structure of companies, and witnessed a transition to issue and
underwriting services.
• A transition from issue management/underwriting to providing creative
credit products such as bridge financing, mezzanine financing, equity
financing, issuing letters of credit, and facilitating international fund transfer,
apart from other services.
Continuation
• FERA Regulations 1973 gave a boost to merchant banking In India, led to
increased participation of other developmental banks and financial
institutions.
• The buoyancy of the capital market in the 1980’s was the next driver of
Merchant banking services in India.
• Merchant Bankers roles changed drastically post economic globalisation,
Liberalization and Privatisation of 1991 and continues to change with the
changing needs of customers.
• There are currently 135 Merchant banks registered with SEBI.
Providers of Merchant Banking Services In India
• Commercial Banks and Subsidiaries- SBI capital markets ltd, IFCI financial services
ltd.
• Foreign banks –Goldman Sachs (India) securities pvt ltd, Morgan Stanley (india)
• All India Financial institutions and Developmental Banks such as ICICI, IDBI, IFCI.
• State level Financial Institutions such as State Industrial Development Corporations and
state Financial Corporations.
• Private financial consultancy firms and brokers such as J.M Financial and Investment
services, DSP financial Consultants etc.
• Technical consultancy services specializing in advisory component.
• Professional Merchant Banking Houses such as VMC project technologies.
Services provided And Functions Of Merchant bankers
• Marketing and Underwriting of New issue.
• Restructuring Strategies.
• Advisory services for raising funds.
• Project Promotion and Project Finance and project counselling(corporate
counselling services)
• Management of debt and equity offerings of companies
• Portfolio services and Insurance services .
• Venture capitalists for small high potential companies.
Functions of Merchant bankers.
• Syndication of Rupee Term loans.
• Dealership in government securities , bonds, and commercial papers of
companies.
• Handling government consent for industrial projects .
• Stock broking services
• Services to private sector units.
• Special assistance to small companies.
continuation
• Management of Interest and Dividend.
• Off shore financing
• Placement and distribution services.
Qualities of A Merchant banker
Formalities
There are four categories of Merchant bankers
• SEBI has specified norms that are to be complied by each of these
categories.
• Must obtain certificate of registration and fulfil two sets of norms
A) Operational capabilities
B) Capital Adequacy norms.
Personal qualities
a) Versatile knowledge
b) Integrity and Honesty
c) Requisite customer –banker relationship
d) Innovative Approach
Commercial Banking vs Merchant Banking
• Common man – corporate firms.
• Individuals can open a bank Account- cannot open a bank account.
• Deals with equity related capital whereas M- banking deals with debt
related financing.
• Higher Risk –Lower Risk.
• Management oriented – Asset oriented
• Capital restructuring, underwriting, portfolio management – role of
financers.
You might also like
- Final Merchant Banking in IndiaDocument15 pagesFinal Merchant Banking in IndiaSnehal Sambhaji AkhadeNo ratings yet
- Marketing of Consumer Financial Products: Insights From Service MarketingFrom EverandMarketing of Consumer Financial Products: Insights From Service MarketingNo ratings yet
- Module 3 2020Document68 pagesModule 3 2020Hariprasad bhatNo ratings yet
- Understanding Commerce: A High School Student’S CompanionFrom EverandUnderstanding Commerce: A High School Student’S CompanionNo ratings yet
- Merchant BankingDocument20 pagesMerchant BankingDileep SinghNo ratings yet
- Mastering Trade Lines "A Guide to Building Credit and Financial Success"From EverandMastering Trade Lines "A Guide to Building Credit and Financial Success"No ratings yet
- Merchant Banking Venture Capital: Kirana Store Kirana StoreDocument12 pagesMerchant Banking Venture Capital: Kirana Store Kirana StoreIshtiyaq AhmadNo ratings yet
- Merchant BankingDocument14 pagesMerchant Bankingamitmali.armNo ratings yet
- Merchant Banking Final 2Document29 pagesMerchant Banking Final 2ABYBP Batch 10No ratings yet
- MERCHANT BANKDocument5 pagesMERCHANT BANKSwaroop RajNo ratings yet
- Merchant Banking Functions and RegulationsDocument41 pagesMerchant Banking Functions and RegulationsPooja balwaniNo ratings yet
- Merchant Banking 35889Document19 pagesMerchant Banking 35889nfitnesshubNo ratings yet
- Merchant BankingDocument19 pagesMerchant BankingMiral PatelNo ratings yet
- M BankerDocument41 pagesM BankerNishi SinghNo ratings yet
- Merchant Banking 35889Document16 pagesMerchant Banking 35889Manish GargNo ratings yet
- Merchant BankingDocument53 pagesMerchant Bankingakash deepNo ratings yet
- Merchant BankingDocument25 pagesMerchant Bankingsshishirkumar50% (2)
- MBFS Unit 1Document22 pagesMBFS Unit 1Vimala Selvaraj VimalaNo ratings yet
- Merchant BankDocument50 pagesMerchant BankGOVIND JANGIDNo ratings yet
- Role of Commercial Banks in IndiaDocument24 pagesRole of Commercial Banks in IndiakanikaNo ratings yet
- Unit 7 Merchant BankingDocument14 pagesUnit 7 Merchant BankingSravani RajuNo ratings yet
- Origin of Merchant Banking in IndiaDocument3 pagesOrigin of Merchant Banking in IndiakisaspNo ratings yet
- Merchant Banking I M ComDocument18 pagesMerchant Banking I M Comselvam sNo ratings yet
- Merchant BankingDocument23 pagesMerchant Bankingmukeshdilse100% (1)
- CHP 1 - Introduction To Merchant BankingDocument44 pagesCHP 1 - Introduction To Merchant BankingFalguni MathewsNo ratings yet
- Merchant Banking and Non-Banking Finance CompaniesDocument19 pagesMerchant Banking and Non-Banking Finance CompaniesArunRGowdaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 FSM - 85456Document24 pagesChapter 2 FSM - 85456AmishaNo ratings yet
- Kokila Mani Vivek College of CommerceDocument54 pagesKokila Mani Vivek College of Commercekokilamani1191103No ratings yet
- Merchant Banks Vs Commercial BanksDocument57 pagesMerchant Banks Vs Commercial BanksLeo PaulNo ratings yet
- Session 7 - Investment BankingDocument43 pagesSession 7 - Investment BankingYogesh GovindNo ratings yet
- Merchant Banking FinalDocument20 pagesMerchant Banking FinalMiral PatelNo ratings yet
- 1.1.26.11.2012 Financial ServicesDocument329 pages1.1.26.11.2012 Financial ServicesfunshareNo ratings yet
- Merchant Banking: - 17 Century, Metamorphic ChangesDocument7 pagesMerchant Banking: - 17 Century, Metamorphic ChangesRajesh DassNo ratings yet
- Banking 130730020756 Phpapp02Document48 pagesBanking 130730020756 Phpapp02Vaibhav BairagiNo ratings yet
- 1.IFS and Functions of Merchant BankerDocument27 pages1.IFS and Functions of Merchant BankerDr.R.Umamaheswari MBANo ratings yet
- Merchant Banking: What Is It and What Do They DoDocument38 pagesMerchant Banking: What Is It and What Do They DoSmitha K BNo ratings yet
- Commercial Banking in IndiaDocument11 pagesCommercial Banking in IndiaTony SharmaNo ratings yet
- Merchant BankingDocument56 pagesMerchant BankingAkhil RajNo ratings yet
- Merchant BankingDocument55 pagesMerchant Bankingsuhaspatel84No ratings yet
- UNITIDocument60 pagesUNITIAmrendra KumarNo ratings yet
- Merchant Bank and Issue Management: January 2022Document24 pagesMerchant Bank and Issue Management: January 2022MD ARIFNo ratings yet
- Banking Regulation and Structure in IndiaDocument69 pagesBanking Regulation and Structure in IndiaShaifali ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Merchant BankingDocument22 pagesMerchant BankingJames RossNo ratings yet
- Merchant Banking vs. Investment BankingDocument12 pagesMerchant Banking vs. Investment BankingShweta SinghNo ratings yet
- Merchant BankingDocument29 pagesMerchant BankingramrattangNo ratings yet
- Unit 1.2Document7 pagesUnit 1.2demoid921No ratings yet
- Mrs Ekta Saraswat Assistant Professor (Finance) : Prepared byDocument69 pagesMrs Ekta Saraswat Assistant Professor (Finance) : Prepared byEkta Saraswat VigNo ratings yet
- Banking: Prepared by DR Deepak Tandon IMI New DelhiDocument118 pagesBanking: Prepared by DR Deepak Tandon IMI New Delhidev mhaispurkarNo ratings yet
- BankDocument62 pagesBankashishshuklaonlineNo ratings yet
- Banking Mob 1 PptDocument79 pagesBanking Mob 1 PptDeepak TandonNo ratings yet
- COMMERCIAL BANKING FUNCTIONS AND REFORMSDocument48 pagesCOMMERCIAL BANKING FUNCTIONS AND REFORMSharshadashitoleNo ratings yet
- Unit 1: Merchant Banking in India What Are Merchant Banks?Document4 pagesUnit 1: Merchant Banking in India What Are Merchant Banks?NidhiNo ratings yet
- Chapter-5 Merchant: BankingDocument29 pagesChapter-5 Merchant: BankingaswinecebeNo ratings yet
- INSTITUTE-University School of Business Department - ManagementDocument30 pagesINSTITUTE-University School of Business Department - ManagementAbhishek kumarNo ratings yet
- Banking - Retail - Global Industry PrimerDocument7 pagesBanking - Retail - Global Industry PrimerAnonymous NeRBrZyAUbNo ratings yet
- Ubfb3023 CBM Lecture 1Document70 pagesUbfb3023 CBM Lecture 1zijun 008 sawNo ratings yet
- Merchant BankingDocument4 pagesMerchant BankingSUNIL DUGANWANo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 IntroductionDocument25 pagesChapter 1 IntroductiondhitalkhushiNo ratings yet
- 1st-Merchant Banking 03Document10 pages1st-Merchant Banking 03jainnitinkumarNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3. 2 Grameen Bank PDFDocument24 pagesAssignment 3. 2 Grameen Bank PDFNatoy AbkilanNo ratings yet
- 1 MicrofinanceDocument30 pages1 Microfinancenishant haweliaNo ratings yet
- Ncene (Duicknper Opdalgain: Nis Hank Hauseua Seuicrs Alfealue LntuentDocument3 pagesNcene (Duicknper Opdalgain: Nis Hank Hauseua Seuicrs Alfealue Lntuentnishant haweliaNo ratings yet
- Use The Demand Curve Diagram Below To Answer The Following QuestionDocument6 pagesUse The Demand Curve Diagram Below To Answer The Following Questionnishant haweliaNo ratings yet
- International Introduction To Securities and Investment Ed11Document208 pagesInternational Introduction To Securities and Investment Ed11nishant haweliaNo ratings yet
- Price Elasticity ExplainationDocument3 pagesPrice Elasticity Explainationnishant haweliaNo ratings yet
- Supply Demand and Equilibrium Practice ProblemsDocument2 pagesSupply Demand and Equilibrium Practice ProblemsAashu Kedia0% (1)
- Global Securities OperationsDocument264 pagesGlobal Securities Operationsnishant hawelia100% (1)
- The Digitization of Just About Everything PDFDocument4 pagesThe Digitization of Just About Everything PDFSadia RahmanNo ratings yet
- Supply Demand EquilibriumDocument2 pagesSupply Demand Equilibriumnishant haweliaNo ratings yet
- INTRODUCTIONDocument62 pagesINTRODUCTIONnishant haweliaNo ratings yet
- India - Market Challenges: India Country Commercial GuideDocument5 pagesIndia - Market Challenges: India Country Commercial Guidenishant haweliaNo ratings yet
- Unit IV: Marketing Communication: Sandeep Kumar Singh, Assistant Professor, Dept. of Commerce, CHRIST UniversityDocument32 pagesUnit IV: Marketing Communication: Sandeep Kumar Singh, Assistant Professor, Dept. of Commerce, CHRIST Universitynishant haweliaNo ratings yet
- RBC Case Decision SheetDocument2 pagesRBC Case Decision Sheetnishant haweliaNo ratings yet
- Unit IV: Marketing Communication: Sandeep Kumar Singh, Assistant Professor, Dept. of Commerce, CHRIST UniversityDocument34 pagesUnit IV: Marketing Communication: Sandeep Kumar Singh, Assistant Professor, Dept. of Commerce, CHRIST Universitynishant haweliaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1: Sandeep Kumar Singh, Assistant Professor, Dept. of Commerce, CHRIST UniversityDocument40 pagesUnit 1: Sandeep Kumar Singh, Assistant Professor, Dept. of Commerce, CHRIST Universitynishant haweliaNo ratings yet
- Coh432 Marketing Managemt Unit 1 (Krishna)Document48 pagesCoh432 Marketing Managemt Unit 1 (Krishna)nishant haweliaNo ratings yet
- Brac Bank PresentationDocument24 pagesBrac Bank PresentationSumi Islam100% (2)
- P 50Document2 pagesP 50Emily DeerNo ratings yet
- Assymetric Information - Adverse Selection and Moral HazardDocument6 pagesAssymetric Information - Adverse Selection and Moral HazardRayniel ZabalaNo ratings yet
- FAR 4309 Investment in Debt Securities 2Document6 pagesFAR 4309 Investment in Debt Securities 2ATHALIAH LUNA MERCADEJASNo ratings yet
- Contract of Loan Inter AffiliateDocument3 pagesContract of Loan Inter Affiliatealexandro_novora6396No ratings yet
- Adjusted Adjusted Trial Balance Income Statement BalanceDocument1 pageAdjusted Adjusted Trial Balance Income Statement BalancedreaNo ratings yet
- Accounting For Management: Total No. of Questions 17Document2 pagesAccounting For Management: Total No. of Questions 17vikramvsuNo ratings yet
- Solved Problems in Engineering Economics: CLSU-AE Board Exam Review Materials 1Document49 pagesSolved Problems in Engineering Economics: CLSU-AE Board Exam Review Materials 1Abas Acmad50% (2)
- Umali Vs CADocument2 pagesUmali Vs CAMekiNo ratings yet
- Bonds valuation and amortization assessmentDocument2 pagesBonds valuation and amortization assessmentJohn FloresNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Income TaxDocument30 pagesChapter 2 - Income TaxRochelle ChuaNo ratings yet
- Internship Report On: Submitted byDocument50 pagesInternship Report On: Submitted bysumaiya sumaNo ratings yet
- Vulture CapitalistDocument2 pagesVulture Capitalistjosh321No ratings yet
- CIMA F1 Financial Operations KitDocument433 pagesCIMA F1 Financial Operations KitAnonymous 5z7ZOp67% (3)
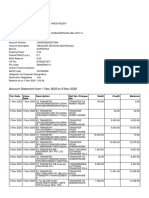
- Account Statement From 1 Nov 2020 To 9 Nov 2020: TXN Date Value Date Description Ref No./Cheque No. Debit Credit BalanceDocument2 pagesAccount Statement From 1 Nov 2020 To 9 Nov 2020: TXN Date Value Date Description Ref No./Cheque No. Debit Credit Balancevinod reddyNo ratings yet
- Berkshire 2022ltrDocument10 pagesBerkshire 2022ltrZerohedge100% (1)
- Financial RatiosDocument30 pagesFinancial RatiosVenz LacreNo ratings yet
- Joint Venture Tax ExemptionsDocument3 pagesJoint Venture Tax ExemptionsalexjalecoNo ratings yet
- Alicorp Earnings Call Presentation 4Q21 VFDocument42 pagesAlicorp Earnings Call Presentation 4Q21 VFCesar MelgarNo ratings yet
- Money MattersDocument2 pagesMoney MattersAndrew ChambersNo ratings yet
- Private Sector Banks in India - A SWOT Analysis 2004Document23 pagesPrivate Sector Banks in India - A SWOT Analysis 2004Prof Dr Chowdari Prasad67% (3)
- Role of GovtDocument4 pagesRole of Govtakshay kharteNo ratings yet
- IASB Update May 2013Document15 pagesIASB Update May 2013Euglena VerdeNo ratings yet
- LOMA FLMI CoursesDocument4 pagesLOMA FLMI CoursesCeleste Joy C. LinsanganNo ratings yet
- 1 - An Overview of Financial ManagementDocument14 pages1 - An Overview of Financial ManagementFawad Sarwar100% (5)
- Equity Risk Premium Determinants, Estimation and ImplicationsDocument143 pagesEquity Risk Premium Determinants, Estimation and ImplicationsKojiro Fuuma100% (1)
- HBR: Realize Your Customers' Fukk Profit PotentialDocument5 pagesHBR: Realize Your Customers' Fukk Profit PotentialAnuj AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Planet Starbucks Case AnalysisDocument3 pagesPlanet Starbucks Case AnalysisJugraj Dharni50% (2)
- Personal Share PortfoliosDocument1 pagePersonal Share PortfoliosBruce BarclayNo ratings yet
- This Is A System-Generated Statement. Hence, It Does Not Require Any SignatureDocument5 pagesThis Is A System-Generated Statement. Hence, It Does Not Require Any Signaturegaming boyNo ratings yet